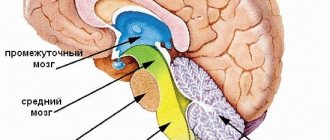
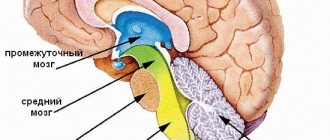
Brain studies, including echoencephalography (Echo-EG), can detect disorders and anomalies, congenital and acquired lesions throughout life, which may indicate serious illnesses. Untimely detected brain diseases can lead to complications and even death. Echo-EG is an effective research method that is based on the use of ultrasound and waves that can be reflected from the tissues being examined. In medicine, this technique is also called echoencephaloscopy.
Indications
In fact, there is a fairly wide list of indications for such an examination.
This is due to the fact that any suspicion of brain pathology and alarming symptoms must certainly be checked with equipment, since the consequences can be extremely serious. Typically indications include the following:
- Dizziness.
- Nausea (often attacks and does not depend on meals).
- Shake.
- Frequent headaches.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Head injuries and bruises of any severity.
- Noises in the ears.
- Epilepsy.
- Nervous tics.
- Visual impairment.
- Restless sleep (or even insomnia).
- Sharp memory deterioration.
- Cramps.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Inability to concentrate.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of already prescribed treatment.
Echoencephalography in M-mode in children
For pediatric patients, the study is carried out in the following cases:
- head bruises;
- sleep disorders;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- attention deficit hyperactivity;
- delayed physical development;
- enuresis;
- nervous tics, stuttering;
- hydrocephalus;
- neurological diseases requiring diagnostic monitoring.
At a reception at the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. A.K. Eramishantsev can learn in detail about echoencephalography in M-mode: what it is, how it is carried out and what it shows. The examination can be completed in our clinic at any convenient time. The contact phone number is listed on the website.
Indications for testing
h22,0,0,0,0–> p, blockquote5,0,0,0,0–>
Doctors refer for ECHO of the head for the following pathologies:
p, blockquote6,0,1,0,0–>
- Neoplasms are malignant and benign.
- Tuberculosis, ischemia, cerebral infarction.
- Encephalopathy.
- Swelling, abscess.
- Shaking paralysis.
- Tumor of the anterior pituitary gland.
Two-dimensional echoEG is necessary for:
p, blockquote7,0,0,0,0–>
- Traumatic brain and neck injuries.
- Migraines.
- Noise, ringing in the ears.
- Head spinning.
- Headache attacks.
- Shell shock.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident.
- Vascular or hypertensive encephalopathy.
- Vertebro-basilar syndrome.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Necrotic processes in the brain.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Poor circulation due to damage to the vertebral artery.
What's next?
For some reason, some patients tend to believe that the conclusion of an ES is already a sufficient reason to prescribe independent treatment, but this is certainly a big mistake.
A specialist diagnostician, of course, deciphers the echogram quite accurately, but the conclusion made on the basis of the examination results still includes only a preliminary diagnosis. A more accurate diagnosis can only be made by the attending physician who has a medical history and the results of other studies. You also need to take into account the fact that additional diagnostic methods and tests may be needed.
- Why is a study of the blood vessels of the brain and neck performed?
Thus, we must not forget in any case that after ES, you need to contact your doctor with its results, but definitely not draw up a treatment regimen for yourself.
As follows from the above, echoencephalography is a fairly reliable, informative, safe and certainly accessible method of studying the brain. There are no obstacles to its implementation and therefore, if there are specific indications, it is worth giving preference to this particular diagnostic method.
How to prepare for the examination?
The research algorithm differs depending on the age of the child. The general rule is to wash your hair the day before the electroencephalogram is taken to remove sebum from its surface.
An EEG of an infant is often done primarily during sleep, so the selected time for the study should coincide with the sleep schedule. Before the study, you need to feed the baby.
If the baby is over a year old, an important condition is to comply with all the doctor’s requests. Parents must first have a conversation with their children, preparing them psychologically for the session:
- For children 2-3 years old, you can try to imagine research in the form of an exciting journey, let them be superheroes.
- An assiduous child is recommended to take his favorite toy or picture book with him.
- Teach your baby to open and close his eyes, while keeping his breathing even and without fear.
If a child is prescribed medications, they cannot be refused. An exception is when anticonvulsants are discontinued 1-3 days before the examination at the request of the attending physician. Ask to reschedule the study if it coincides with a respiratory disease accompanied by severe catarrhal symptoms (runny nose, cough).
The patient’s behavior during the session affects the information content of the data obtained, so take your preparation seriously.
Try, if possible, to reduce the load on the nervous system on the eve of the examination. This applies not only to emotional overexcitation, but also to errors in nutrition. You should not give your child tonic drinks the day before. At the same time, it is better to feed him two hours before electroencephalography so that the child can better tolerate the study.
Data decryption
h24,0,0,0,0–> p, blockquote17,0,0,0,0–>
EchoEG is based on three complexes (or bursts):
p, blockquote18,0,0,0,0–>
- The initial complex is formed by sound waves reflected from the dense bone tissue of the skull, skin and superficial brain structures from the side located next to the sensor.
- The average complex is obtained when ultrasound waves collide with brain structures located between the hemispheres.
- The final complex is obtained from the soft tissue and dura mater on the opposite side of the sensor.
ECHO of the head connects these signals and, based on the received impulses, reflects them on the monitor in the form of a graphic diagram. Decoding begins with data analysis:
p, blockquote19,0,0,0,0–>
- M-echo is a signal with the highest amplitude, occupying an average position between the two complexes. Displacement up to 5 mm is allowed. In neurological disorders, a displacement of more than 6 mm is an alarming factor requiring additional diagnostics.
- A dilated or disrupted signal received from the third ventricle indicates high intracranial pressure.
- The ripple of M-echo signals should not exceed 30-40%. If the indicators are at the level of 50-70%, then this is a clear sign of hydrocephalic syndrome.
- The SI or average sellar index is within the range of 3.9-4.1. If it is low, then this indicates high intracranial pressure. This indicator is not assessed in children.
”alt=””>
p, blockquote20,0,0,1,0–>
- Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke: what it is, symptoms and consequences
What is the research?
To conduct an EEG of the brain in children, use a room that, if possible, does not allow light and sound to pass through. Before the examination, a special cap with sensors is put on the patient’s head, which transmit signals to a device (electroencelograph).
The session duration ranges from 30 minutes as part of a routine examination to multi-day video-EEG monitoring as part of the presurgical diagnosis of epilepsy. The examination of children from one year onwards takes place in several stages:
- Taking an encephalogram at rest. In this case, the child should be in a sitting or lying position.
- Carrying out the test with eyes open and closed. This is done to determine the basic rhythm.
- In the future, the examination technique will differ depending on the purpose of the study.
- The hyperventilation test involves deep exhalations and inhalations in order to provoke pathological brain activity.
- During a photostimulation test, the light bulb flashes at certain intervals. The child at this moment is with his eyes closed.
- Additionally, sound stimulation, clenching and unclenching of fists, and a psychological assessment can be performed.
- An EEG of sleep (daytime, nighttime) is also recorded.
The next step is to decipher the results in order to identify deviations from the norm and determine pathological processes.
Types of echoencephalography
Echoencephalography can be performed both in one-dimensional mode (the so-called M-study) and in two-dimensional mode (ultrasound scanning). In the first case, the result of the study is a graphic image of the reflected signals (echoencephalogram). The two-dimensional technique displays on the echoencephalograph screen the image obtained as a result of scanning the brain in two planes (echoencephaloscopy - ECHO-ES).
One of the varieties of two-dimensional echoencephalography is neurosonography - an ultrasound method for studying the structures of the brain of children through the large fontanel.
A child in the first year of life must undergo screening neurosonography.
Echoencephalogram indicators
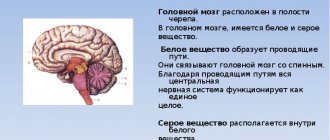
An echoencephalogram is a recording of ultrasound signals that vary depending on the presence of a space-occupying formation in the brain substance. The main cerebral structure involved in the display of the impulse determines the formation of:
- initial complex. It detects the high frequency wave sent;
- M-echo. The main signal formed with the participation of the septum pellucidum, 3 ventricle and pineal gland;
- final complex - echolocation signal of the bone wall of the skull of the opposite side;
- lateral echoes. Fixed after the initial and before the final complexes (before and after M-echo). Their occurrence is due to the reflection of the signal from the lateral ventricles.
It is diagnostically important to conduct several EchoEG studies in the process of monitoring the patient’s condition. Repeated observations make it possible to assess the severity and nature of damage to the brain and its vessels at various stages of the disease.
Interpretation of results
The interpretation and description of the study results is carried out by a neurologist or a specialist in a neurophysiological laboratory. Physiological is considered to be the same distance to the M-echo on one side and the other. Deviations should not exceed 1-2 mm (in children, an error of 3 mm is acceptable). In this case, brain symmetry is diagnosed.
Volumetric processes in the brain substance shift the M-echo signal and change the shape and duration of responses. Echoencephalography is performed if the patient has a suspicion of any structural dislocation pathological process . It can be:
- Cerebral ischemia: what is it and how to treat it?
- cerebral neoplasms;
- intracranial hematomas;
- tuberculomas;
- gummas;
- abscesses;
- cerebral strokes.
An ultrasound procedure can also be used to indirectly assess the condition of the cerebral vessels.
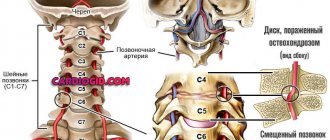
In this case, the direction of the median deviations indicates the localization of the lesion. The distance to the M-echo on the side of the pathological process increases compared to the opposite side. However, in a number of diseases during the regeneration stage, the M-echo may shift towards the affected hemisphere. This occurs due to a decrease in the volume of one hemisphere under the influence of regenerative processes (scarring resorption). Most often, the cause of this phenomenon is the consequences of inflammatory reactions and hemorrhagic stroke.
The diagnostic accuracy of the study depends on the qualifications of the doctor and the characteristics of the echoencephalograph - probing depth and resolution of the device.
ECHO-EG for various diseases
An echoEG study is intended not only to detect displacement of the midline structures of the brain. Electroencephalography suggests the nosology of the pathological process .
- Oncology. Intracerebral malignant tumors produce more significant displacement compared to extracerebral benign neoplasms.
- Injuries. Brain contusions can cause minor displacements of up to 3 mm due to swelling of the nerve tissue. The formation of post-traumatic cysts can cause the formation of pronounced lateral echo signals.
- ONMK. The greatest asymmetry is shown by intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, in this case, the diagnostic significance of lateral echo signals increases due to the presence of additional possibilities for reflecting the signal from the hemorrhagic focus. Cerebral infarctions produce minor transient displacements of the midline structures.
- Hydrocephalus. A characteristic sign of disturbances in liquorodynamics is the bifurcation of the M-echo wave with the divergence of the apices by more than 7-8 mm. Additionally, the echoencephalogram shows many lateral echoes.
However, Echo-EG cannot accurately indicate the nosology of the disease, but can only suggest it. To clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are required - EEG, scanning of the vessels of the head and neck, neuroimaging.
Methods for diagnosing brain diseases
The quality of our life depends on many nuances of the state of the body. The most important of these is the functioning of our brain. Stress, depression, poor ecology are constant companions of almost every inhabitant of the Earth, so many diseases, including brain diseases, are much more common than a hundred years ago. In addition, diseases are “getting younger” and are observed in a huge number of adolescents and even children. Sometimes we no longer pay attention to the symptoms, get used to frequent headaches, ignore dizziness, try once again not to “listen” to our feelings, and mindlessly take pills. It is important not to numb the pain with medications, but to understand the cause by examining the brain for the presence of structural and functional disorders. Maria Yuryevna Alekseeva , a functional diagnostics doctor, a doctor of the highest category, told how to do this
If you have any complaints, you should immediately consult a doctor. It will help determine the necessary path of examination. But, there are a number of studies that can be done before the consultation to save time. I would like to remind you a little about such diagnostic techniques as EEG, REG and ECHO-EG.
All of them are screening tests, as they have a number of positive properties: painless, harmless, without age restrictions, low cost, quick, and informative. With the results of these studies, the specialist will have a more complete picture of what is happening in your body.
What is EEG?
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method for studying the functioning of the brain, based on recording its electrical activity. Brain activity can be normal and pathological. So, when recording an EEG, we provide a description of normal brain activity taking into account age-related assessment criteria, and also indicate the presence or absence of pathological activity, which includes epileptic activity.
What are the indications for an electroencephalogram?
Mainly it is the diagnosis of epilepsy.
It can also be any complaints about the head (headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, loss of consciousness, panic attacks), seizures, any sleep disorders, a constant feeling of fatigue.
EEG is prescribed for various brain diseases: traumatic brain injuries, meningitis, encephalitis, strokes, brain tumors, autism, speech disorders, delayed psychomotor development, tics, neuroses, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In addition, EEG allows you to observe the dynamics of the disease, adjust treatment methods and evaluate the effect of drugs. It is also included in the screening program when passing a medical examination.
Is EEG performed on children?
This examination is very common in childhood, since the onset of many diseases of the nervous system occurs in children. Even for an infant, this technique is completely safe and does not harm health. Thanks to a timely EEG, it is often possible to defeat a serious illness at the earliest stages of its development.
How is the procedure performed?
No special preparation is needed, the procedure will not take much time and will not cause any discomfort. A special cap is placed on the head, to which electrodes are attached. Before applying them, the electrodes are moistened with a special gel so that the contact with the scalp is more dense.
The procedure lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. When recording an EEG, functional tests are usually carried out, “provocations” of hidden pathological conditions, convulsive attacks: photostimulation (light flashes at different frequencies), hyperventilation (deep breathing). These are different types of stress for the brain, which help to identify violations of its functioning.
What is REG? What is the essence of the method?
Rheoencephalography is a study of cerebral circulation, namely the functional state of blood vessels, their walls (tone), how they (quickly or not) fill with blood, venous outflow. The reaction of blood vessels to turning and tilting the head and holding the breath is also assessed. The procedure is based on recording the electrical resistance of brain tissue.
What are the indications for the procedure?
This study has wide application in childhood. After all, vascular disorders, unfortunately, are often found in modern children.
Rheoencephalography is advisable to use in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular pathology of a functional nature (vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine), in atherosclerosis, acute and chronic cerebrovascular disorders, as well as in assessing the effectiveness of certain medications and non-drug treatment methods. REG studies are highly informative in identifying the effect on cerebral vessels in pathologies of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondylitis, consequences of injury, etc.).
REG can be prescribed both for diagnostic purposes and routinely, since it is absolutely safe. This is especially true for mature and elderly patients, since over time the characteristics of blood vessels only worsen, and any pathology is best recognized in advance.
How is the examination carried out?
REG does not require special training. In general, the procedure is similar to an EEG: electrodes are installed on the patient’s head and connected to a machine that records the results. The whole procedure lasts 5-10 minutes.
What are the advantages of REG?
There is an opinion that REG research has been used for quite a long time and can be considered obsolete, especially with the advent of ultrasound and tomographic techniques. However, the simple conditions for the procedure and its painlessness for the patient are the main advantages of REG. At the same time, the device takes readings about the work of arteries and veins separately, which simplifies diagnosis at any stage of the disease.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography, as well as Doppler ultrasound, are more detailed, but not as accessible to the public. In addition, there are categories of patients who need to undergo such research regularly, for example, during the postoperative period.
REG in childhood is especially relevant, since sitting in a rubber cap for 5 minutes in the presence of parents is much easier for a child than being alone inside a huge humming device (tomograph). Therefore, doctors do not stop turning to rheoencephalography.
What is ECHO-EG of the brain?
Echo-EG of the brain (ECHO-ES or Echoencephalography) is a method of one-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of the brain followed by computer processing.
ECHO-EG reveals displacement of the midline structures of the brain, which occurs due to head injuries or neoplasms. The midline structures include the ventricles of the brain (these are natural cavities between the hemispheres). In case of pathological processes on the right or left, they shift to the healthy side.
This method also helps in diagnosing increased intracranial pressure.
In what cases should an ECHO-EG be done?
Mainly traumatic brain injuries.
Also, ECHO-EG is indicated:
- for severe regular headaches,
- general weakness, the causes of which are not clear;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- fainting.
In addition, echoencephalography allows you to see indirect signs of increased intracranial pressure.
How is the procedure performed?
No special preparation is required. The doctor places small ultrasound sensors on the patient’s head and periodically moves them during the examination. In this case, the patient does not experience any discomfort. It is done very quickly (5-10 minutes), the result is given immediately.
What are the advantages of ECHO-EG?
Echoencephalography is a simple, safe and harmless diagnostic method that has no contraindications or age restrictions. It is especially relevant in patients with contraindications to MRI (for example, an installed pacemaker, or built-in metal structures). Or in early childhood with head injuries, which happen quite often. In such cases, global examinations such as MRI are not always justified, and ECHO-encephalography comes to the rescue.
What are the features of conducting EEG, REG and ECHO-EG at the Center for New Medical Technologies?
To conduct these studies, our Center uses the latest equipment, and modern computer programs are used for analysis. Patients are received by highly qualified specialists by appointment, without queues. We have extensive experience working with children of different ages (including newborns), and with various pathologies. Research results are prepared quickly.
In conclusion, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that, whatever the reason why you or your child needs an EEG, REG or ECHO-EG, after the examination you must consult a neurologist to interpret the results and treatment. Be healthy!