- What problems does drug treatment solve?
- Stages of drug treatment
- Diagnostics
- Classic detoxification – for all types of drugs
- Ultra-rapid detoxification (URD) – for opiates
- Withdrawal relief - for all types of drugs
- Post withdrawal syndrome
- Maintenance therapy
- Pros and cons of drug treatment
- Approved medications
- Prohibited drugs
- Do medications cure drug addiction?
Modern addiction treatment programs work with personality changes and provide a gentle, sensitive and voluntary approach . But at the stage of an acute painful condition, medications are needed. They help quickly remove dangerous substances from the body, reduce pain, restore well-being and reduce the risk of complications.
What problems does drug treatment solve?
- accelerates recovery: quickly removes toxins, normalizes body function;
- facilitates drug withdrawal: relieves pain, improves sleep, calms nerves;
- increases the effectiveness of treatment in the first stages: the fear of quitting drugs partially disappears.
Drug addiction is a mental illness. It is accompanied by a lack of willpower and a pathological craving for drugs.
An addicted person always alternates between two states:
- Intoxication – poisoning during use;
- Abstinence is withdrawal symptoms during the period of giving up substances.
Psychoactive substances (surfactants) are toxic and affect all organs. Addicts face serious health complications. Also, many die within 10 years. Every day could be your last, so don’t put off asking for help.
Don't know where to start?
Start by talking to an addiction counselor for free.
7
- or -
Some of the substances that enter the body are permanently retained in adipose tissue. After a period of elimination of possible toxins, poisoning is replaced by withdrawal syndrome - withdrawal.
Drugs act on the receptors of the nervous system, so the patient experiences: euphoria, a surge of energy, relaxation, etc. When the drug is not in the body, it begins to react painfully.
Withdrawal is the body's need for drugs.
The patient is physically ill without the drug, and he tries to get it by any means. Addicts think that withdrawal lasts a few days, but in fact the process lasts several months.
When I used heroin, I always thought that I only needed to wait three days and my condition would return to normal. I will be able to return to a normal lifestyle. Stop using drugs for three days and everything will be as before. In 20 years of use, I have rarely managed to last three days. But even when I gained by some miracle these 3 days. At the first thought about the drug, I still went to use it. It took me time for all biochemical processes to return to normal.
Modern medicine helps if the patient is in an acute condition: relieves pain, improves sleep, relieves acute emotional stress.
Doctors use drugs that:
- Removes drugs from the body
Surfactants accumulate in adipose tissue and lead to chronic intoxication. The body is poisoned by substances. When the fat cell breaks down, drugs enter the bloodstream along with lipids, which cause an instant “response” and the desire to get a new dose.
A person who abstains from drugs for several days does not understand why the condition can sharply worsen, why withdrawal symptoms return. The pain has to be relived when it already seems that everything is over. Toxins also cause complications. The drugs help quickly remove them from the body.
- Abstinence is stopped
When the concentration of drugs in the blood decreases, a person experiences withdrawal symptoms. Abstinence does not depend on the reason for the decrease in the concentration of surfactants in the blood: as a result of natural metabolic processes or after a special medical procedure.
Abrupt withdrawal from substances leads to various disorders in the addict’s body. First of all, it affects mood and physical well-being.
Drugs disrupt the production of dopamine, serotonin, GABA and other neurotransmitters. A few weeks or months after quitting drugs, their production will be restored. But during the recovery period, the recovering person will suffer from unpleasant symptoms:
- pain;
- weaknesses;
- mental discomfort;
- increased excitability, etc.
Symptoms depend on what drugs he used: withdrawal after stimulants such as salts, mephedrone, amphetamine, etc. causes weakness and depression; after opiates and cannabinoids, a person suffers from irritability, anxiety, and insomnia.
Withdrawal relief helps eliminate all unpleasant symptoms before the body fully recovers. During drug withdrawal, the addict does not feel pain, can fall asleep, and is less irritable. Treatment is carried out using drugs that are selected after examination and study of the clinical picture.
- Helps improve health
Maintenance treatment replenishes the deficiency of essential substances and prevents the development and exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
Such measures are not mandatory, but the better the patient feels during treatment, the higher the patient's motivation, and the lower the risk that he will experience a relapse. In addition, the goal of treatment is not just quitting drugs, but returning to an active, fulfilling and healthy life.
Don't know where to start?
Start by talking to an addiction counselor for free.
7
- or -
Hallucinogens
Drugs with a hallucinatory effect lead to mental changes. Patients hear voices, see colorful pictures, and clearly sense non-existent tastes and smells. There are quite a few drugs that cause these effects.
Most often, drug addicts take:
- LSD.
- Mescaline.
- Amphetamines.
- Cyclodol.
The harmful effects of these drugs are still being studied. It has now been established that hallucinogens very quickly destroy memory and lead to the birth of children with developmental defects and anomalies. Women often suffer from infertility. Under the influence of drugs, criminal acts and suicides are often committed.
Stages of drug treatment
In Russia, the treatment plan is prescribed in the clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health: diagnostic criteria, drugs, methods and stages of therapy are indicated there. Doctors who use a scientifically based approach recommend including drugs in drug treatment programs at the first stage of working with an addicted patient.
But patients come for treatment with different clinical presentations. They took different drugs, have different length of addiction, medical history, age, gender and even character. Therefore, the doctor does not copy the recommendations of the Ministry of Health, but adapts them to each patient.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics helps to choose more accurate prescriptions:
- examination and questioning of a psychiatrist-narcologist and other doctors according to indications;
- biochemical analysis of blood and urine;
- identification of surfactant components in blood, urine, saliva;
- Ultrasound and radiography of the abdominal organs;
- electrocardiogram and EEG of the brain.
Based on the diagnostic results, the attending physician prescribes medications: psychotropic, specific, systemic. Further possible procedures are also prescribed.
Literature:
- Bad habits and their prevention: textbook / comp. Gorskaya I.Yu., comp. Gubareva N.V. - Omsk: Publishing house SibGUFK, 2010. - 212 p.
- Prevention and suppression of offenses in the field of illegal consumption and trafficking of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances: textbook / O. A. Kalenitsky, N. A. Sapronova; Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Russian Academy of National Economy and Public Administration under the President of the Russian Federation, Western Branch. — Saratov: Amirit, 2021. — 95 p.
- Oxicological chemistry. Metabolism and analysis of toxicants: a textbook for universities: a textbook for students of medical and pharmaceutical universities / E. Yu. Afanasyeva et al.; edited by N.I. Kaletina. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 1015 p.
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Classic detoxification
To remove drug components from the blood, a dropper with a special solution is used - infusion. It neutralizes and removes toxins from the body.
Appointments usually include:
- plasma replacement solutions;
- diuretics;
- vitamin complexes;
- means for symptomatic therapy.
Medicines are administered for several days until physical condition is restored:
- heroin, cocaine addiction – 7-15 days;
- use of synthetic drugs – 5-7 days;
- methadone – up to 20 days.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. If internal organs are damaged, they can purify the blood using extracorporeal methods - plasmapheresis and hemodialysis.
Classic detoxification is prescribed for drug addicts who use any type of drug: stimulants, euphoretics, opiates, cannabinoids, hallucinogens, etc.
Ultra-rapid detoxification (URD)
UBOD is intended for the treatment of patients taking opiates. This group includes: heroin, morphine, methadone, poppy and its alkaloids.
The procedure was developed relatively recently. It became widespread only at the end of the twentieth century. It has two features that distinguish it from classic detox:
- the procedure is performed under general anesthesia;
- detoxification and withdrawal symptoms take only 4-6 hours.
A regular detox can be uncomfortable. The doctor will relieve most of the symptoms, but the patient may feel slightly unwell.
If a person cannot tolerate the physical or mental effects of withdrawal, they may go into medicated sleep. When the procedure is over and the anesthesiologist wakes the patient, he will feel almost healthy.
The substance naltrexone (naloxone), an opioid receptor blocker, helps achieve this result.
To understand how the method works, you need to know about the role of brain neurotransmitters in the formation of addiction.
- Each area of the brain is responsible for specific functions. The limbic system controls the functioning of internal organs, plays a role in learning (perceiving, remembering and reproducing information), but most importantly, the reward system is located there.
- This system is responsible for positive reinforcement: if a person experiences pleasure, the system is activated and causes the desire to have a pleasant experience again. The catalyst for this reaction can be food, falling in love, sensual pleasures, as well as chemicals: ethanol (alcohol), drugs, tobacco.
- Activation of the system is accompanied by the release of dopamine, the hormone of pleasure, motivation and anticipation. Other neurotransmitters are also involved in the process, for example, serotonin, GABA, choline, but the role of dopamine is still considered dominant by scientists. If there are not enough neurotransmitters in the body, it is more difficult for a person to get pleasure - this happens with depression.
But the pleasure of a drug addict is much stronger than the pleasant sensations of delicious food or a massage. This is due to the fact that drug components bind to opioid receptors and cause a powerful euphoria, which becomes more difficult to achieve with each new dose.
Due to the drug regularly entering the bloodstream, the body reduces the production of dopamine. This is why without a drug a person feels psychologically bad: the world seems gray and gloomy, habitual activities do not bring pleasure, and drug intoxication seems to be the most accessible way to restore well-being.
During UBOD, a large number of opioid receptor blockers are introduced into the patient’s body, based on the principle of rapid saturation, which displace drugs and relieve withdrawal symptoms in just a few hours.
But the faster detoxification occurs, the more difficult it is to bear. Therefore, the addict is put into medicated sleep so that he does not encounter unpleasant sensations.
Contraindications
The technique is contraindicated in severe exhaustion, serious pathologies in the acute stage, chronic renal failure and pregnancy.
Removing withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal is a withdrawal syndrome that is an important trigger for addiction.
The discomfort during abstinence can be so strong that a person cannot stop using it even with good motivation for recovery.
There is no targeted treatment for withdrawal symptoms: you cannot take a drug that will eliminate all the unpleasant sensations associated with withdrawal of surfactants. Therefore, withdrawal withdrawal in narcology means:
- reducing the patient’s craving for drugs;
- elimination of unpleasant symptoms;
- restoration of the functioning of internal organs.
There is no clear boundary between detox and withdrawal: these two procedures are carried out simultaneously and belong to the first stage of systemic therapy: liberation from physical cravings for drugs.
Content:
- What are the consequences of taking drugs?
- How do psychotropic drugs affect a person?
- Types of psychotropic drugs
- Opiates
- Hallucinogens
- Psychostimulants
- Synthetic blends
- What are “soft” drugs?
- Pharmacy drugs
The concept of “drug” in medicine refers to substances of both plant and synthetic origin that consistently cause numbness, stupor, loss of pain sensitivity or change the mental state of a person. Each country has its own list of medicines and other drugs that are psychotropic drugs. Regular use of drugs leads to the development of mental and physical dependence and serious complications. Drug addiction causes desocialization, disability and early mortality.
Post-withdrawal syndrome
When withdrawal is over, other signs of illness appear, which are associated with several factors:
- damage to the central nervous system due to drug intoxication;
- disorders of cerebral circulation and neurotransmitter system;
- difficulty in adapting a dependent person to society.
Some patients experience mild post-withdrawal symptoms, while others suffer more severely. Characteristic signs of the condition are:
- depression, accompanied by a feeling of weakness and meaninglessness of life;
- cognitive impairment, due to which a person cannot concentrate attention on one object;
- sleep problems: constant drowsiness or insomnia;
- irritability, outbursts of anger and tearfulness.
The addict's body is trying to get used to sober life. At this stage, breakdowns often occur, so narcologists recommend that patients go to rehabilitation during post-withdrawal syndrome.
In some cases, psychological recovery does not exclude the use of drugs. This is especially true for Chinese synthetic drugs: salts and mephedrone. Psycho-emotional state correctors, sleeping pills and adaptogens prescribed by a doctor will ease symptoms and make quitting more comfortable.
Without treatment, post-withdrawal syndrome can last for weeks or even months. Few people survive this and return to drugs.
Signs of a Pharmacy Addict
The external signs of drug addicts largely depend on the substance they use. But there are also common features that are characteristic of all drug addicts:
- sudden weight loss,
- loss of appetite,
- unnatural pupil size,
- bouts of vomiting,
- convulsions, tremors of limbs,
- anxiety,
- panic attacks,
- insomnia,
- irritability,
- thoughts about suicide.
Maintenance therapy
My physical condition suffers greatly from drug use. The following can help the body cope with the consequences of chronic intoxication and withdrawal syndrome:
1. Nootropics (neurometabolic stimulants) – protect the brain from the influence of harmful factors, increase performance and mood, reduce asthenia and depression.
2. Hepatoprotectors – restore and protect liver cells from damage.
3. Vitamin complexes - replenish the deficiency of substances necessary for the body, restore the functioning of organs, metabolic and biochemical processes.
Antidepressants, tranquilizers and other prescription drugs play a major role in maintaining the addict’s well-being. They are effective and well tolerated when prescribed correctly. However, like drugs, they can cause withdrawal symptoms. Therefore, self-medication or arbitrary changes in dosage may worsen your health.
We strongly discourage self-medication. This will only make the situation worse. If you need specialist advice on further actions, call.
Don't know where to start?
Start by talking to an addiction counselor for free.
7
- or -
Detoxification products
The main purpose of detoxification pharmaceuticals is to bind and remove alcohol residues, its breakdown products and other toxic particles. Detoxification does not cure alcoholism, it only helps the body quickly cope with poisoning,
The following groups of detoxification drugs are most often used to overcome binge drinking:
- Absorbents designed to collect and retain toxins on their surface or in their pores. The most striking representative is activated carbon. This is a cheap, natural, safe and quite effective first aid remedy for alcohol poisoning. It is taken at the rate of 1 capsule or tablet per 10-12 kg of weight. The maximum single dose is 15 tablets. Enterosgel, Smecta, Polysorb can be used as absorbents. They are available in tablet or powder form and are taken orally.
- Infusion detoxification solutions. Prescribed to increase blood volume and accelerate the removal of toxins from excess fluid through the kidneys. In this case, crystalloid (based on sodium chloride), colloid solutions - polyglucin, reopliglucin, hemodez, gekodez, and other plasma substitutes can be used. Administered intravenously.
- Laxatives and emetics. The greatest effect is provided by fast-acting medications - castor oil or 25% magnesium sulfate solution.
You need to understand that taking laxatives and absorbents is justified only in cases of minor poisoning or short-term binge drinking, in which there is no significant deterioration in well-being. In all other situations, infusion therapy is required.
Pros and cons of drug treatment
Drugs in narcology are an opportunity to make treatment more comfortable and achieve remission faster. This approach reduces the patient's fear when visiting a doctor. The sooner you turn to specialists, the less likely it is to develop serious complications: somatic and mental.
Of the minuses, it can be noted that the drugs are not used to suppress the patient’s personality.
Punitive drug addiction is a myth that originated in the USSR. Since the mid-twentieth century, narcologists, having separated from psychiatrists, have followed the path of consciously changing the personality of patients. They proved that only a voluntary, conscious decision to return to a sober life can lead to long-term remission. And medications are an additional tool that only alleviates the patient’s suffering.
The advantages of the medication approach in the treatment of drug addicted patients are:
- effectiveness even with a long history of addiction;
- rapid elimination of the consequences of drug addiction;
- easier drug withdrawal.
Unfortunately, no medicine is a panacea. Drugs will not save a person from the true causes of drug addiction (genetic, psychological, environmental, personal) and cannot change the behavioral patterns he or she has formed.
In addition, if prescribed incorrectly, the risk of side effects and allergic reactions remains. Especially when combining several drugs. The body of a dependent person is weakened, so paradoxical reactions can occur even when taking proven medications.
Approved medications for the treatment of drug addiction
The clinical recommendations compiled by specialists from the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation for Russian narcologists list the following drugs:
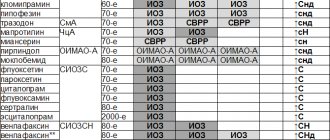
1. Antidepressants - prescribed for low mood (Duloxetine, Venlafaxine), anxiety (Amitriptyline, Pipofezin, Fluoxetine), asthenia (Imipramine), post-abstinence (Clomipramine, Maprotiline, Tradazone), hypochondria (Sertraline). Can cause withdrawal syndrome and acute affective disorders.
2. Neuroleptics - improve sleep (Alimemazine), relieve psychosis (Haloperidol, Risperidone) and other acute conditions during abstinence and post-abstinence (Zuclopentixol, Tiapride), reduce the risk of relapse (Zuclopentixol decanoate) and affective disorders (Risperidone). They are considered heavy drugs, so they are usually used for emergencies and psychopathic-like disorders.
3. Naltrexone and Naloxone are opioid receptor blockers that prevent relapses and temporarily stop cravings for drugs and alcohol.
In case of intoxication, standard therapeutic agents are used according to indications, taking into account the health characteristics and current condition of the patient.
Prohibited drugs for the treatment of drug addiction
In a number of countries, replacement therapy is used for drug addicts: instead of a dangerous drug, the patient takes an analogue under the supervision of a doctor. The dose is gradually reduced until complete withdrawal.
For example, methadone is an opiate used to treat heroin addicts. It is no safer than other opiates. But when a person gets it from a doctor, the risk of taking a drug with dangerous impurities is reduced. Patients are also provided with clean syringes to avoid contracting concomitant diseases: HIV, hepatitis and others.
In Russia, it is prohibited for use in any form, even under medical supervision.
Synthetic blends
Over the past two decades, various mixes containing different ingredients have become widespread among drug addicts, especially young people. They have caused multiple complications, disability and death.
The so-called “club” drugs have particularly aggressive properties:
- Spices.
- Salt.
- AIDS.
- Ecstasy.
Spice is a tobacco mixture used for smoking. Manufacturers claim that the composition does not contain anything other than harmless herbal ingredients. But laboratory tests confirm the presence of narcotic substances in them. Smoking these mixes causes serious complications.
Salts are a disguised name for very aggressive drug compounds that cause a pronounced stimulating effect, leading to rapid destruction of the body. Salt mixtures are taken intravenously, by inhalation through the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and smoking.
Speeds are derivatives of amphetamine and form similar psychostimulation. Particularly dangerous is the inability to control the amount of the substance taken, which often leads to overdoses and dangerous health problems.
Ecstasy is a powerful methamphetamine whose effects are based on a combination of stimulation and empathogenicity. Under its influence, a person very quickly establishes contacts with people around him and maintains energy for a long time.
Do medications cure drug addiction?
No! Anyone who says that drug treatment will solve the problem of addiction is not competent in the treatment of drug addiction. When drugs are used as part of systemic treatment, they are necessary and beneficial. Medications for the medical treatment of drug addiction relieve symptoms of withdrawal and post-abstinence. They cleanse the body of traces of drugs during detoxification. However, drug treatment does not solve the problem of drug addiction and does not protect against delayed relapse. After drug treatment, a course of rehabilitation, psychotherapy or support groups is required. There, work takes place on internal problems and the reasons for the development of addiction.
To learn more about the disease of addiction and treatment methods, subscribe to our mailing list or become a member of an anonymous telegram chat, where people share with each other their experiences of how they encountered addiction in life and cope with this misfortune. There you will receive a free consultation with a psychologist or chemical dependency counselor.