Content
- Drugs for blockade
- Sciatic nerve block
- Expert opinion
- Cost of treatment
- We recommend reading
Pain levels
0 — 3
Mild pain
- does not interfere with everyday activities, but you can adapt to the pain.
4-6
Moderate pain
- prevents you from doing business, prevents you from concentrating, the patient remains independent
7-8
Strong pain
- it is impossible to carry out daily activities, it is difficult to think about anything other than pain, the patient cannot function independently
9-10
Unbearable pain
- requires urgent care, bed rest, disables the patient
How much does the procedure cost?
In the multidisciplinary clinic CELT, the cost of the blockade ranges from 5 thousand rubles. You can find out the exact cost of the procedure in the corresponding section of our website, by calling us or visiting a consultation. The cost of the procedure depends on the following factors:
- type of drugs used;
- the affected part of the spine on which the procedure will be performed;
- equipment that will be involved in the process.
Drugs for blockade
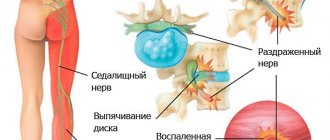
Before the doctor prescribes a blockade in the area of the piriformis muscle, it is necessary to diagnose and clarify the indications:
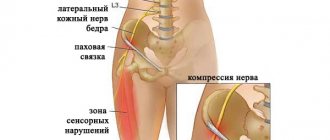
- Aching pain in the gluteal region;
- Pain when trying to cross your legs;
- Inflammation and swelling in the piriformis muscle area.
Several drugs are used simultaneously for blockade:
- Local anesthetics – lidocaine, novocaine.
- Hormonal drugs - diprospan, dexamethasone, kenalog, hydrocortisone.
- Homeopathic remedies – Tzel-T, Traumeel-S.
- B vitamins.
It is worth noting that after administering an injection for blockade, a positive effect is observed after 15-20 minutes. Acute pain and swelling go away, muscles relax, and blood circulation normalizes.
You can read reviews about piriformis blockade and blockade for muscle pain on our website.
To relieve spasm of the piriformis muscle, use a “medicinal cocktail” consisting of at least 2-3 drugs. This simultaneously solves several problems - rapid pain relief, muscle relaxation (spasm is eliminated) and reduction of inflammation.
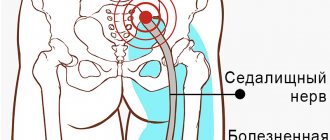
| Blockade for pinched sciatic nerve |
Sign up for treatment
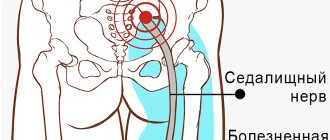
Diagnosis for pain in the gluteal region
To identify the causes of pain and make a diagnosis, a physical examination by a neurologist is necessary. As objective methods of diagnostic search, in medical in Rostov-on-Don, high-precision modern equipment is used, which allows you to quickly determine the cause of pathological processes.
1) Using computed tomography, not only the structure of the bones, but also the vertebral discs are examined in detail. A tomograph is indispensable in diagnosing hernial protrusions, tumor formations and damage caused by trauma.
2) Magnetic resonance imaging examination allows us to identify the nature and extent of damage to the sciatic nerve plexuses and the features of the processes occurring in them.
The price for instrumental diagnostics is affordable. It includes the examination itself, its result on disk, and a transcript from the diagnostician.
Why do they contact us?
- No queues
No need to wait, we work by appointment
- All in one day
Doctor's appointment, diagnosis and treatment on the day of treatment
- Let's relieve the pain
We relieve pain in just 1-2 visits to us
- We guarantee
Professional approach, affordable prices and quality
- Doctor's appointment 0 RUB!
If the cost of treatment is more than 20,000 rubles
- Three treatment options
We will select several methods and offer optimal treatment
ADVANTAGES OF THERAPEUTIC BLOCKS IN THE CLINIC NAMED AFTER N.I. PIROGOV IN ST. PETERSBURG
- Appointments are conducted by doctors with extensive experience, authors of scientific papers and patents. Our specialists accurately diagnose neurological diseases, are fluent in modern and traditional therapeutic techniques, and select the optimal treatment tactics for each patient;
- The clinic is equipped with modern equipment from leading foreign companies;
- The Pain Treatment Department regularly holds promotions and offers discounts.
Therapeutic blockades are an effective means of relieving pain! Make an appointment
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of lumboischialgia, it is recommended:
- eat rationally;
- move more often;
- exercise;
- perform exercises that strengthen the back muscles and stretch the muscles;
- when doing physical work, use the principles of biomechanics;
- balance the load with the body’s capabilities;
- fight excess weight;
- promptly treat diseases of the spine, blood vessels and digestive system;
- don't get too cold.
Advantages
- fast, complete and long-lasting pain relief;
- additional therapeutic effect due to the acceleration of recovery processes;
- possibility of repeated use;
- minimum of adverse reactions.
For tonic syndromes caused by muscle tension, blockades can relieve discomfort for several months or even years. For more serious diseases, anti-inflammatory and hormonal agents are added to the anesthetics, as well as chondroprotectors for cartilage regeneration. When introduced into a sore spot, they are much more active than droppers, tablets or ointments. Therefore, therapeutic blockades in neurology are much more effective than pharmaceutical drugs and physiotherapy.
Possible complications
If you want to minimize the risk of complications from conduction anesthesia
in Moscow, contact the CELT clinic. Our doctors have performed this procedure many times and know how to avoid them. It is customary to distinguish the following types of complications:
- toxic - arise as a result of incorrect selection of dosage and concentration of the drug or its penetration into the vascular bed, characterized by various symptoms: from dizziness to falling into a coma;
- inflammatory - appear as a result of improper procedure, use of an inappropriate or expired drug, and are characterized by the development of periostitis, meningitis;
- allergic - characterized by various symptoms, ranging from itching and drop in blood pressure to difficulty breathing and cardiac arrest;
- traumatic - consist of damage to blood vessels, nerves, pleural or abdominal cavity during a procedure with corresponding symptoms.
Surgery
The operation is indicated if conservative therapy is ineffective and severe pain that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods persists for more than 6 weeks, as well as in the presence of:
- large intervertebral hernias;
- spondylolisthesis;
- spinal deformities;
- hemangiomas, chondromas and other spinal tumors;
- severe dysfunction of the pelvic organs, leading to urinary or fecal incontinence.
In such situations, conservative therapy will, at best, slow down the development of these pathologies, but not eliminate them completely. But if in the isolated existence of, for example, an intervertebral hernia, this is enough to improve the patient’s condition, then in cases where the presence of spinal pathology provokes the addition of sciatica, such measures will not be enough.
After all, the cause of the pinched sciatic nerve remains, it continues to suffer and cause the corresponding clinical picture. Therefore, in such cases, surgery is the only way to achieve a lasting improvement in the condition, restore a normal quality of life and eliminate the risk of loss of ability to work.
But even if there are indications, surgical intervention cannot always be performed. It is contraindicated for:
- pregnancy;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- serious respiratory or heart failure.
A timely operation can completely eliminate the causes of sciatica.
Surgical treatment of sciatica for intervertebral hernias
Herniated discs are a common cause of sciatica. Moreover, the severity of symptoms of nerve entrapment does not always depend on the size of the protrusion. Sometimes even small hernias can cause serious pain, limited mobility and neurological disorders.
Today, the problem of intervertebral hernia can be completely solved only by surgery, but the type of operation directly depends on the size, location and other features of the hernia. For small protrusions, preference is given to percutaneous surgical methods: nucleoplasty and hydroplasty.
In both cases, the essence of the operation is to destroy part of the nucleus pulposus of the disc, which leads to a reduction in the size of the hernia or even its retraction due to the creation of reduced pressure inside the disc. Percutaneous surgery techniques involve the use of thin cannulas, the diameter of which does not exceed several millimeters.
Operations of this type can be performed under general or local anesthesia. The instruments are inserted into the disc under the control of the image intensifier, which allows the neurosurgeon to precisely control the direction and depth of needle insertion, and also practically reduces the likelihood of injury to nerves or large blood vessels to 0.
Using cold plasma, radio waves, thermal laser energy or liquid pressure (during hydroplasty), part of the nucleus pulposus is destroyed. The volume of intervention is clearly controlled by the surgeon. Once the desired effect is achieved, the cannula is removed, and the remaining postoperative wound does not even require sutures. It is covered with a sterile bandage, and within a few hours the patient can leave the clinic and return to daily activities.
But nucleoplasty and hydroplasty are effective only for hernia sizes up to 0.7 cm. In other cases, other methods are used:
- Microdiscectomy – involves removing the hernia through an incision of about 3 cm in the projection of the affected disc. Special miniature instruments are used to perform the operation. Microdiscectomy allows you to remove a hernia of almost any size and location, while the small size of the incision ensures ease of rehabilitation and speed of recovery.
- Endoscopic surgery is a gentle method of surgical treatment of intervertebral hernia, which involves removing it with special instruments that are inserted into the patient’s body through punctures up to 1 cm in diameter. Through endoscopic surgery it is also possible to remove almost any hernia, but if its location is complex, the technique is powerless.
Surgery for sciatica caused by spondylolisthesis
Surgical treatment is indicated for spondylolisthesis, accompanied by a displacement of the vertebra by more than 50% relative to the normal axis. It can be carried out in two ways, and the choice of a particular one is based on the results of the MRI. But with sciatica, stabilization of a displaced vertebra in a normal position is permissible only after removal of the anatomical formation that provokes compression of the nerve and the development of neurological symptoms of sciatica.
In almost all cases, stabilization of a displaced vertebra is carried out using a special plate, which is fixed to a healthy and slipping vertebra using screws. This eliminates the possibility of it being re-displaced from its anatomically correct position. But first it is necessary to carry out:
- Discectomy – removal of the intervertebral disc is indicated if, against the background of spondylolisthesis, an intervertebral hernia forms and impinges on the spinal root. If complete removal of the disc is required, it is replaced with an endoprosthesis or a graft of the patient's own bone. The first option is preferable, since modern endoprostheses are in no way inferior in functionality to natural intervertebral discs.
- Foraminotomy - is performed when a nerve is pinched in the foraminal openings of the spine as a result of a decrease in their size due to the proliferation of bone tissue or other reasons.
- Laminectomy is a radical operation used only in extreme cases when spondylolisthesis has led to stenosis of the spinal canal. During a laminectomy, both individual anatomical structures and entire vertebrae can be removed. In the latter case, the removed vertebra is replaced with appropriate implants.
Surgery for sciatica caused by scoliosis
Scoliotic deformity of the spine often provokes pinching of various nerves and the development of sciatica in particular. Therefore, if the deformity cannot be corrected conservatively, surgical intervention is resorted to.
There are several types of operations performed for scoliosis. The specific tactics for restoring the correct axis of the spine are determined individually, but in all cases special metal structures are used that fix the vertebrae in the correct position. Sometimes they involve correcting the position of the vertebrae after surgery with gradual tightening of the screws to form a more correct axis of the spine.
But if previously all operations to correct scoliosis involved long incisions along almost the entire length of the spine, today this is possible even in a minimally invasive way. As a result of eliminating spinal deformity, the nerves are freed, which helps eliminate the causes of sciatica and progressively improve the patient’s condition.