- Location and functions of the facial nerve
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
- Folk remedies
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Pathology of the facial nerve is registered annually in 2–3 people out of 10 thousand people. It occurs due to various reasons, the nature of which largely determines the treatment of facial neuritis. Taking into account the anatomical connection of this formation and the ENT organs, with neuritis of the facial nerve the patient needs to consult not only a neurologist, but also an ENT doctor.
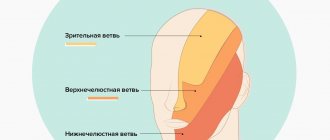
Location and functions of the facial nerve
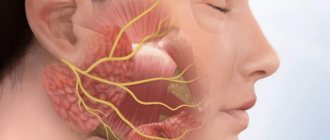
The facial nerve controls muscle movements in this anatomical region. This gives a person the opportunity to smile, express emotions with facial expressions, cry, and wink. Facial neuritis can lead to severe physical disability that is poorly tolerated psychologically. Although in most cases the symptoms of the disease gradually disappear, this requires long-term rehabilitation.
The facial nerve is the seventh of 12 paired cranial nerves. Each person has 2 facial nerves, corresponding to the right and left halves of the face. This nerve is adjacent to the eighth nerve, the auditory nerve, and passes through the structures of the middle ear, the mastoid process, and the parotid salivary gland, where it splits into many small branches.
Introduction to the topic
Weakening of the muscles of one half of the face, the inability to control facial expressions, and perform chewing movements - all these are manifestations of neuropathy of the facial nerve. The nerve ending from the brain exits into the narrow ear canal, so any swelling or compression due to damage to the jaw can lead to unpleasant consequences.
The causes of the disease can be infectious diseases, bruises and damage to the temporal lobe, otitis media, viral diseases, and blood circulation disorders.
You can cope with the symptoms and prevent the consequences of such lesions with the help of exercise therapy of the facial nerve. A set of exercises is prescribed by the doctor, based on the area of the lesion and the reasons for the manifestation of such a symptom.
Causes
Facial neuritis occurs under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- in 15% of patients this is damage to the branches of the nerve during surgical interventions on the middle ear, mastoid process, and also associated with otitis media and other lesions of the hearing organ, for example, cholesteatoma;
- in rare cases, the disease is caused by infection - herpes virus (Hunt syndrome), mumps, polio, influenza, as well as Lyme disease, transmitted through tick bites;
- in 75% of cases, the cause of neuritis of the facial nerve cannot be determined; in this case, they speak of Bell's palsy, which worsens after hypothermia and colds.
Other causes include head trauma, surgery on the salivary gland, and removal of an acoustic neuroma.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease occur acutely, within a few hours, for a maximum of 3 days. The gradual appearance of signs is most typical of compression of the nerve by a tumor growing from the surrounding tissue.
Depending on the severity, neuritis of the facial nerve is accompanied by the following symptoms:
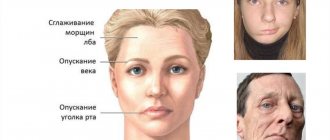
- movements of the facial muscles are weakened, up to barely noticeable, disruption of conjugate contractions of symmetrical areas of the face;
- facial asymmetry, even disfiguring;
- difficulty closing the eyes; in severe cases, the palpebral fissures do not close completely;
- disorders of swallowing, chewing, speech;
- when the disease is complicated by keratitis, vision loss gradually develops;
- taste disturbance, weakening or strengthening of sound sensations;
- lacrimation;
- with simultaneous damage to the trigeminal nerve - severe pain in the facial area.
Signs of intoxication and fever are uncharacteristic and usually occur due to the infectious nature of neuritis of the facial nerve.
Prevention of neuropathy
No one is immune from the appearance of unpleasant and painful symptoms of neuropathy. Inflammatory processes, brain diseases and even ordinary hypothermia can cause the appearance of one of the forms of neuralgia: inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. To avoid illness, you need to adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- Eat rationally and balanced;
- Temper the body;
- Exercise;
- Avoid hypothermia and sudden temperature fluctuations;
- Do not use air conditioning for a long time in hot weather.
It is also important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to prescribe adequate treatment for diseases of the ear, nose and throat. During treatment, follow all doctor's recommendations and strict bed rest.
Diagnostics
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is prescribed after an examination, which includes:
- general blood and urine tests, blood glucose levels;
- if the infectious nature of the disease is suspected (Lyme disease, HIV infection, syphilis and others) - appropriate serological tests;
- if sarcoidosis or brucellosis is suspected, chest X-ray;
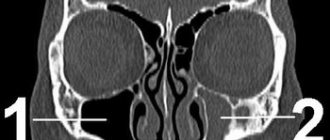
- in the case of a prolonged course (more than 3 weeks), if damage to the brain stem or cerebellopontine angle is suspected, MRI is prescribed, and if the pathological process is localized in the area of the temporal bone, computed tomography is more informative;
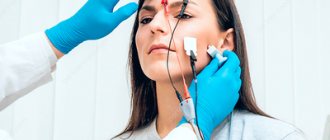
- Electroneuromyography is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment;
- If a nerve tissue infection is suspected, a lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination are performed.
If the patient has already been diagnosed with ear diseases, or has discharge from the ear canal or hearing loss, he should definitely consult an ENT doctor.
Facial neuritis is differentiated from Lyme disease, Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome.
Treatment
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is carried out on an outpatient basis. The exception is cases of illness associated with ear pathology that require surgical intervention.
- At home, it is necessary to spare the organs of vision. Due to incomplete closure of the eyelids, the cornea of the eye quickly dries out, so it must be constantly moistened with special drops, wear dark glasses during the day, and cover the eyes with a bandage at night.
- The basis of treatment for facial neuritis is glucocorticoid preparations (prednisolone), which are often supplemented with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
- If facial neuritis is caused by damage to the part of the nerve that runs in the labyrinth, middle ear or mastoid process, then only surgery will bring the best results.
- In severe cases, accompanied by paralysis of facial muscles, microsurgical neurological operations are performed to stitch or transplant nerves.
Reconstructive surgeries that are performed on patients with severe cases of facial neuropathy:
- movement of the branches of the hypoglossal nerve to the distal end of the facial nerve;
- transposition of the temporal muscle to the corner of the mouth, which allows you to learn how to raise its corner;
- transplantation of a muscle flap from the thigh while preserving the nerve branches;
- plastic surgery – brow lift, face lift, partial lip resection, eyelid correction.
Correction and hypercorrection of the muscles of the healthy side are carried out with a certain force, so that the antagonist muscles of the paretic side are sufficiently free in their actions and do not experience the pull of the muscles of the healthy side. The fixation of the free end of the patch to the helmet must be rigid, otherwise healthy muscles will not be kept in a state of correction. Attaching the free end of the patch directly to the skin of the affected side is ineffective: in this case, healthy muscles will immediately go beyond the control of traction and pull the skin and underlying muscles in their direction, returning facial asymmetry. It is necessary to monitor the areas of skin to which the patch is attached, preventing irritation with the help of massage and nourishing cream after the position correction procedure.
To reduce the palpebral fissure (lagophthalmos), one or two narrow strips of adhesive tape are attached to the skin of the eyelid in the middle of the palpebral fissure and gently pulled outward upward, attaching the free end to a stationary helmet. The tension force can be easily determined by the appearance of double vision in binocular vision. However, the narrower the palpebral fissure is when stretched, the easier it closes during involuntary blinking; the eye is moistened with tears, protecting the cornea from drying out.
Adhesive plaster tension is carried out in fractions on the first day - 2-3 times for 30-60 minutes, mainly during active facial actions, then the treatment time is increased to 2-3 hours a day.
Massage helps restore blood and lymph circulation, improves muscle excitability and creates the readiness of neuromuscular formations to perceive volitional impulses. To a certain extent, massage reduces muscle tone when contractures begin or increases the tone of paretic muscles. Methodically correct massage in combination with physical exercise helps reduce swelling of the facial nerve. Before each massage procedure, the patient must do a simple set of general tonic gymnastics, bending and turning the head; only after this it is advisable to begin the massage. It is recommended to start the massage procedure from the collar area, the back of the head, including the area of the mastoid process and neck, preparing the main vessels of the neck to more freely receive lymph from the face and head. The direction of the massage movements should correspond to the direction of the lymph flow; they are carried out mainly along the sternocleidomastoid muscle from top to bottom. After such preparation, begin facial massage. In the first week, massage of paretic muscles is superficial, limited to light stroking. The main attention is paid to massage the healthy side of the face in order to relax the muscles, thereby reducing the overstretching of paretic muscles to the healthy side. Impact on bony protrusions - mastoid processes, orbital edges, upper jaw, chin - helps to increase the volume of facial movements. In addition to general tonics, special exercises are included in LG classes.
The main attention is paid to the muscles of the healthy side:
- dosed tension and relaxation of individual muscles (zygomatic, laughter muscles, etc.) and entire muscle groups (zygomatic, buccal and orbicularis oculi muscles);
- isolated tension and relaxation of those muscle groups that provide certain facial expressions (smile, laughter, attention, sadness, etc.) or are actively involved in the articulation of certain labial sounds (for example, “p”, “b”, “m”, “f” , “u”, “o”, etc.) to minimally noticeable muscle tension, especially in the muscles surrounding the oral cavity.
LH classes last 10-12 minutes twice a day. In the main period (from the 10-12th day from the onset of the disease to 2-3 months), as a rule, spontaneous restoration of muscle function begins. Active treatment is carried out with special exercises. The duration of correction increases to 4-6 hours per day; it is alternated with exercise classes and massage. Gradually increase the tension of the adhesive tape, achieving hypercorrection with a significant displacement to the affected side in order to achieve stretching and thereby weakening of healthy muscles. The massage is carried out with light and deeper stroking, rubbing, and vibration at the points (acupressure techniques).
Most massage techniques are acupressure, so that the displacement of the skin is insignificant and does not stretch the skin of the weakened half of the face. The main massage is carried out from inside the mouth, it performs the functions of reduction (muscle designation) and massage, enhancing blood circulation, trophic processes in paretic tissues, etc. All measures to correct facial movements must be carried out with the active participation of the patient. To do this, the methodologist explains and demonstrates techniques in front of a mirror, cultivating in the patient the ability to control voluntary movements.
The following help significantly in mastering missing movements:
- preliminary relaxation of the muscles with light massage movements and performing individual exercises: - simultaneous and alternate puffing of the cheeks;
- snorting, pronouncing the sound “p” with a preliminary active delay at the initial phase of movement;
- the indication (pointing movement) carried out by the methodologist is a short stroke stroking the skin of the face in the area of paretic muscles. The direction of the indication corresponds to the facial movement. This technique gives the patient an idea of the direction of movement and helps to implement it;
- manual assistance when performing movements - this assistance from a methodologist is necessary to perform complex facial movements, for example, when closing the eyes, wrinkling the forehead, smiling, etc.
The methodologist models the facial act, corrects its execution, eliminates unnecessary movements, and then helps weakened muscles to engage in work;
- resistance to the main movement provided by the methodologist to increase the strength of paretic muscles - K. Lewit’s method, “post-isometric muscle relaxation” (PIRM): preliminary stretching of the facial muscle, dosed resistance with the hands of the methodologist and manual retention of the performed movement (isometric tension) followed by muscle relaxation .
In the residual period (after 3 months), all means of exercise therapy that were used in the main period are used. Rehabilitation therapy is aimed at training weakened muscles, eliminating the imbalance of antagonist muscles, improving afferentation, restoring the old and creating a new optimal stereotype of muscle relationships. Along with this, stereotypical facial acts are developed within the limits of satisfactory self-correction (smile, attention, surprise, etc.). During this period, paresis of the facial muscles is often accompanied by contracture of the corresponding muscles, which increases facial asymmetry and contributes to the occurrence of synkinesis. To overcome muscle contractures, the patient is recommended (first with the help of a methodologist, and then independently) to systematically carry out stretching movements with the first fingers along the muscle fibers, gradually, from session to session, increasing the applied force.
Methodological features of stretching facial muscles: muscle stretching is carried out from the center of the muscle to the periphery; Stretching the circular muscles is performed with successive movements, alternating fingers along the muscle fibers. In PH exercises, two types of stretching movements are most often used:
- the movements of the fingers are directed in opposite directions, they simultaneously stretch a small area of the muscle; then the hands are moved to the adjacent area. This procedure is repeated along the entire length of the muscle;
- one of the fingers fixes the muscles to the underlying tissues or bone, the other stretches the muscle in a small area along the fibers; then a similar movement is repeated on the adjacent muscle section.
Both types of movements complement each other. It is usually recommended that after simultaneous muscle stretching (type 1), stretching with sliding fixation (type 2) is performed.
For better stretching of contracted muscles, along with finger movements along the course of muscle fibers, stretching across their course is used.
The muscles located in the thickness of the cheek are accessible for stretching from the mucous membrane. The methodologist inserts the index finger into the patient’s mouth and creates support for stretching the contracted muscle with the hand located outside. After stretching, the muscles are better involved in voluntary motor acts. To consolidate the results of treatment measures, the patient is given an adhesive bandage (positional correction).
Synkinesis distorts the physiological functioning of the facial muscles, prevents the patient from fully and efficiently performing a given movement, and sometimes makes it impossible to contract a certain muscle. Good results are achieved by a relaxing massage of additionally contracting muscles. In some cases, point pressure on the muscles that perform synkinesis is effective; in combination with tensing the arm muscles or clenching the teeth, the required movement can be performed. It is necessary to fix the patient's attention on this. Then they achieve voluntary execution of a friendly movement, after which synkinesis is gradually eliminated.
Original article www.eurolab.ua Illustrations from the site: © 2011 Thinkstock.
Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve, which occurs secondary to serious diseases of the middle ear, requires urgent surgery. During the intervention, the doctor relieves excess pressure on the nerve (decompresses it) by removing part of the bone wall of the nerve canal that runs in the middle ear. Subsequently, treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed, as a result of which the function of the affected facial nerve is also restored.
If the pathology develops at an early stage of acute otitis media, a decision may be made on conservative treatment of facial neuritis:
- vitamin therapy with ascorbic acid and group B preparations (Milgamma);
- decongestants (furosemide);
- glucocorticoids for rapid relief of inflammation and pain;
- after acute manifestations subside, actovegin, solcoseryl, and other drugs that affect the metabolism of nervous tissue are prescribed;
- If conservative treatment is ineffective, different types of surgical interventions are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic methods are included in the complex of restorative treatment measures:
- therapy with UHF, quartz radiation, laser;
- electrophoresis with B vitamins, lidase;
- acupuncture and massage, especially performed on the inside of the cheek;
- applications of therapeutic mud, ozokerite, paraffin;
- physical therapy aimed at restoring the activity of the muscles of the lower part of the face.
Exercises for the main period of therapy
Classes during the main period, which lasts up to 3 months, are aimed at restoring the facial activity of muscle tissue. At this time, it is important to involve the entire peripheral muscle system in training in order to achieve the desired effect.
The duration of position therapy at this time is increased to 6 hours per day. It is alternated with acupressure facial massage and exercise therapy.
During this period, physical therapy is the most important component of treatment. It is better to perform exercises in front of a mirror to observe facial changes. The first classes must be conducted under the guidance of an experienced exercise therapy instructor.
Note!
During training, control the symmetry of the movements performed! To achieve this, muscle movement on the part of the face undamaged by the disease is limited with the hand.
Let's consider examples of performing exercise therapy for neuritis of the facial nerve at this time:
- Move your eyebrows up and down;
- Close your eyes, shifting your gaze with closed eyelids, which you need to hold with your hand;
- Smile without opening your mouth;
- Squint;
- Exhale air, vibrating your lips (snorting);
- Flare nostrils;
- Lift one and then the other lip successively so that the gum is visible;
- To frown;
- Smile with your mouth wide open;
- Light a match and blow out its flame;
- “Rinse” water in your mouth with your mouth closed, trying to “retain” all the liquid without spilling it;
- Whistle;
- Take air into your cheeks and release it;
- Take air into your cheeks and “drive” it from one cheek to the other;
- Lower the corners of your lips;
- Stick out your tongue and try to roll it into a tube;
- Show tongue;
- Stick out your tongue, moving it left and right;
- Close your mouth, fold your lips like a duck, stretching them forward;
- Moving your finger in a circle, carefully follow it with your eyes;
- Close your mouth and pull your cheeks in as much as possible;
- Try to cover your lower lip with your upper lip;
- Close your mouth and run your tongue along the gums from above and below.
Gymnastics are also performed to improve articulation abilities:
- Draw out the sounds o, i, u;
- “Cover” the upper row of teeth with your lower lip and pronounce p, f, v;
- Say oh, pu, vo, fu, ko, fi;
Pronounce syllable by syllable words that contain the following syllables: i-vol-ga, o-kosh-ko, etc. Once nerve conduction has been restored, resistance exercises can be used. The hand acts as a resistance tool. It “prevents” you from performing the necessary movements, thereby increasing muscle tension.
All exercises can be used 5 times each, taking short breaks to rest between them.
If the functionality of facial expressions cannot be fully restored, the exercises are distributed in such a way as to limit the moving part of the face. This technique will help “mask” the defect.
Folk remedies
At home, you can use traditional medicine recipes to warm up and relieve inflammation:
- three times a day for 20 days, warm the sore side with a bag of warm table salt;
- massage your face with essential oil of fir or cedar twice a day for two weeks;
- 3 times a day for 2 weeks, make warm compresses with linden blossom infusion or gruel from fresh black elderberries;
- 3 times a day for 15 days, rub with a composition consisting of equal parts of horseradish juice and olive oil;
- before going to bed, make compresses from fresh wormwood leaves for 30 minutes;
- make compresses from cottage cheese and honey: mix 4 parts of low-fat cottage cheese and 1 part of linden honey, wrap in gauze and apply to the affected half of the face for 1 hour, wrap with a scarf; do 2 compresses a day for 2 weeks.
Of course, folk recipes cannot replace drug therapy, much less surgery. However, they are not prohibited from being used to speed up recovery in complex treatment.
Residual stage
Starting from the 4th month of the development of the disease, with proper and regular training, a residual period begins. This is the time when there are clear improvements in the facial abilities of the affected half of the face, but residual symptoms are still preserved. The duration of the period is 2-3 months.
For good dynamics and consolidation of the results obtained, it is important to continue performing exercises from the main stage of training. The main task at this time is to increase muscle activity so that facial symmetry is restored.
Compliance with all medical recommendations, a combination of therapeutic exercises and massage will be the key to sustainable recovery of facial muscles.
Possible complications
Treatment of facial neuritis cannot be delayed. The later therapy is started, the greater the likelihood of developing complications:
- With a long course of the disease, the patient develops a persistent contracture of the facial muscles on the affected side: the muscles are involuntarily tense, contracted, and involuntary movements are possible. Recovery from such a complication is extremely difficult.
- The appearance of the face can change greatly: immobile muscles create a significant cosmetic defect.
- Persistent disturbances of taste.
- Corneal ulcers, infection, cataract formation, blindness.
- Constant spasm of the muscles of the face or eyelid.
Prevention
Taking into account the main causes of the disease, its prevention includes protection from colds, hypothermia, as well as timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. It is useful to harden the body, treatment in sanatoriums on the seashore, and a diet rich in B vitamins.
After suffering from facial neuritis, self-massage of the face with essential oil of fir or cedar is useful to prevent recurrence of the disease. It can be done at night during the cold season.
The paid services department of NIKIO invites patients with neuritis and neuropathies of the facial nerve for treatment. The patient is examined by an experienced doctor; a consultation with a candidate or doctor of medical sciences is possible. The clinic uses modern physiotherapy equipment. If necessary, the patient undergoes surgery to quickly restore the function of the damaged nerve.
Massage technique
To treat neuropathy, 2 main massage techniques are used:
- Spot;
- Stroking.
Acupressure on certain points of the human body, which are recognized as biologically active zones, is called acupressure. For neuritis, apply gentle pressure movements to the following points:
- Above the eyebrows;
- Above the eyes;
- On the temples;
- Under the cheekbones;
- On the wings of the nose;
- In front of the ears;
- In the dimple on the chin.
Each point is massaged for 10-15 seconds. In this case, both sides of the face “participate” in the massage: the sick and healthy.
Note!
There should be no pain during massage movements. Therefore, all movements should be soft.
Acupressure is performed in front of a mirror to control the response of facial muscles to the massage effect. If it is performed by another person, the patient is placed on a hard surface.
After 3-4 minutes of massage, the stroking movements are replaced with rubbing ones. Light pinching is also included in the process.
The total duration of the massage effect should not exceed 10 minutes.