Schizophrenia is an unpredictable mental illness that can occur in different forms. Some patients have only one or two attacks in their entire lives, while others lose touch with reality in a matter of months. Some types of pathology develop rapidly, and some of them progress over years. Residual schizophrenia belongs to the second type. It is characterized by a long period of negative phase. In the article we will look at what its features are.
In this article
- Total information
- Residual schizophrenia
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Forecast
Total information
Schizophrenia is a polymorphic endogenous disease that affects the human mental apparatus. Polymorphism suggests that it occurs in different forms. The reason for its origin is the internal state of the psyche, so we are talking about an endogenous nature. As for the direct impact on a person, schizophrenia affects the brain, or more precisely, thinking and emotional reactions.
This psychopathology is detected in approximately 1% of people. The peak incidence occurs at 20-28 years in men, and at 26-32 years in women. However, schizophrenia is also diagnosed in children, as well as in the elderly. Moreover, it is often combined with anxiety disorders, depression, alcoholism and drug addiction, so it is not always possible to identify the disease at an early stage.
Many people believe that schizophrenia is a split personality. Others believe that it is always accompanied by hallucinations. In fact, “multiple personality disorder” is too simple a word for such a complex disease. In schizophrenic disorders, there is a disintegration of personal qualities and a person’s loss of contact with reality.
If we talk about hallucinations, they do not occur with every type of pathology. Moreover, the presence of this symptom may not indicate a schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Residual schizophrenia refers to those forms in which hallucinations are extremely rare.
What is cerebral encephalopathy?
Encephalopathy is a group of brain diseases of a non-inflammatory nature. The disease can manifest itself in people of different age categories, with corresponding distinctive features. Treatment of encephalopathy involves a comprehensive diagnosis. Starting from identifying the causes of the disease, ending with courses of medication, manual and physical therapy. A general classification divides encephalopathic pathology into perinatal and acquired.
The congenital form of encephalopathy is a consequence of negative intrauterine effects on the fetus, genetic inheritance or birth trauma. This type, although rare, is the most severe in its manifestations and often leads to disability.
The acquired form of cerebral encephalopathy is more common. Acts as a consequence of severe systemic diseases of the body, injuries, exposure to harmful external factors. In medicine, there are several stages of encephalopathy:
- Subjective neurological symptoms; mild neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Clinically defined neurological syndrome; significant neuropsychic disorders.
- Several syndromes; dementia is a severe neuropsychiatric disorder.
Where does this unpleasant, dangerous disease come from?
Residual schizophrenia
Residual schizophrenia is also called residual schizophrenia. It is registered after exacerbations (attacks) and is characterized by stable remission without pronounced signs of psychosis. Although it can be asymptomatic, it is also impossible to say that a person is completely healthy in this condition.
The patient does not have hallucinations or delusions, but his behavior is very passive and uninitiative. The patient may say that everything is fine. However, relatives are usually concerned about his behavior and are very worried. They have cause for concern, since the disease can worsen at any time, despite the fact that sometimes a person remains in this state for years without any signs of psychosis.
Residual schizophrenia is rare - only 2.6% of patients.
Treatment is carried out not only during attacks, but also during remission. The further development of the pathology depends on its quality.
Advantages of treatment at the Ardenium clinic
Correct diagnosis is important for the successful treatment of residual encephalopathy, which can be very difficult.
Highly qualified neurologists with many years of experience practice at the Ardenium clinic. In their work, they use modern equipment of the latest generation, which ensures correct diagnosis and contributes to successful treatment. If you notice the slightest deviation in your health, do not ignore the problem. Contact a specialist, which will allow you to identify and cure the disease as soon as possible, preventing dangerous consequences that lead to personality degradation.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist by calling (3412) 52-50-50, or by ordering a call back.
Causes
Nothing is known for sure about the causes of any schizophrenia. Scientists have not yet been able to describe the mechanism of development of the pathology. It has only been established that its focus is in the brain, but what exactly causes its occurrence and how it progresses remains a mystery.
Doctors have at their disposal a group of factors that can hypothetically provoke schizophrenia:
- Genetic predisposition. The likelihood of developing psychopathology increases if it has been identified in relatives. The closer the relationship, the higher the risk. A child with two schizophrenic parents has less than a 50% chance of avoiding the disease.
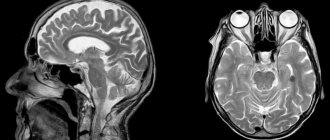
- Brain abnormalities. MRI shows that in schizophrenic disorders there is enlargement of the ventricles, atrophy of the hippocampus, temporal lobes and other areas.
- Problems that arise during pregnancy. We are talking about injuries, infections, unhealthy lifestyle of the mother, complicated childbirth and birth injuries.
- Social conditions. In families with alcoholics, drug addicts, psychopaths and other antisocial personalities, children may develop schizophrenia, psychopathy, schizoaffective disorder and other diseases. He definitely cannot avoid psychological trauma.
- Upbringing. As a rule, schizophrenics appear in families with oppressive parents or, on the contrary, in permissive conditions. Also, the likelihood of developing psychopathologies increases if no one cares for the child at all and no one loves him.
- Dependencies. Alcohol, drug addiction and smoking are not the direct culprits of schizophrenia, but they can serve as an impetus for its development. If a person began using psychoactive substances in childhood, the risks increase markedly.
Also, trauma, acute or chronic stress, prolonged depression, etc. can lead to schizophrenia or its exacerbation. The patient's medical history is studied carefully, but it is not always possible to draw a direct connection between one or another event and an attack of psychopathology.
Treatment of encephalopathy
Treatment of brain encephalopathy involves symptomatic complex therapy. This includes:
- Massage is a reflex effect on the muscular system. Effective for migraines and limb tremors.
- Exercise therapy and physiotherapy have a beneficial effect on all organs and activate defenses at the cellular level. For severely ill patients they are mandatory, since in stage III encephalopathy the patient becomes disabled and has limited movement.
- Dietary nutrition - helps to reduce weight, alleviating problems associated with blood pressure, especially in overweight people, and minimizes the presence of harmful substances in the body.
- The use of pharmacological drugs - a complex effect on the causes of the disease, slows down the progression of encephalopathy.
- In 20-30% of cases, provided that therapy is started in a timely manner, treatment allows you to completely get rid of the disease, which is a very good indicator.
In medical centers and specialized clinics, in addition to the listed methods, they treat brain encephalopathy with blockade, acupuncture, osteopathy, manual therapy, and surgery.
The composition of the programs and the duration of treatment are determined individually. Depending on the severity of the manifestations of the disease and the causes that caused it. The predominant symptoms of the disease also affect the range of methods and drugs used. The total duration of therapy can be 2–3 years, and the patient can undergo the course on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. What other features of treatment are highlighted by experts, we will consider further.
Treatment of encephalopathy in children
In very young children, birth trauma or hypoxia are common causes of encephalopathy. However, experience shows that this is not entirely true. There are many children who had a birth injury, but subsequently do not have encephalopathy. At the same time, there are children who have not had any trauma, but subsequently have even severe encephalopathy. This fact, as well as the very diversity and sometimes complexity of the symptom complex of encephalopathy, clearly show that encephalopathy is not only and not so much a problem of the brain. This is always a problem for the whole organism.
While monitoring your child, if signs of abnormalities are detected, you should immediately see a doctor. The doctor will be able to prescribe treatment in a timely manner, and parents must strictly follow the prescribed instructions and recommendations.
Treatment of encephalopathy in children is complex and lengthy. The main goal is to eliminate the cause that led to the disease, as well as restore already damaged nerve cells. A positive outcome directly depends on the participation of parents in the treatment of a child. Providing the baby with a healthy, nutritious diet, arranging regular walks in the fresh air, doing therapeutic exercises, and other physical exercises both in exercise therapy groups and at home is the direct responsibility of parents. To treat brain pathology in a child, the following drugs are used:
- neuroprotectors - restore and help prevent damage to neurocytes;
- medications that improve blood circulation and accelerate the outflow of venous blood;
- tranquilizers, sedatives - necessary to reduce pulsation in neurocytes;
- B vitamins that improve metabolism in nerve cells.
The diagnosis of encephalopathy in a child requires immediate registration with a neurologist. This is necessary for periodic examination and prescription of courses of treatment.
Prevention of encephalopathy should begin before the baby is born. Expectant mothers are required to take care of their health during pregnancy. Stop abusing bad habits, register on time, regularly visit your gynecologist, listen to doctors regulating childbirth, and follow their instructions. Much also depends on the responsibility of doctors during childbirth. Being attentive to the woman in labor and preventing birth trauma are their main tasks.
Throughout life, it is important to ensure that the child avoids stressful situations, eats well, develops physically, increases the effectiveness of the immune system, and knows the rules of safe behavior on the street, at home and in child care institutions in order to prevent traumatic brain injury. Taking vitamin and mineral complexes prescribed by a doctor will be a powerful prevention of many diseases.
Treatment of encephalopathy in adults
Encephalopathy of the brain in adults is an acquired form of the disease due to concomitant diseases and lifestyle. Therefore, it is important to devote all your efforts to eliminating the root cause.
- Lifestyle correction: getting rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs), weight loss, eliminating unhealthy foods from the diet (salt, spicy foods), moderation of physical activity.
- Physiotherapeutic measures: magnetic therapy, ozone therapy, acupuncture, ultraviolet irradiation of blood, extracorporeal blood purification (plasmapheresis, hemosorption).
- Treatment with pharmaceuticals. Aimed at reducing the rate of disease progression. Involves taking vasodilators and diuretics, neuroprotectors, and B vitamins.
- Surgical intervention. In severe cases, it becomes the most effective technique. To restore the functioning of cerebral vessels, endovascular operations are used. They have the greatest efficiency and safety.
Treatment of encephalopathy in the elderly
With age, natural biological changes occur in all organs and tissues of the body. Under aggravating conditions of chronic lack of oxygen and glucose, the functioning of the central nervous system begins to malfunction, which leads to serious disorders. Of course, such changes are more often observed in elderly and senile patients.
Treatment programs for the elderly are more gentle and long-lasting, but may be less effective due to age and slow reversible processes.
Treatment of toxic encephalopathy
Toxic encephalopathy occurs against the background of organic damage to brain tissue. Which is a consequence of poisoning with heavy neurotropic poisons, intoxication with nitrogenous compounds.
Toxic encephalopathy manifests itself through contrasting periods of excitation and decline. At the same time, at the peak of activity, aggression, convulsions, hallucinations, and epileptic states appear. During the decline, there is an almost complete absence of reactions to external stimuli.
The basis of treatment is a strict diet and the use of medications. Unfortunately, most often the disease occurs in a progressive trend. The patient dies from hepatic coma, since toxins primarily disrupt its functioning.
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy
Alcoholic encephalopathy is damage to brain cells as a result of long-term alcohol consumption. Usually develops towards the end of stage II - beginning of stage III of alcoholism. The approximate duration of continuous alcohol consumption before the first signs appear is 7-20 years. It can occur in acute or chronic forms.
Accompanied by various disorders: mental, somatic, neurological. Characterized by a decrease or absence of appetite, weight loss, impaired coordination of movements of the musculoskeletal system, anxiety, mood instability and memory impairment, hallucinations. Treatment is conservative. First of all, completely abstain from alcohol.
Treatment of residual encephalopathy
This type of disease occurs when the consequences of concussions are ignored and the course of treatment is ineffective. Damaged, unrepaired brain cells continue to die, leading to the progression of the disease. Therapeutic measures for emergency restoration of blood supply to the brain are the primary prescriptions of the doctor. This form of encephalopathy most often uses radical surgical methods.
Treatment of vascular encephalopathy
It occurs against the background of arterial hypertension, as a combination of blood pressure disorders and organic brain lesions. The development of vascular encephalopathy provokes focal ischemic brain damage and atherosclerotic damage. In this case, treatment begins with careful suppression of blood pressure with various antihypertensive drugs, antithrombic therapy, and a cholesterol-lowering diet.
Treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
The pathogenesis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is similar to vascular encephalopathy. The difference is that ischemic brain lesions are not isolated, but are represented by multiple foci. Their spread leads to cerebral infarction and vasogenic edema of brain tissue.
Due to the complexity of research on this type of encephalopathy, doctors are limited in the evidence base of medications for the treatment of DEP. It is obvious that treatment should be carried out comprehensively, including measures to prevent further damage to blood vessels and brain matter, improve the stabilization of cognitive functions, reduce disorders, and correct other clinical manifestations of the disease.
Drugs for the treatment of encephalopathy
Medicines prescribed to alleviate encephalopathy syndrome and its treatment are divided into several groups.
Group of drugs:
- Vasodilators (vasodilators)
- Nootropics (stimulants)
- Antioxidants (oxidizing inhibitors)
- Metabolic agents
- Venotonic
- Antiplatelet agents
Only a small part of the drugs is shown, since the list of originals and generics is very large. All prescriptions are made by the doctor, selecting the medicine individually for each patient.
Symptoms
Any form of schizophrenic disorder has two sets of symptoms - positive and negative. The first are called so not because they are “good”, but because they are a consequence of the activity of the psyche. Typical signs of productive symptoms are hallucinations and delusions.
In such a state of psychosis, the patient may be inadequate. Moreover, in most cases, he does not realize that he is sick, even if he sees grandiose and fantastic hallucinations.
The nature of hallucinations is individual. Some hear voices, while other patients see or touch objects that do not exist in reality.
With residual schizophrenia, there are usually no such symptoms. The patient is in a negative phase, which is revealed when the mental apparatus is passive. The main manifestations of residual schizophrenic disorder are:
- No signs of psychosis for 1 year or more. This period is considered as remission.
- Decreased motivation. A person does not want anything and does not strive for anything. He is not even interested in those activities that previously brought him pleasure.
- Emotionality. The patient may not respond to others and circumstances, including dramatic and difficult situations.
- Fatigue, weakness, both physical and moral, loss of strength. As soon as the patient takes up something, he immediately gets tired. Performance is practically zero.
- Closedness. With residual schizophrenia, a person does not want to communicate with anyone, he strives for loneliness, his speech is empty and meaningless. Often he tries not to speak at all.
- Poor hygiene. Over time, the patient stops taking care of himself - washing, shaving and washing clothes. Outwardly, he looks unkempt, but he doesn’t care.
- Strange behavior. The patient may talk loudly to himself in the presence of others, wander, collect garbage and bring it home (pathological hoarding).
- Superstitions. Belief in both the supernatural and complete absurdities, superideas, telepathy, etc. is possible.
To make a diagnosis of residual schizophrenia, four of the following symptoms must be observed. In this case, it is necessary to avoid organic brain damage, dementia and chronic depression, which are also characterized by negative symptoms.
Delusions, illusions, catatonia and hallucinations can occur in residual schizophrenia, but they are mild and do not cause vivid emotional experiences.
A person can be in remission for more than a year, but an exacerbation is possible at any time.
Then positive symptoms will appear, and probably even more intensely than during the previous attack. But this depends on how well the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, as well as on the timeliness of therapy if the condition worsens.
Symptoms of encephalopathy
Symptoms characteristic of encephalopathy:
- memory impairment;
- pain and noise in the head;
- absent-mindedness;
- dizziness;
- depression to the point of wanting to die;
- high fatigue;
- irritability for no apparent reason;
- physical weakness even after proper rest.
The symptoms are quite common and may not only relate to encephalopathy. Only a complete examination prescribed by a doctor can clarify the real picture.
A medical examination of the patient reveals an apathetic state, confusion in thoughts and reasoning, speech problems (difficulty pronouncing words). Patients have severe daytime sleepiness and a significant narrowing of the range of interests in everyday life.
Various diagnostic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis for schizophrenia, like treatment, is not interrupted even during remission. The patient must periodically visit a psychiatrist and undergo certain tests. Thanks to this, you can notice signs of exacerbation at the initial stage. The same applies to therapy. In fact, after a diagnosis of schizophrenia is made, a person becomes a patient for the rest of his life, regardless of how often attacks occur or whether they occur in principle.
Treatment methods for exacerbation and remission are somewhat different. For residual schizophrenia, the following medications and techniques are used:
- Taking antipsychotic drugs. Their task is to restore dopamine activity, which malfunctions in schizophrenic diseases. With negative symptoms, the production of dopamine is insufficient, which is why the person is passive.
- Taking antidepressants. With their help, it is possible to activate the psyche by stimulating the production of serotonin.
- Hospitalization. In remission, the patient usually remains at home. He might even get a job. But sometimes doctors advise temporarily going to the hospital and undergoing additional examination, especially if there is a risk of an exacerbation.
- Psychotherapeutic sessions. They are individual and group. They are considered one of the most effective methods of treating schizophrenia during remission. The patient can talk to the doctor and also listen to other patients with similar diseases. This helps improve your mood and increase motivation.
- Working with loved ones. Relatives of a schizophrenic person consult a psychiatrist about the rules of communication with their loved one who is in the grip of schizophrenia. They must learn to communicate with him and quickly identify the symptoms of an attack.
- Education. In some cases, the patient is taught vocational skills so that he or she can work. Locking yourself in is much more dangerous. It is much more productive for the patient to work. In this case, monotonous and manual labor is preferable.
In general, treatment for residual schizophrenia is aimed at the patient’s social adaptation and reducing the negative impact of the pathology on the psyche.
Forecast
Predicting the development of schizophrenia is quite difficult. It is incurable, and therefore a person is constantly at risk. He has the opportunity to prolong remission, but only with an integrated approach to his health, not only mental, but also physical.
The earlier schizophrenia manifests itself, the more devastating its consequences.
It is recommended to exercise (except extreme sports), eat right, walk in the fresh air every day, take vitamins and communicate with other people. Alcohol, drugs, smoking and other psychoactive substances should be eliminated from your life forever. If you adhere to these rules, the risk of a new attack is noticeably reduced.