General information
A cyst is a cavity that is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It is located in the membranes or directly in the substance of the brain. If the size of such a formation is small, then it does not provoke pronounced symptoms, and is diagnosed accidentally, during a neuroimaging examination of the head. If the formation increases, the patient develops intracranial hypertension .
The ICD-10 disease code is G93 (Other brain lesions). Brain cysts are found in people of different ages - both children and adults. Sometimes symptoms in a person with a congenital cyst appear only at 40-50 years of age. Treatment of the disease is carried out only when symptoms are severe and complications develop. If the cyst does not grow or progresses slowly, the doctor uses a wait-and-see approach and conducts periodic examinations.
How brain cysts can manifest themselves, and what treatment methods are practiced if necessary, will be discussed in this article.
Development options
Most often, the cyst does not interfere with brain activity. In case of an increase in the volume of the tumor and the appearance of neurological abnormalities, the options for the development of the cyst will depend on the timeliness of diagnosis and correct treatment.
When pressure increases in the head, serious problems with speech, hearing, vision and memory can occur. Persistent neurological disorders may occur. A sharp increase in the size of the tumor can provoke its rupture and death of the patient. If diagnosis and therapy are carried out on time, the prognosis is quite optimistic and after treatment the patient recovers 100%.
Pathogenesis
A cyst in the brain can develop under the influence of unfavorable factors observed during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. In particular, this may be associated with hypoxia , intrauterine infections, the use of certain medications by a woman, etc. The cause of this formation may also be intrauterine intoxication as a result of smoking or alcohol addiction of the mother.
Acquired cysts develop as a result of injuries, inflammatory diseases, and circulatory disorders. In dystrophic and degenerative processes, the cyst can replace cerebral tissue. The growth of the cyst can be facilitated by strokes , difficulty in venous outflow and other vascular problems.
Cystic-gliotic changes also lead to the formation of cysts. Speaking about what cystic-gliotic changes in the brain are, it should be noted that with this pathology there is a proliferation of tissue responsible for the delivery of nutrients to neurons. This transformation leads to disruption of the normal functioning of the brain. As a result, the neurons die and scar tissue forms instead of healthy tissue. Against the background of pathological processes, a cerebrospinal fluid cyst and other types of cysts can form. A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a formation with liquid contents, which in some cases can lead to the development of neurological symptoms.
Drug treatment of lacunar cyst
You need to understand that if a patient was diagnosed with a cyst that developed during the period of intrauterine growth, then it is most likely a hereditary disease. It is impossible to insure yourself against this type of tumor.
If the cyst is diagnosed as an acquired pathology, this means that it was the result of some kind of somatic disease. For example, it appeared as a complication after meningitis or traumatic brain injury. Diabetes mellitus, thrombosis, and hypertension can lead to the appearance of a cyst.
Often, frequent concussions can cause the appearance of a tumor in the brain. This phenomenon occurs in professional sports, where an athlete often receives traumatic brain injuries, for example, boxing or other martial arts.
Post-ischemic lacunar cyst has become widely known in medical circles. From the name it is clear that it was a consequence of ischemic brain disease, which, in fact, leads to chronic hypertension.
Postischemic lacunar cysts of the brain are studied and treated simultaneously with stroke. Often they become the cause of craniotomy and brain surgery. But lacunar cerebrospinal fluid cyst is amenable to radiation therapy, and surgery in this case is not always required.
If the cyst does not bother the patient, does not increase in size and does not pose a danger, then it is not subject to special treatment. In this case, therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of its occurrence.
For example, if a patient has suffered a severe viral disease such as meningitis or encephalitis, then he is treated with antibiotics and immune-strengthening drugs. The specific type of drug, its dosage and regimen of use are prescribed individually depending on the general condition of the patient.
Classification
Depending on their origin, congenital and acquired cysts are distinguished.
Depending on the structural features, single-chamber and multi-chamber formations are distinguished.
Depending on the characteristics of the formation, the following types of brain cysts are distinguished:
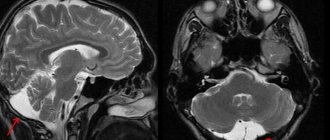
- An arachnoid cyst of the brain is usually a congenital formation or develops after an injury. Primary cysts of this type are congenital - this is the norm. Secondary ones develop under the influence of various factors. This is a liquor cyst, the walls of which are formed by arachnoid cells or scar collagen. This formation is located between the surface of the brain and the arachnoid membrane. The most common diagnosis is an arachnoid cyst of the posterior cranial fossa. Clinical manifestations of such formations are observed only if there is a large accumulation of fluid in the cyst. Then its size increases, and if this happens suddenly, the likelihood of cyst rupture increases, which can be fatal. According to statistics, formations of this type are more common in men.
- A cerebral pineal cyst is a cystic formation of the epiphysis (pineal gland), also called a pineal cyst. According to statistical data, a cyst of the epiphysis of the brain can be asymptomatic if its size is up to 5 mm. Cysts larger than 1 cm are less common. In this case, cystic transformation leads to the development of symptoms. When cystic transformation of the pineal gland occurs, a formation of significant size can block the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to occlusive hydrocephalus.
- An epiphysis cyst is a fairly rare occurrence. Occurs mainly in children. Due to the location of the tumor, a cerebral pineal gland cyst of 5 mm or more cannot always be removed. In this case, radiation therapy is used.
- Choroid plexus cyst - mainly located in the anterior region of the third ventricle, sometimes in the fourth ventricle and in the area of the transparent septum. This formation is filled with viscous content. It can be detected in the fetus by ultrasound at approximately 20 weeks of pregnancy. In most cases, they resolve within a few weeks, do not affect the brain, and are no longer detectable in a newborn. If the formation remains after birth, in some cases symptoms of epilepsy or intracranial hypertension are observed.
- A retrocerebellar cyst of the brain is a formation that is located in the posterior cranial fossa behind the cerebellum. The term “retrocerebellar” indicates the location of the formation. Therefore, the diagnosis may sound like “retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain.” The size of a retrocerebellar cyst of the brain can vary. If the cyst is small, it may not appear throughout life and treatment is not required. As for what size is dangerous, a cyst up to 2 mm does not require treatment. A size of up to 10 mm is considered to represent a medium degree of danger. Larger formations - from 10 mm - are considered especially dangerous. Thus, if the size of the cyst, for example, is 12 x 15 x 20, then in this case the formation should be considered dangerous.
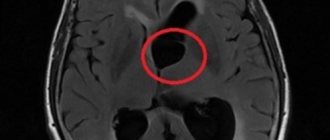
- Subependymal cyst - develops in the area of the walls of the lateral ventricles. In a newborn child, such formations can be combined with choroid plexus cysts.
- Intermedius velum cyst – This condition is common in newborns. It is characterized by expansion of the intermediate sail tank. As a rule, no treatment is required. But with large formations, obstructive hydrocephalus may develop.
- Rathke's pouch cyst is an epithelial formation that appears in the area of the sella turcica. It is assumed that it is formed from the remains of Rathke's pouch, in which the pituitary gland . Most often it is congenital, at first it is asymptomatic. As it increases, endocrine disorders and headaches may develop.
- A lacunar cyst is a formation that appears between the membrane of the cerebral cortex and the lacunae that develop as a result of inflammation. Such a cyst puts pressure on the vessels that surround the brain and on its soft tissues. As a result, pathologies of varying severity may develop. A lacunar cyst on the right in the area of the right thalamus is determined using modern research methods.
- Cyst of the transparent septum of the brain is a capsular tumor with liquid contents localized in the brain cavity. A septum pellucida cyst is often diagnosed in premature babies.
- A dermoid cyst (epidermoid) is an abnormality of intrauterine development when the cells from which skin, hair and nails are formed remain inside the brain.
Characteristics by location
The cyst in question may be located:
- in the temporal lobes;
- in the parietal part;
- in the frontal region;
- in the region of the cerebellum;
- in the spinal canal;
- in the spinal column;
- in the lumbar region.
In the posterior cranial fossa
This cyst in the posterior cranial fossa (posterior cranial fossa) is accompanied by symptoms:
- persistent headaches;
- vomit;
- failure to coordinate movements;
- intermittent paralysis of body parts;
- convulsive syndrome;
- mental disorders;
- hallucinations.
According to statistics, tumors of this type are more often observed in men, in addition, the increase in the volume of the cystic cavity in men occurs more actively than in women. With a very large cyst, speech defects, hearing loss, and temporary memory problems may occur.
In the sacral canal
An arachnoid type cyst in the sacral region is a cavity. In it, the spinal membrane forms web-like walls. If the cyst size is more than 1.5 cm, the patient may complain of:
- lower back pain with increased loads;
- numbness, paresis, impaired functionality of the limbs;
- headaches, blood pressure surges, dizziness;
- if the cyst is located at the S2 level, sexual function is impaired, and intestinal problems also arise.
In the temporal lobe
A cyst in the temporal lobe is most often observed on the left side. This is due to the more delicate structure of the left-sided meninges and their increased sensitivity to infections. A person with a cyst in this area experiences:
- unsteady gait;
- lack of motor coordination;
- deterioration of sensitivity of the limbs;
- convulsions;
- blackouts;
- mental disorders.
These symptoms are caused by hydrocephalus - the accumulation of fluid in the skull. A cyst of the right frontal lobe is accompanied by a similar clinical picture.
Causes
The formation of congenital brain cysts occurs at the stage of intrauterine development under the influence of a number of factors, which may include:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- Rhesus conflict;
- infectious diseases;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- fetal hypoxia during childbirth;
- use of certain medications;
- taking drugs, alcohol, smoking during pregnancy .
Acquired formations may appear under the influence of the following factors:
- injury to the baby's head during childbirth;
- inflammatory diseases of the brain;
- TBI;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- complications after surgery;
- degenerative and dystrophic processes;
- parasitic infections.
Vascular disorders, head injuries, neuroinfections, inflammatory processes, etc. can provoke an increase in existing cysts.
Symptoms of a brain cyst
In most cases, in the presence of a congenital cyst, a person does not develop symptoms throughout his life. As a rule, there is no oncological risk with such formations either.
If the formation increases, this leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, eventually developing the following symptoms:
- Headache.
- Weakness and deterioration in performance.
- Insomnia.
- Pressure in the eye area.
- Hallucinations.
- Spasms of the limbs and face.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Speaking about the dangers of a cyst in the head, it is necessary to take into account that such formations sometimes quickly increase in size. If a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain and other types of such formations increase in size, this leads to the degradation of certain brain structures, as a result of which the cells lose their functions.
The consequences of a cyst in the head of a newborn are sometimes manifested by delayed psychomotor development. The consequences depend on which part of the brain is affected by the education. Thus, a newborn may have problems with motor activity, a child or an adult may experience speech disorders, tremors , paresis , etc. Cystic-glial changes can lead to the development of the symptoms described above, as well as to the appearance of problems with hearing, vision, memory, etc.
But in general, it is possible to clearly say what is dangerous about a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain, or what threatens a pineal gland cyst only after a comprehensive examination and a specialist’s opinion.
Sometimes this condition may be accompanied by other disorders (coelomic pericardial cyst, etc.).
Symptomatic manifestations
This cystic neoplasm is characterized by an asymptomatic course .
Most often, such neoplasms are detected during a patient examination for neurological pathologies with similar symptoms.
The clinical signs of the cyst are nonspecific; their severity depends on the size of the tumor and its location. Patients may complain of general cerebral symptoms, which are associated with compression of brain areas. A focal clinical picture is observed in rare cases, and is most often caused by the presence of hygroma or rupture of the cystic cavity.
The main features are:
- dizziness , which are not associated with pregnancy, taking certain medications, severe fatigue, iron deficiency, and so on;
- vomiting , which is also not associated with gastrointestinal poisoning, taking medications, and so on;
- mental disorders, hallucinations ;
- convulsive syndrome;
- loss of consciousness;
- hemiparesis , decreased sensitivity in the limbs;
- failure to coordinate the activity of the body muscles;
- headaches that are not relieved by painkillers;
- a feeling of fullness , pressure, compression and increased pulsation in the affected area;
- visual and hearing problems;
- extraneous sounds in the ears;
- heaviness in the skull;
- painful or uncomfortable sensations when turning the head.
Reference! Secondary arachnoid cystic neoplasms may be accompanied by symptoms of injury or primary disease, which served as an impetus for the development of the disease.
Tests and diagnostics
The presence of a cyst in the brain can be suspected if appropriate symptoms are present and based on neurological status data. Sometimes it is necessary to conduct an examination by an ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist to determine the presence of vision and hearing problems.
- During the examination, audiometry, perimetry, visometry, and ophthalmoscopy are performed.
- Echo-encephalography is also performed, which allows you to diagnose increased intracranial pressure.
- In the presence of epileptic paroxysms, electroencephalography is also performed.
- If you suspect a cyst in the brain, it is also important to differentiate a cyst from an abscess , tumor, or hematoma .
- Even at the stage of intrauterine development, an ultrasound examination is performed, which makes it possible to diagnose some types of cysts.
- The newborn undergoes neurosonography before the fontanelle closes.
- Adults are prescribed CT or MRI with contrast.
- If necessary, additional research is carried out.
Treatment of arachnoid cyst.
As I said above, most congenital arachnoid liquor cysts are asymptomatic and do not require any treatment. Sometimes a neurosurgeon may recommend dynamic monitoring of the size of the cyst; for this, it will be necessary to periodically perform computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
In rare cases, when an arachnoid cyst is accompanied by the symptoms described above and has a mass effect, surgical treatment is resorted to.
In some cases with a sharp deterioration, due to rupture of the arachnoid cyst or hemorrhage into it, urgent surgical treatment is resorted to.
There is no standard size for an arachnoid cyst. Indications for surgery are determined taking into account the location and symptoms of the arachnoid cyst, and not just its size. This can only be determined by a neurosurgeon during an in-person examination.
Absolute indications for surgery:
- intracranial hypertension syndrome caused by an arachnoid cyst or concomitant hydrocephalus;
- the appearance and increase of neurological deficit.
Relative indications for surgery:
- large “asymptomatic arachnoid cysts” that cause deformation of neighboring lobes of the brain;
- progressive increase in cyst size;
- deformation of the cerebrospinal fluid tract caused by the cyst, leading to disruption of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation.
Contraindications for surgery:
- decompensated state of vital functions (unstable hemodynamics, breathing), terminal coma (coma III);
- the presence of an active inflammatory process.
There are three possible options for surgical treatment of arachnoid cysts. Your treating neurosurgeon chooses the tactics, taking into account the size of the cyst, its location and your wishes. Not all three methods are suitable for all arachnoid cysts.
Evacuation of an arachnoid cyst through a burr hole in the skull using a navigation station. The advantage is simplicity and speed of implementation with minimal trauma to the patient. But there is a drawback - the high rate of cyst recurrence.
Open surgery, that is, craniotomy (cutting out a bone flap on the skull, which is placed in place at the end of the operation) with excision of the walls of the cyst and fenestration (drainage) into the basal cisterns (cerebrospinal fluid spaces at the base of the skull). This method has the advantage of allowing direct examination of the cystic cavity, avoiding a permanent shunt, and is more effective for the treatment of arachnoid cysts consisting of multiple cavities.
Shunt surgery with installation of a shunt from the cyst cavity into the abdominal cavity or superior vena cava near the right atrium through the common facial vein or internal jugular vein. Many foreign and domestic neurosurgeons consider shunting of an arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst to be the best treatment method, but it is not suitable in all cases. The advantage is low mortality and low rates of cyst recurrence. The disadvantage is that the patient becomes dependent on the shunt, which is installed for life. If the shunt becomes blocked, it will have to be replaced.
Complications of the operation.
Early postoperative complications - liquorrhea, marginal necrosis of the skin flap with dehiscence of the surgical wound, meningitis and other infectious complications, hemorrhage into the cyst cavity.
Treatment with folk remedies
Any folk remedies can only be used as additional treatment. In particular, it is recommended to prepare decoctions of plants - both collections and individual herbs. It is recommended to prepare decoctions of elecampane, hemlock, wormwood, chamomile, yarrow, calendula, chamomile, etc. To prepare the decoction, you need to take 1 tbsp. l. selected plant or mixture thereof, pour boiling water (200 ml) and simmer over low heat for 10 minutes. Drink 150 ml three times a day before meals.
Alcohol infusions can be prepared from the listed plants. For this purpose, 100 g of the plant is poured with 300 ml of alcohol and infused in a dark place for two months, shaking occasionally. Take 1 tsp. a day before meals.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cysts in the brain, you should adhere to the following rules of prevention:
- Treat all infectious diseases and brain diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid exposure to provoking factors during pregnancy: give up bad habits, eat right, do not take medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- Ensure proper management of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Avoid overexertion and stress.
- Avoid head injury. When engaging in traumatic sports, wear a protective helmet.
- If your blood pressure is high, take measures to reduce it.
- Stop smoking and do not consume alcohol.
Brain cyst in a child
In modern medicine, a cyst in a child’s head is found quite often. According to statistics, a newborn has a cyst in the head in approximately 40% of cases.
The reasons for such formation in a newborn child are often associated with exposure to negative factors during pregnancy. The consequences of such influence often manifest themselves in children.
Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus can be diagnosed during fetal development. Sometimes ultrasound reveals a cyst in the posterior cranial fossa in the fetus. If such a pathology is determined by ultrasound in the fetus, there is no need to worry about this prematurely. Often such formations disappear on their own, and in the infant the formation of the posterior cranial fossa or in other places is no longer detectable. If a diagnosis of “choroid plexus cyst of the brain” is made in an infant, the doctor monitors it over time and prescribes treatment only if necessary.
A subependymal brain cyst in a newborn is a more serious pathology. The cause of this phenomenon is considered to be a violation of blood flow in the area of the ventricles of the brain. Whether a subependymal cyst requires treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the disease. For example, the famous pediatrician Komarovsky does not advise immediately using medications.
However, if we are talking about a large cyst, and the child develops symptoms in the form of headaches, seizures, etc., it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and undergo the prescribed treatment or undergo surgery.
Retrocerebellar type formation
This is a fairly rare pathology, which is diagnosed in 5% of the population.
This neoplasm combines several types of neoplasms that differ in location:
- arachnoid,
- intracerebral - can form in any part,
- inferior retrocerebellar.
This cyst is spoken of when the tumor is localized only in the cerebellum. In this case we observe:
- migraine;
- vomit;
- paralysis and paresis;
- problems with balance;
- the image before your eyes becomes unclear;
- decreased concentration;
- deterioration of character;
- loss of consciousness;
- twitching of the eyeballs;
- deterioration of thinking;
- violation of orientation in space and time;
- decreased muscle tone.
Diet
Diet number 12
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2-3 weeks
- Terms: 21 days or more
- Cost of food: 1590-1680 rubles per week
If you have a brain cyst, your diet should be complete, varied, and enriched with vitamins and minerals. It is useful to introduce the following products into your diet:
- Fruits and vegetables.
- Whole grain porridge, bran.
- Seafood, fish, seaweed.
- Nuts.
You should not consume fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, preservatives, and alcohol.
Consequences and complications
As the formation progresses, the following complications may develop:
- Encephalitis.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Developmental delay of the child.
- Epilepsy.
- Brain hernia.
- Cyst rupture is a serious complication that can be fatal.