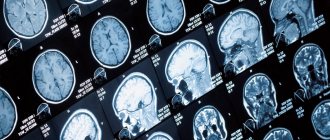
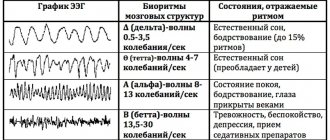
Cystic formation and internal hydrocephalus on MRI of the head with contrast (T1 VI, sagittal projection)
Patients are often interested in whether it is possible to independently decipher an MRI photo, what the dark and light areas in the images mean, and where to see examples of images of a healthy brain. We will answer these questions in our article.
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most informative diagnostic methods. The technology is non-invasive and absolutely safe for people of any age. The attending physician prescribes the procedure if a tumor is suspected or if the patient has a history of vascular pathologies (diagnosis is especially important after strokes), hormonal disorders, or epileptic seizures. Decoding MRI of the brain helps to identify the causes:
- nausea and vomiting in the morning;
- persistent increase in blood/intracranial pressure;
- regular headaches (in people over 50 years of age, this symptom may indicate a pre-stroke condition);
- sudden deterioration of vision;
- convulsive attacks;
- sudden change in behavior;
- tinnitus, dizziness;
- frequent loss of consciousness and other symptoms of organ damage.
MRI is necessary in case of suspected tumors (diagnosis will show the degree of tumor invasion into healthy tissues), to monitor the dynamics of the pathological process, and monitor the results of treatment, including surgery.
For children, scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is done to determine the causes of developmental delays, seizures, severe hydrocephalus (one of the signs of an anomaly is an increase in the size of the head), etc. The use of contrast expands the possibilities of research: additional imaging tools make it possible to identify diseases of the cerebral vessels, cancer and other processes.
What are the main advantages of magnetic resonance imaging?
MRI examination of the brain should not be neglected if the doctor prescribes a referral for such diagnostics. This procedure is very important for identifying serious deviations in its functioning in the early stages.
This is a non-invasive examination technique. During such diagnostics, the patient does not feel any discomfort, except for the fact that he has to be inside the tomograph. In this case, the devices are closed and semi-closed. The second type is used to examine people who are afraid of closed spaces.
The positive properties of this procedure include its painlessness. It does not require surgical intervention. It allows you to examine all parts of the human head.
MRI can be performed on patients of all ages. Diagnostics makes it possible to detect pathologies when they are just beginning. Timely diagnosis is very important when it comes to health.
MRI images of the brain clearly show whether there are pathological changes in its parts or not. When they are identified, the doctor prescribes effective treatment. The earlier therapy begins, the greater the chance that it will be successful.
Other benefits of MRI of the brain include:
- Possibility of examining all parts of the head, regardless of the presence of bone structures.
- No toxic effects.
- Obtaining a clear “picture” of vessels and soft tissues located at different levels, even if a contrast agent is not used during the procedure.
The decision on how to perform an MRI of the brain with or without contrast is made by the attending physician, based on the available indications.
Why is the procedure performed?
The list of indications for which a brain examination needs to be performed includes:
- headache;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- memory problems;
- ischemic heart attacks;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
MRI makes it possible to assess the degree of activity of the cerebral cortex. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to assess how much damage this organ has suffered as a result of injury. With its help, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases, benign and malignant neoplasms are detected.
Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed for schizophrenia and other mental disorders to assess the impact they have on the structure of the brain.
If there are violations in the integrity of the myelin sheath of the cortex, MRI will reveal them. The procedure helps diagnose cysts, carcinomas, brain hemorrhages, and detect inflammatory and infectious processes. It is often prescribed for autism and multiple sclerosis. Cerebral perfusion makes it possible to assess blood flow in various areas. Before such a thorough diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo tests. Their results will indicate the area of the head that is subject to more detailed examination. For example, if a patient has elevated prolactin levels, this may indicate problems in the cerebellum.
An MRI image of the brain allows us to assess the condition of not only the cerebellum, but also other parts that are responsible for memory and the thought process. Carefully examine the occipital lobes, which are responsible for the visual perception of objects, and evaluate the density of gray and white matter.
X-ray radiation is not used during MRI and this is a big plus. You don’t have to wait long for the results of the procedure; deciphering them takes a minimum amount of time. This procedure is highly diagnostic. In recent years, it has become indispensable in identifying brain pathologies.
Interesting but true
Endoprostheses can degrade the quality of the resulting images. Metal can seriously distort the image. It is also important to remove all metal objects from your pockets and remove jewelry.
Interestingly, even a tattoo can negatively affect the study. There may be metal particles in the paint. Therefore, a tattoo is a contraindication for MRI. Its owners will not only receive incorrect results, but will also suffer from severe pain during the procedure.
The picture will be ruined by braces. You must notify a specialist about their presence. They must be removed during examination.
Features of the MRI procedure, principle of operation
The tissues being examined are exposed to electromagnetic waves within a magnetic field that contain varying numbers of hydrogen atoms. They generate a certain amount of energy, which is recorded and processed by a special device. We are talking about a tomograph. This processing makes it possible to obtain images of various parts of the brain. The development of pathological phenomena is characterized by structural transformations in the tissues of the organ. As a result, the content of hydrogen atoms in the affected area changes. This leads to changes in the signals received during the examination.
MRI of the head visualizes various parts of the brain and gives their characteristics. The main goal of such diagnostics is to detect affected areas in the brain, determine their shape, size, nature and exact location.
When carrying out such a diagnosis, it is impossible to miss a tumor; it determines the tissue of origin of the tumor, distinguishes atrophic areas from post-traumatic ones. Allows you to determine the nature of strokes, identify infectious lesions, brain swelling, displacement of its structures, and assess the condition of the ventricles.
MRI of a healthy brain does not reveal any abnormalities. If there is a suspicion of a tumor in the head, this procedure must be carried out. It reveals not only primary tumors, but also metastases and pituitary lesions.
Even with a minor head injury, an MRI is recommended. The procedure allows us to exclude brain abscess and meningoencephalitis. It is carried out in the presence of symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Doctors prescribe magnetic resonance imaging for frequently recurring headaches and motor dysfunction. This examination is indicated for people who faint for no reason. Those who have behavioral and cognitive dysfunctions.
MRI is indispensable both in the neurological field and in endocrinology, psychiatry, and other areas of medicine.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography scans are often done after surgery to evaluate the results of surgery. The technique is indispensable in dynamic observation. With its help, they examine not only the brain, but also other organs - the pancreas, gall bladder.
What brain lesions and tumors look like on MRI
Focal brain damage is characteristic of multiple sclerosis, some parasitic, viral, bacterial diseases, and age-related changes in nervous tissue. On the tomogram it is visualized as a small area, differing in its characteristics from the surrounding structures. The lesions can be single or multiple, scattered throughout all hemispheres or located within the boundaries of a particular region. They lead to displacement and changes in other areas of the brain that are not involved in the pathological process.
Metastases and brain tumor on MRI
The tumor is a single formation that compresses the surrounding structures. Benign neoplasias have clear contours, grow slowly, but still gradually compress the brain in the confined space of the skull. Malignant neoplasms are characterized by rapid growth rates, irregular shape, and lack of clear outlines. Assessment of the vascular bed, which is present in each tumor, also allows us to judge the size and boundaries of the latter.
Another type of neoplasm - cysts - is a fluid-filled cavity surrounded by a capsule. They form at the site of hemorrhages and abscesses. Cysts do not have their own vessels. Sometimes they begin to grow due to an increase in the fluid they contain, which will also lead to compression of the brain.
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging
There are few contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging, but they do exist. These include:
- The presence of an implant in the body (including a pacemaker).
- Excessive mobility of the patient, for example, if he is intoxicated. During an MRI, the subject must lie still.
- Foreign objects in the body (during the examination they may move and damage blood vessels).
Relative contraindications include illness, children under 7 years of age, metal prosthetic joints outside the range of electromagnetic waves, blood diseases (in this case contrast cannot be used), severe claustrophobia (the patient’s condition may sharply worsen in a closed space).
How to prepare for the examination?
There is no need to prepare long or thoroughly for an MRI of the brain. A couple of hours before the diagnosis, it is advisable to refrain from eating. You should not use decorative cosmetics before the procedure. You must leave your phone, bank cards and watches outside the room where the diagnostics are carried out.
The doctor will definitely tell the patient about the progress of the examination. If he suffers from a fear of closed spaces, he will prescribe sedatives.
If necessary, a procedure with contrast will be performed to obtain a more accurate picture. After administration of the contrast agent, headache and nausea may occur. Before using contrast, a sensitivity test must be performed.
Preparing for an MRI of the brain
The head MRI procedure does not require any special preparation. A person does not need to change his usual diet, food intake or give up medications. The day before undergoing diagnostic tests with contrast, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol. Alcohol promotes vasospasm, as a result of which problem areas may not be sufficiently visualized during the examination.
If a nursing mother undergoes contrast tomography, it is necessary to prepare food for the baby for the day, since the dye penetrates into the milk.
Foci of gliosis in the white matter of the brain
How is the procedure done?
Before being diagnosed by an MRI machine, the patient is asked to sign a consent form. After this, he is asked to put on a robe (you can also be examined in your own clothes, the main thing is that there are no metal elements on them) and lie with your back on a special platform. The subject's head is fixed to ensure its immobility.
The platform, with the patient lying on it, slides into the “pipe” of the tomograph. The equipment makes noise during operation, so it is recommended to use earplugs.
The MRI room is equipped with a two-way voice communication system. The doctor monitors the progress of the procedure from the next room.
The examination takes approximately half an hour. When using contrast, about 50 minutes. The contrast is administered simultaneously or with a dispenser.
results
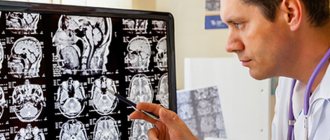
The interpretation of the results of magnetic resonance imaging is carried out by a radiologist with the appropriate qualifications. He analyzes the results obtained and draws a conclusion based on this. The patient receives the scan results on a DVD, after which he hands them over to the doctor.
In our medical center, MRI of the brain and abdominal organs is performed using modern equipment.
We use the best tomographs that guarantee high accuracy of examination results. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Types of vascular MRI
Currently, there are several types of magnetic resonance examination of cerebral vessels:
- Arteriography of vessels with contrast
- Venography - a detailed examination of the venous network
- Comprehensive examination of veins and arteries
In the resulting image, the doctor is able to examine every part of the circulatory system, detect the slightest defects and disorders, including tumors, atherosclerotic manifestations, and so on.
This type of MRI is an indispensable stage in diagnosing a patient after a stroke, to assess the degree of brain damage after an injury, and also makes it possible to identify thrombosis and abnormalities in the structure and location of the vascular network.
A general examination is prescribed for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the brain, for example, before or after surgery. Using the resulting image, the doctor can reliably assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method and correct it in time if necessary.
Make an appointment now!