Ultrasound of the child’s brain (neurosonography) is performed at the Health 365 clinics at the address: st. Bazhova, 68, Ekaterinburg.
An ultrasound examination of brain structures must be performed on a child by the age of 1 month, and, without fail, at 3 months. Neurosonography is performed on a child, first of all, to exclude congenital pathology. In addition, it is necessary to assess the maturity of brain structures and measure the external and internal liquor spaces.
As you know, bone tissue interferes with the passage of ultrasonic waves. In newborns and infants, the bones of the cranial vault do not fit tightly together, leaving areas called “fontanelles.” Ultrasound doctors use this “window of opportunity” and perform neurosonography through the large fontanel. By one year, and in some children even at 3-4 months, the child’s large fontanel closes and a qualitative study becomes impossible. That is why it is important to perform an ultrasound of the child’s brain in early infancy.
Of course, it is possible to examine the structures of the brain in an older child, but these are other studies - MRI, CT, transcranial ultrasound, which have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Description of the procedure
As a rule, an examination such as an ultrasound of the brain is prescribed for infants or children whose age is no more than 1 year. This is due to the fact that in newborn children the bone structure of the skull, in certain areas of the head, unlike adults, does not fit tightly in relation to each other.
Such places where the connective tissue has not yet had time to transform into a bone structure are called fontanelles. Therefore, in this case, it is not difficult to perform an ultrasound on the baby and obtain detailed examination results. This method of neurosonography is called transfontanelle.
However, it should be noted that in some cases, such diagnostics as ultrasound of the brain can also be used to examine children whose age is more than 1 year. In this case, so-called transcranial neurosonography is performed. It involves conducting an examination directly through the so-called temporal bone of the skull. Transcranial neurosonography is advisable to use when examining children and adolescents whose age does not exceed 17 years.
On a note! Neurosonography is a mandatory procedure. It is prescribed to infants whose age ranges from 1 to 1.5 months. In some cases, it may be prescribed to children aged 3 to 9 months.
Ultrasound of the brain is an absolutely safe and painless procedure, which has no contraindications for use or implementation. This examination method has been actively used in world medicine since the 80s of the last century. To conduct an ultrasound, you do not need to carry out any preliminary preparations. In addition, this examination can be carried out even in cases where the child is asleep.
Neurosonography is an accurate type of diagnosis
Neurosonography is very important in the diagnosis of pathology in children in the first month of life in identifying various hemorrhages. Both isolated subependymal hemorrhages and hemorrhages in the ventricles of the brain with their spread to the brain parenchyma are well defined. Neurosonography has high sensitivity. Neurosonography is an accurate type of diagnosis. Neurosonography allows you to diagnose focal and multifocal necrosis, foci of periventricular leukomalacia, foci of subcortical leukomalacia.
In the acute phase, ischemic foci in the gray matter of the brain on the echogram are represented by areas of increased echo density. Sarklinik believes that the diagnosis of damage to the thalamus opticus and subcortical nuclei is better determined in the presence of hemorrhagic necrosis. Neurosonography is of great importance in the diagnosis of infectious and inflammatory processes. Neurosonography makes it possible to monitor the development of inflammatory and infectious processes and to promptly identify complications such as hydrocephalus, subdural hygroma, ventricular abscess, and cerebral abscess.
Neurosonography perfectly identifies congenital malformations of the central nervous system, changes in the size, shape, location of the ventricular system, and other anatomical structures of the brain. Using neurosonography, it is possible to diagnose various forms of pathology such as congenital hydrocephalus, Dandy-Walker malformations, holoprosencephaly, aneurysm of the vein of Galen, agenesis of the corpus callosum, Arnold-Chiari syndrome. Neurosonography plays a certain role in the diagnosis of brain tumors. Sonographic signs of tumors are nonspecific. They can manifest themselves in the form of cystic formations against the background of hydrocephalus, or areas of increased echo density. Often the tumors are asymmetrical and are accompanied by displacement of the midline structures of the brain.
Indications
For preventive purposes, this examination is recommended for newborn children in the first months of life. Also, ultrasound of the brain is prescribed for children whose age is about 90 days. This is due to the fact that some pathologies in the brain may manifest themselves gradually, and in the first days of a newborn’s life they simply will not be diagnosed.
A procedure such as neurosonography is performed directly in the maternity hospital. This examination can also be carried out in other medical institutions. In addition, a brain ultrasound may be prescribed to a child in the following cases:
- impaired breathing;
- occurrence of various head injuries;
- low birth weight of the baby;
- the occurrence of intrauterine hypoxia in a woman in labor;
- unusual, non-standard shape of the skull in a newborn;
- infection of the fetus with diseases such as herpes, toxoplasmosis, mycoplasmosis;
- when cytomegalovirus is detected in the fetus;
- the appearance of symptoms related to neurological pathologies (convulsions, facial asymmetry, hyperexcitability).
In addition, a brain ultrasound is prescribed to a child if there is a suspicion of the presence of so-called chromosomal diseases, including if there is a suspicion of a disease called Down syndrome. Also, such an examination is prescribed in cases where the baby has retraction of the connective tissue in the head area (fontanel).
Important! Ultrasound of the brain is a mandatory procedure in cases where the birth took place with complications. For example, this diagnostic method is prescribed in cases where a caesarean section was performed or when a child is born before the due date (premature birth). The presence of asphyxia and injuries is also a serious reason for mandatory ultrasound examination of the brain.
How is neurosonography performed?
The examination is painless and does not require special preparation.
Neurosonography is performed while the child is at rest or asleep. Next, a special transparent gel is applied to the skin of the area under study, which is necessary to ensure close contact between the skin and the ultrasound sensor of the device. Having installed the ultrasound sensor in a certain position, the doctor examines continuously changing images (“scans”) on the monitor. Once the ultrasound examination is completed, the gel will be wiped off the skin.
Usually the conclusion is issued immediately after the end of the study. The ultrasound doctor interprets the results, and he can also discuss the results with you, but the final word remains with the doctor who referred the child for neurosonography.
What does neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) show?
As a rule, brain ultrasound is prescribed to children at an early age (up to 6 months). Thanks to this procedure, diseases and pathologies such as:
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Various developmental anomalies.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hemorrhage.
- Aneurysm.
- Benign as well as malignant formations.
- Ischemia.
In addition, through ultrasound examination of the cerebral cortex, it is possible to detect the occurrence of various complications, which, as a rule, arise after injuries or infectious diseases. The information obtained, after passing this diagnosis, allows you to make a more accurate diagnosis of the patient and prescribe the most effective course of treatment.
Evaluation of results
Ultrasound examination allows you to study:
- Condition and structure of brain tissue. Darkening in the image allows one to suspect the presence of tumors, cystic formations, and hemorrhages. Increased tissue density can also be a symptom of inflammatory processes.
- Large vessels and choroid plexuses. Enlargement of some areas of the vessels may indicate the presence of an aneurysm.
- Ventricles of the brain. Changing their size makes it possible to diagnose pathologies such as rickets or hydrocephalus.
- Symmetry of brain structures. Slight asymmetry is considered a variant of the norm.
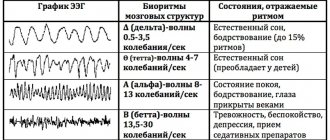
Identification of any abnormalities is a reason for the doctor to prescribe other studies, such as electroencephalography or rheoencephalography.
Timely diagnosis of neurological pathologies allows treatment to begin in the early stages of the disease, on which its effectiveness directly depends.
In what cases is NSG performed?
Most often, neurosonography is prescribed for infants. There are a number of indications for performing this procedure. Among them:
- birth injuries that the child received;
- obstructed labor of the mother;
- resolution of the burden earlier and later than the due date, that is, prematurity and postmaturity;
- intrauterine infection;
- C-section;
- Rh conflict during pregnancy;
- a genetic disease that the mother suffers from;
- congenital defects detected in a newborn (unequal eye sizes, ears positioned at different heights, etc.);
- inflammatory processes diagnosed in an infant;
- a viral infection that the child suffered seriously. In this case, neurosonography allows us to exclude signs of meningitis and encephalitis.
There are symptoms that should alert you and prompt you to perform NSG even in the absence of the indications listed above. The procedure is recommended if:
- the baby behaves unusually - does not show activity, sleeps shallowly, shows poor appetite, often burps, arches its back, throws its head back;
- the newborn has a poor reaction to sound and visual stimuli - he does not respond to the voice of adults, is unable to look at his mother’s face without looking away, does not follow a moving toy;
- the child develops convulsions and fainting;
- he fell and hit his head hard.
IMPORTANT! The Russian Ministry of Health recommends neurosonography for all infants when they reach the age of 1 month.
If for one reason or another the study was not carried out at this age, it is worth doing it at 3 months. This rule is advisory in nature, the final decision is made by the parents, however, you should not miss the deadline and refuse the procedure - at an older age, when the fontanel closes, the NSG will become much less informative.
What diseases can neurosonography detect?
Experts consider this diagnostic study to be highly informative, since it reveals a number of pathological conditions and deviations from the norm - namely:
- Abnormal bone development due to disturbances in the body's metabolic processes and a deficiency of lime salts - rickets;
- Disorders of brain development due to the accumulation of excessive amounts of fluid in it - hydrocephalus;
- Pathological local expansion of the lumen of the cerebral artery - aneurysm;
- CSF cysts filled with fluid that press on areas of the brain and can cause symptomatic epilepsy;
- Inflammatory processes of the soft membranes of the brain caused by pathogenic viruses and bacteria - meningitis;
- Ischemic brain damage, in which nerve cells die due to lack of oxygen;
- Brain neoplasms of various natures are extremely rare in newborns.
Neurosonography can determine the pathology of the brain of newborns and infants
What does neurosonography show in children? Hypoxic damage to the central nervous system, traumatic damage to the central nervous system, trauma, periventricular edema, increased peripheral vascular resistance, vascular spasm, periventricular leukomalacia, periventricular hemorrhage, cyst (diameter 1, 2, 3 or more cm), pseudocyst, vascular abnormalities, hydrocephalus, hypertensive -hydrocephalic syndrome, hypertensive syndrome, infectious brain lesions (infections), congenital malformations of the brain, central nervous system, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain, subependymal cysts, cysts of the choroid plexus of the brain, expansion of the subarachnoid space, expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces, hemorrhages in the substance of the brain , hemorrhage into the ventricles (intraventricular hemorrhage, IVH grades 1, 2, 3, 4), cerebral ischemia.
Who undergoes neurosonography?
Neurosonography is mandatory for all premature babies. Children who required intensive care or resuscitation after birth, with birth trauma or after traumatic obstetric care, large newborns, and babies with intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, the study is prescribed for children with defects and anomalies of other organs and systems. But, in general, every child needs to have neurosonography done at least once. To exclude changes that may manifest themselves only after a year, when the fontanel has already closed.