The brain is one of the most important organs, the central computer of the body. His research was always fraught with difficulties and precautions. However, with the advent and implementation of magnetic resonance imaging, diagnosing brain pathologies has become faster and easier. MRI is a non-invasive test. It is based on the use of high-frequency pulses, magnetic fields, a computer system and special software that allow you to obtain the most detailed image of the brain. “Treatment and Diagnostic Center on Vernadsky” offers MRI at a cost that is one of the lowest in the capital.
Types of MRI examinations
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head is performed with or without a contrast agent. In the first case, the subject is injected with special substances (usually based on gadolinium salts), which make it possible to create a contrast between different tissues. In some cases, the contrast agent may cause allergic reactions. The type of study (with or without contrast) is determined by the specialist.
Psychological and neurological effects
Although resonance scanning is generally a physically harmless method, mental complications do occur. Mentally sensitive individuals experience problems such as unexplained difficulty breathing, palpitations, and excessive sweating.
The need to lie for a long time in a forced, motionless position leads to circulatory problems. In particular, changes in blood circulation in the cervical vessels lead to such manifestations as noise or ringing in the ears, dizziness, nausea (irritation of the cochlea and vestibular apparatus). The patient decides independently how much further presence on the MRI is acceptable, based on the severity and tolerability of the symptoms.
Since the physical effects are usually minor, the main problem is mental disorders, the role of proper preparation for the study and withdrawal from the procedure is important.
Before starting work, medical staff reassures the patient and explains the safety of MRI. Having completed the examination, he answers questions, trying to ensure that past sensations are perceived adequately, in a positive way. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging
- Pathologies and diseases of cerebral vessels.
- Head injuries and bruises, which are accompanied by internal bleeding.
- Speech impairment and hearing loss.
- Tumors of the brain, cerebellopontine angle.
- Paroxysmal states.
- Infectious diseases of the central nervous system (abscess, meningitis, HIV infection).
- Pituitary adenoma.
- Abnormal development of the blood vessels of the head (thrombosis, aneurysms).
- Epilepsy.
- Systematic headaches of unknown origin.
- Sinusitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases.
- Pathology of the base of the skull.
Recommendations from experts
When identifying and monitoring the development of a disease, the optimal frequency of magnetic resonance scanning is that which allows the doctor to receive timely information about changes in the patient’s condition. If a stroke is suspected, the frequency of the study reaches 3 times in 2 days. Even in severe cases, the procedure is carried out repeatedly over 7 days. The frequency of MR imaging for some diagnoses is shown in the table.
| Diagnosis | Multiplicity of research (if the patient's condition is stable) |
| encephalopathy | Once a year (once every 4-5 years) |
| brain tumors | up to 4 times in the first 12 months (then every 6-12) |
| hydrocephalus | newly diagnosed or unoperated - on the recommendation of the attending physician; for non-obstructive form and after surgical correction - once every 4-5 years |
| multiple sclerosis | 1-2 times a year |
| Alzheimer's disease | every 12 months |
| after operations | up to 4 examinations in the first year (every 1-1.5 years) |
It is advisable to carry out preventive examinations of the brain:
- persons under 30 years of age - according to indications or in the presence of alarming symptoms;
- up to 45 - once every 2 years;
- up to 60 years - every 12 months;
- for older people - once every six months (native and with the use of contrast).
MRI of the head
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
Relative:
- severe claustrophobia;
- the presence of non-ferromagnetic implants, insulin pumps, heart valve prostheses;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- drug or alcohol intoxication;
- presence of tattoos containing metallic compounds in the ink;
- heart failure.
Absolute:
- the presence of metallic foreign objects in the patient’s body;
- hematopoietic anemia (with magnetic resonance imaging with contrast);
- use of electronic devices such as pacemakers, etc.
MRI for a sore head
What are the capabilities of MRI diagnostics for identifying pathologies of the brain and other head structures? We are talking about this with Vadim Vyacheslavovich Cherkasov, a radiologist at the Expert Clinic Omsk.
– Tell me, Vadim Vyacheslavovich, is MRI the best option for brain studies?
– MRI is better suited than all other methods for diagnosing the brain. If MSCT - multislice computed tomography - is effective for visualizing bones or, for example, kidney stones, then for soft tissue structures of the brain the best option is, yes, magnetic resonance diagnostics.
More information about the capabilities of computed tomography can be found here
– What does the doctor see when an MRI of the head is done?
– This type of research makes it possible to detect abnormalities in brain development and visualize vascular changes in the structure of the brain. An MRI will show some volumetric changes, including oncological processes, changes in the pituitary gland. We may see signs of infectious diseases, intracranial hypertension (increased intracranial pressure). Infectious or inflammatory processes of the meninges and the brain itself are successfully diagnosed - for example, meningitis, encephalitis.
In acute pathologies in the head - ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke - we see changes characteristic of these processes.
“In simple terms, in an ischemic stroke, damage to brain tissue occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel, and in a hemorrhagic stroke, it occurs due to its rupture and hemorrhage.” Quote from the material “How to prevent a brain catastrophe?”
Post-traumatic hematomas are clearly visible both inside the brain and in the skull as a whole. This, by the way, is a very dangerous situation: when we find such hematomas, we call an ambulance right here, in our center, and the person is hospitalized (of course, with his consent).
– What types of MRI of the head are there?
– Studies of the arteries of the brain are carried out - it is clear where and which vessel is narrowed, you can measure its diameter, see the abnormal arrangement of the vessels. For neurologists, this is important information in terms of choosing further treatment tactics. Magnetic resonance venography is used to examine the venous system of the brain.
You can read more about MRI of cerebral vessels here
MRI can also clearly visualize the eye orbits - retinal detachment, clouding of the lens, that is, cataracts, nerve atrophy, space-occupying formations in the orbital area. The condition of the chiasma - the crosshairs of the optic nerves - is assessed; we see the asymmetry of the extraocular muscles and their pathological changes.
You can look at the ear canals. New growths in the internal auditory canals are clearly visualized.
MRI is also used in the study of the maxillary, frontal, sphenoid sinuses, and cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth. They can identify inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis, sphenoiditis), polyps and cysts. Injuries may cause fractures of the walls of the sinuses - sometimes they are also visible.
What will an MRI of the sinuses show? Read our article
After craniotomy, osteoplastic defects are clearly visible. Some meningiomas (tumors of the meninges) can displace the brain - this displacement, and the meningiomas themselves, can also be seen.
Demyelinating diseases are best diagnosed using MRI: various forms of multiple sclerosis (including atypical ones), acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. When diagnosed early, these dangerous diseases can be treated quite successfully. The earlier they are detected, the more effective the treatment. Here it is important to carry out studies over time: we do the first one, then repeat it after some time, the doctor looks and describes what changes have occurred in the brain during therapy and, if necessary, makes some adjustments to the treatment.
Malignant brain formations, metastases, and suppurative processes are also visible - for example, a brain abscess. Neurodegenerative diseases - Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, age-related changes - are successfully diagnosed. As a rule, in cases of studying neurodegenerative processes, targeted studies are used - the cutting step is reduced to 2-3 millimeters, which allows a more detailed examination of the brain structures of interest. To obtain more complete information, in some cases, MRI studies use a hypoallergenic contrast agent.
Read more about why contrast is needed in MRI here
Based on the data obtained using MRI diagnostics, we can guide the attending physician regarding the condition of the patient’s brain, so that the doctor can draw up the most effective plan for further treatment.
– How often can an MRI of the head be done?
– In addition to good visualization of soft tissue structures, the magnetic resonance imaging method has another big advantage: it does not involve radiation exposure. That is, X-rays are not used here. And the impact of the electromagnetic field during our research is completely harmless to humans. Therefore, you can do an MRI at least every day. Provided that the person does not have any metal structures or metal fragments in his body, and does not have a pacemaker, insulin pump or inner ear prostheses installed.
When is it possible and when not to do magnetic resonance imaging? Yuri Podlevskikh, executive director of Clinic Expert Orenburg, answers these and other questions
– If a person feels dizzy from time to time or constantly, will an MRI help determine the cause?
– Your head may feel dizzy for various reasons. Let's say, due to a violation of the spinal axis - that is, due to manifestations of osteochondrosis. In humans, the vertebral arteries pass through the cervical region, which perform a very important function for supplying blood to the brain. To understand whether this is the reason, it will be necessary to do an MRI not only of the head, but also of the cervical spine with MR angiography and, perhaps, then examine the entire spine.
Dizziness may be accompanied by headaches. Clinicians are not always able to find the cause of headaches. In this situation, a research method such as neurovascular conflict can help. Sometimes the vessels pass next to the nerves, and one of them can put pressure on the nerve, causing pain. The situation is quite common; many people suffer from headaches. After our conclusion, the doctor chooses treatment tactics.
The root of the problem may lie in cancer, changes in high blood pressure. All this is best visualized with magnetic resonance imaging. But taking an MRI of the head does not mean that a final diagnosis has been made: in order to obtain complete information about the problem, a comprehensive examination should be carried out, using other diagnostic methods.
You can sign up for a head MRI here
ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
The editors recommend:
Why undergo an MRI of the brain when nothing hurts?
Will an MRI show meningitis?
What to do when the head is cast iron?
For reference:
Cherkasov Vadim Vyacheslavovich
Graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of Omsk State Medical University (2015). Internship in the specialty "Traumatology and Orthopedics" - 2021. CHUDPO "Institute for Advanced Training of Medical Personnel" in the specialty "Radiology" (Voronezh) - 2021. Currently a radiologist at the "Expert Clinic" Omsk. Receives at the address: Omsk, st. Liza Chaikina, 7, bldg. 1.
Preparing for an MRI of the brain
Usually, there is no need to do any complicated steps before the examination. Sometimes the specialist may ask the patient to refrain from eating and drinking before the procedure. The person being examined must remove all metal jewelry. In many centers, the patient is given a loose shirt, in some they are allowed to remain in their own clothes, provided that they are loose and free of metal parts. Before a brain MRI, women should inform their doctor about the possibility of pregnancy. The patient is also obliged to inform the doctor about recent operations and diseases, allergies and the presence of metal implants. If the person being examined suffers from claustrophobia or is very worried before the procedure, he may ask the doctor for a sedative.
Harm from ionizing radiation
The most common example is radiography . It uses small doses of ionizing radiation, so it is absolutely contraindicated for some people (for example, pregnant women), while for others it can be performed a limited number of times. Knowing that such studies are unsafe, patients are cautious and always try to make sure in advance that the procedure will bring more benefit in the form of valuable information than harm from possible complications.
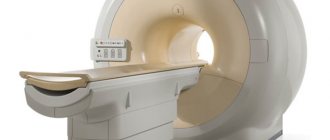
How is an MRI of the brain performed?
- An MRI machine is a cylinder with holes at both ends. The patient sits on a movable table that is placed inside the device during the MRI procedure.
- The length of the tunnel depends on the specific type of apparatus. Some devices only partially surround the table. Tomographs can also be open on the sides. They are used for patients with severe claustrophobia. In closed-type devices, the table slides in completely.
- During the examination, the patient is secured with belts. The less it moves, the more accurate the diagnostic results.
- During magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, devices with wires that receive and send radio waves are placed around the head.
- Patients are often given earplugs. This helps protect your hearing from the loud noise that comes from the MRI machine when it is in operation.
- The table is placed inside the tomograph, and the specialist moves to an adjacent office, which houses a computer system that processes the data. The device takes a series of pictures. Each one takes a few minutes to shoot. As a rule, an MRI of the brain without contrast takes about 20–30 minutes, with a contrast agent – approximately 45–50 minutes.
- An MRI machine takes layer-by-layer images of tissue. During a head scan, data is collected from approximately 20 levels, each 4–5 mm thick. The higher the magnetic field strength of the tomograph and the thinner the sections, the more accurate the research result.
Consequences of contrast
MRI with contrast has an additional effect on the body. In some people, the injection of a contrast agent causes allergic reactions. Therefore, before preparing for an MRI, the diagnostician finds out whether there have been manifestations of hypersensitivity to similar drugs. When contrasting for the first time, the drug is not administered immediately, but with skin tests, or first a small amount intravascularly.
Therefore, conducting research is safe, and the patient is given antihistamines that relieve allergens. The contrasts used in the examination differ in composition. To make the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance more effective, iodine and other chemical elements are introduced into the composition. If you have had allergic reactions to iodine compounds in the past, you should notify your doctor. Then the MRI procedure will be safe and painless.
Since contrast is often eliminated from the body through the kidneys, urine color may change. There is no need to be afraid of this; after the elimination process is completed, the urine acquires its normal color. The same applies to the color of feces.
During the first two days, if a contrast MRI was performed, you should not drink alcoholic beverages. Contrasting creates additional stress on the excretory systems of tissues and organs. Especially on the liver and kidneys, which cleanse the human body of most unnecessary substances. Combination with alcohol slows down cleansing and causes unwanted side effects from internal organs.
When the main excretory organs fail to simultaneously remove contrast and alcohol breakdown products, brain damage occurs. A person feels a headache, weakness is expressed, and severe dizziness occurs. Blood pressure often rises, and there may be pain in the abdominal cavity (along the digestive tract).
In cases of severe renal or liver failure, MRI with contrast is prohibited. With such a contraindication, only a non-contrast procedure is performed. The presence of concomitant diseases is identified by the attending physician, and only patients who do not have contraindications are referred for an MRI diagnostic procedure. To avoid medical errors, we advise you to choose your treating doctor from among the specialists at our clinic.
It should be remembered that the rate of removal of contrast from the body depends on age and chronic pathologies. In young and relatively healthy people, contrast is removed faster. The elderly, and especially those suffering from chronic diseases, need to abstain from alcohol for a longer period of time, 3-4 days. To ensure that foreign substances are released more quickly, it is advisable to increase the daily volume of fluid you drink to at least two liters.
Prices for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in Moscow
Various factors influence how much an MRI costs in each case. The price may change depending on whether the specialist will use a contrast agent, whether the results will need to be recorded on disk, etc. The approximate cost of magnetic resonance imaging is indicated on the page.
You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Diagnostic and Treatment Center on Vernadsky. To do this, call us by phone at any time convenient for you. You can also leave an online application through a special form presented on the website.
How does research affect the body?
MRI is performed using special equipment (tomograph). The device emits a constant and/or alternating magnetic field. It is especially important how water molecules in tissues react to the latter. Hydrogen atoms inside these compounds are arranged in a specific way and change the polarity of the substance. When radio waves pass through, the orientation of the molecules undergoes a transformation with the release of energy. The tomograph's receiving coils capture state conversion, which a computer program converts into images. Body tissues are magnetized to varying degrees, depending on the amount of fluid they contain. This feature ensures high accuracy and detail of scanning results.
MRI does not carry radiation, does not stimulate the formation of free radicals in the body, and does not change the function or structure of cells. There were no cases of harmful effects of the procedure recorded.