General information
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare disorder that is present at birth (congenital).
It is characterized by partial or complete absence (agenesis) of the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum consists of transverse fibers. The cause of agenesis of the corpus callosum is usually unknown, but it can be hereditary in either an autosomal recessive or X-linked dominant pattern. In addition, agenesis can also be caused by infection or injury during weeks 12 to 22 of pregnancy (intrauterine life), resulting in impaired fetal brain development. Prenatal alcohol exposure can also lead to AMT. In some cases, with AMT, mental retardation may occur, but intelligence is mildly impaired, and subtle psychosocial symptoms may also be present.
Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum
Fig.1
Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum
Fig.2
AMT is often diagnosed during the first 2 years of life. Seizures of epilepsy may be the first symptom indicating that a child should be tested for brain dysfunction. The disorder can also remain without visible symptoms in the mildest cases for many years.
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum
This is a serious, but quite rare (1 case in 10,000) anomaly. With hypoplasia, the corpus callosum is present, but it is underdeveloped. The disease develops in the embryo in the 1st-2nd trimester of pregnancy. The reasons are also not fully established, but possible factors influencing the underdevelopment of the corpus callosum are similar to those described above.
The disease is most often diagnosed during fetal development. Consequences that hypoplasia can lead to:
- delayed mental and physical development;
- intellectual impairment (moderate and severe);
- mental retardation (in 70% of cases);
- various neurological problems.
A complete cure for this disease, like agenesis, is impossible with modern medicine. Treatment is aimed at reducing symptoms. Patients are recommended to perform a special set of physical exercises, which helps restore connections between the hemispheres, and information wave therapy.
Thus, despite its small size, the corpus callosum plays a very important role in people's lives.
Therefore, it is very important for mothers to take care of their health during pregnancy. After all, it is during this period that possible deviations in the development of the corpus callosum are formed.
Scientists, despite all their attempts, have not yet been able to fully study this structure. Therefore, there are only a small number of strategies for treating the symptoms of these anomalies. The main ones are drug therapy and physical therapy (PT).
The brain is one single system that constantly receives information and distributes commands to all organs and systems with the help of impulses that are concentrated in the corpus callosum.
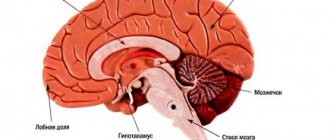
The corpus callosum is a plexus of nerve fibers that unites the right and left hemispheres, coordinating the work of both halves of the brain into one whole.
The corpus callosum is presented in the form of a dense formation, white, elongated from front to back and 7–9 centimeters long. It is located in the longitudinal fissure of the brain.
On the upper surface of the corpus callosum there is a thin layer of gray matter - the gray integument. It is distinguished by the trunk of the corpus callosum, which bends to form a knee and passes into the beak of the corpus callosum. The beak extends into the endplate, but the dorsal compartment of the corpus callosum is thickened.
The transversely approaching fibers of the corpus callosum are distributed radially in either hemisphere and form the brightness of its body.
Callosal fibers of the brain connect symmetrical areas of the cortex of both hemispheres, moving to the nuchal part of the corpus callosum, and the parietal lobes, but the interhemispheric fibers of the frontal part are located in the rostral area, forming its body.
The middle section, the corpus callosum, forms a convexity in the longitudinal direction and is the longest part of the brain. The posterior section is a thickening that hangs freely over the pineal body, roof plate and midbrain. On the upper surface there is a small layer of gray matter. It forms four thickenings in the form of stripes, two on each side of the median sulcus. When performing a horizontal section of the corpus callosum, the side of the brain and the white matter are clearly visible.
Morphology
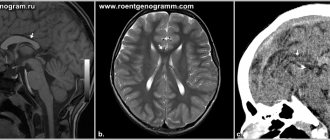
Classic neuroradiological signs of agenesis of the corpus callosum:
- The anterior horns and bodies of the lateral ventricles are widely spaced and parallel (not curved). The anterior horns are narrow and acute-angled. The posterior horns are often disproportionately enlarged (colpocephaly). The concave medial borders of the lateral ventricles are caused by protrusion of the longitudinal fasciculi.
- The third ventricle is usually dilated and elevated with varying degrees of dorsal expansion and mixing between the lateral ventricles. The interventricular foramina are often elongated.
- The interhemispheric groove appears to be a continuation of the anterior section of the third ventricle, since the knee is absent. In the coronal projection, the interhemispheric groove expands downwards between the lateral ventricles towards the roof of the third ventricle. In the sagittal plane, the usual cingulate gyrus is absent, and the middle sulci have a radial or spoke-shaped configuration. Interhemispheric cysts are often visible around the third ventricle. As they increase in size, these cysts can acquire an abnormal configuration and hide underlying defects.
- Absence of the corpus callosum and septum pellucidum.
- Angulation of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles and their depression along the medial surface by Probst's bundles.
- Radial pattern of grooves and convolutions extending from the roof of the third ventricle.
In dry but important remainder
Thus, the corpus callosum of the brain, despite its tiny size, has a great influence on a person’s life. It allows the formation of personality, is responsible for the emergence of habits, conscious actions, the ability to communicate and distinguish between objects.
That is why it is extremely important to take care of your health during pregnancy, since the main metabolic disorders are formed during this period.
We should not forget that the corpus callosum forms the intellect and makes a person a personality. Despite all attempts to study this structure, scientists have not yet been able to uncover all its secrets, and therefore very few methods for treating disorders, if any, have been developed.
The main ones are drug therapy and a special set of exercises - exercise therapy, which allows you to maintain optimal indicators of physical development. Measures to eliminate the symptoms of disorders should be taken immediately, otherwise the desired improvements may not occur.
Signs and symptoms
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) may initially present with the onset of epileptic seizures in the first weeks of life or during the first two years. However, not all people with AMT have seizures. Other symptoms that may begin early in life are problems with feeding and holding the head up. Sitting, standing and walking may also be affected. Impaired mental and physical development and/or hydrocephalus are also early-onset symptoms of this disorder.
Non-progressive mental retardation, impaired hand-eye coordination, and visual or auditory memory can be diagnosed through neurological testing in patients with AMT. In some mild cases, symptoms may not appear for many years. In mild cases, AMT may be missed due to the absence of obvious symptoms in childhood.
Some patients may have deep-set eyes and a bulging forehead. There may be an abnormally small head (microcephaly) or an unusually large head (macrocephaly). Folds of skin in front of the ears, one or more bent fingers (camptodactyly), and slow growth may also be associated with some cases of agenesis of the corpus callosum. In other cases, wide eyes, a small nose with inverted nostrils, abnormally shaped ears, an excessively long neck, short arms, decreased muscle tone (hypotonia), laryngeal abnormalities, heart defects, and symptoms of Pierre-Robin syndrome may be present.
Aicardi syndrome , considered to be inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern, consists of agenesis of the corpus callosum, infantile spasms, and abnormal ocular structure. This syndrome is an extremely rare congenital disorder that affects the middle layer of the eyes (choroid) and retina, as well as the absence of the corpus callosum, accompanied by severe mental retardation. Only women suffer from this syndrome.
Anderman syndrome is a genetic disease characterized by a combination of agenesis of the corpus callosum, mental retardation and progressive sensorimotor disorders of the nervous system (neuropathy). All known cases of this disorder come from the Charlevoux district and the Saguenay-Lac Saint-Jean region in Quebec, Canada. The gene causing this rare form of agenesis of the corpus callosum has recently been identified and is currently being tested (SLC12A6).
XLAG (X-linked lissencephaly with true hermaphroditism) is a rare genetic disorder in which males have a small and smooth brain (lissencephaly), a small penis, severe mental retardation and intractable epilepsy. It is caused by mutations in the ARX gene. In women, these same mutations can cause agenesis of the corpus callosum on their own, while less severe mutations in men can cause mental retardation. Diagnosis of this disorder is available in clinical use.
Skeletal and other abnormalities
- These are basically anomalies that appear as hemivertebrae and missing ribs.
- In medical practice, cases of jaw and facial anomalies are known. Of which, the most noted violations were in the form of protruding incisors and a reduced angle of the nasal septum.
- There were also such anomalies as an upturned tip of the nose, etc. It should also be noted that almost a quarter of the patients had various skin lesions, and just over seven percent had various pathologies of the extremities.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and frequent cases of cancer were also noted.
An effective therapeutic treatment for the syndrome has not yet been created, although developments are ongoing, so symptomatic treatment is mainly used, which is mainly aimed at eliminating infantile spasms.
Septo-optic dysplasia can present as an isolated brain abnormality, but is sometimes observed in association with other syndromes. These include:
- Aicardi syndrome.
- Combination of SOD with brachydactyly (short-fingered) type B and mental retardation.
- Porencephaly syndrome with absence of the septum pellucida.
- Holoprosencephaly.
To date, there are no therapeutic procedures that would help cure a child from agenesis of the corpus callosum. Only corrective techniques are used, which are selected individually depending on the degree of violations and the general condition of the patient’s body.
Treatment can only alleviate the symptoms of the pathology. But most experts say that all generally accepted methods do not give any results. The use of potent drugs is mainly practiced. They try to alleviate the patient’s condition with the help of:
- Benzidiazepines. These are psychoactive substances that have hypnotic, sedative, muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant properties.
- Phenobarbital. It is a barbiturate with antiepileptic action. It reduces the frequency of attacks if there are infantile spasms.
- Corticosteroid hormones. Such as Prednisolone, Dexamethasone. They are usually combined with antiepileptic drugs.
- Neuroleptics. With the help of which psychotic disorders are eliminated.
- Diazepam. It helps reduce behavioral disorders.
- Nootropics that have a specific effect on the mental functions of the brain. Treatment with Piracetam or Semax is usually used. They help improve the nutrition of brain tissue, which has a positive effect on its functioning.
- Neuropeptides. The most commonly used is Cerebrolysin.
In addition to medications, sometimes there is a need for surgical intervention. For example, they can stimulate the vagus nerve. But such therapy is allowed to be carried out only in situations where, as a result of agenesis, serious malfunctions in the functioning of vital organs have occurred. This procedure is performed if other types of surgical interventions fail.
Thanks to the procedure, the frequency of epileptic seizures decreases and they are more easily tolerated. But this treatment works differently for each patient.
Since agenesis of the corpus callosum of the brain can lead to musculoskeletal disorders and causes scoliosis, physiotherapeutic techniques and exercise therapy can be used. Sometimes surgery may be performed.
Related disorders
Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be combined with spina bifida. Some of the contents of the spine may protrude through the abnormal opening, leading to the formation of a meningocele or meningomyelocele.
- hydrocephalus 30%
- arachnoid cysts
- intracranial lipoma 10%
- Dandy-Walker malformation 11%
- Interhemispheric cyst
- Arnold-Chiari malformation 7%
- Median encephalocele
- Porencephaly
- Holoprosencephaly
- Polymicrogyria
- Heterotopia
The big commission is under attack...
Disorders of the corpus callosum are a rare phenomenon, occurring in 2% of all cases of diseases of the brain and central nervous system. In case of diseases of the corpus callosum, the following are observed:
- disorders of various nature and intensity, manifested in the emotional, personal and cognitive spheres;
- physiological problems in the functioning of the limbs;
- problems with the eyeballs and vision in general.
Corresponding diseases develop - agenesis, hypoplasia and dysplasia (dysgenesis) of the corpus callosum of the brain.
Treatment
Treatment is symptomatic and supportive depending on the severity of symptoms. If hydrocephalus is present, it is treated with surgical shunting to reduce the elevated ICP. Genetic counseling may also benefit families with this disorder.
Author: radiologist, Ph.D. Vlasov Evgeniy Alexandrovich
Full or partial reprint of this article is permitted by installing an active hyperlink to the source
If you still have doubts about the conclusions of your MRI, you can order a review of your study with a detailed transcript here:
Agenesis of the corpus callosum: causes, treatment and consequences
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a congenital pathology of the brain, the cause of which in most cases is a genetic factor; a disorder develops in utero in the fetus. This anomaly is quite rare.
The corpus callosum is the plexus of nerves in the brain that connects the right and left hemispheres. The shape of the corpus callosum is flat and wide. It is located under the cerebral cortex.
With agenesis, there are no callosal adhesions connecting the hemispheres, either partially or completely. This pathology develops in one case out of two thousand conceptions and can be caused by heredity or spontaneous unexplained gene mutations.
Pathogenesis and etiology of the disorder
As mentioned above, the development of agenesis can be triggered by heredity, but most often the reasons for its occurrence cannot be determined. This pathology has two clinical syndromes.
In the first case, the patient’s intellectual abilities and motor activity are preserved, and the disease manifests itself as disturbances in the processes of transmitting impulses from the left hemisphere to the right and vice versa.
For example, a patient who is right-handed cannot determine which object is in his left hand, because this requires the transfer of information from the right hemisphere to the left, where the speech zone is located.
In the second case, together with agenesis of the corpus callosum, the patient also has other malformations of the brain, including disturbances in the processes of neuron migration or hydrocephalus. In such cases, patients suffer from severe convulsive seizures and also lag behind in mental development.
Manifestations and signs of anomaly
Agenesis of the corpus callosum of the brain manifests itself in different ways, depending on the degree of the disorder; the main symptoms in the presence of this anomaly are:
- processes of nerve atrophy in the organs of hearing and vision;
- cysts and neoplasms in the part of the brain where the hemispheres connect;
- microencephaly;
- prone to seizures;
- presence of facial dysmorphism;
- the occurrence of defects in the development of the visual organs;
- porencephaly;
- pathological changes in the fundus;
- delays in psychomotor development;
- schizencephaly;
- presence of lipomas;
- disturbances in the development of the gastrointestinal tract and the presence of formations;
- early puberty and so on.
In addition to the above, the disease can manifest itself with Aicardi syndrome. This genetic disease is extremely rare and is characterized by abnormal development of the brain and visual organs. Agenesis also causes changes in bones and skin lesions.
Establishing diagnosis
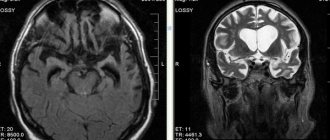
Diagnosis of agenesis of the corpus callosum is quite difficult and in most cases is detected in the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy. The main diagnostic methods include:
However, echography does not make it possible to detect the disease in all cases, and if the agenesis of the corpus callosum is partial, then its detection is even more difficult.
Difficulties in diagnosing the disorder arise because this pathology is often associated with a number of other disorders and genetic symptoms. In order to conduct a more detailed examination of the patient, specialists resort to karyotyping, ultrasound analysis and MRI.
Using a combination of examination techniques, it is possible to obtain a complete picture of the disease.
Basics of therapy
Currently, there are no effective treatments for such an anomaly as agenesis of the corpus callosum. Correction methods depend on the diseases that were caused by this disorder, and therefore are selected individually.
Treatment is aimed at minimizing the manifestations of the disease. But, according to experts, it does not give the desired effect, and besides, the methods have not been fully developed. Therapy for the most part consists of the use of strong medications.
The following drugs can be used:
- benzodiazepines and phenobarbital , which allow you to adjust the frequency of attacks in the presence of infantile spasms;
- corticosteroid hormones (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) in combination with basic anti-epileptic drugs;
- neuroleptics and diazepam drugs , the action of which is aimed at reducing behavioral disorders;
- nootropics (Semax, Piracetam) and neuropeptide drugs (Cerebrolysin);
- Children are most often prescribed Asparkam, Diacarb, Mexidol .
In addition to taking medications, if the need arises, surgical interventions are also performed, for example, stimulation of the vagus nerve is performed. But this can only be done in cases where agenesis has caused serious disruptions in the functioning of vital human organs.
This pathology can cause disorders in the musculoskeletal system and cause scoliosis, so specialists prescribe physiotherapy and exercise therapy. In some cases, surgery is also used.
Nowadays, agenesis is being carefully studied, but no tangible results have yet been achieved.
How many days are available for patients?
In cases where the disorder is not associated with the occurrence of other developmental pathologies, the prognosis is favorable. About 80% of children have no developmental disorders or minor neurological problems.
However, in most cases, agenesis of the corpus callosum provokes the occurrence of various kinds of consequences and associated pathologies, and in such a situation there can be no talk of a good prognosis.
Patients experience intellectual impairment, neurological problems, developmental delays and other symptoms with which they do not live for a long time. Patients are treated according to symptoms and the therapy has little effect.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be classified as a disease with a large number of developmental anomalies and unfavorable prognosis.
All we can do is hope and pray
Although agenesis of the corpus callosum is not an extremely rare disease, it has been poorly studied.
Today, doctors do not have sufficient knowledge about the causes of its occurrence in each specific case; only factors that can serve as an impetus for the development of this pathology have been identified.
Also, no effective methods for treating this condition have been found and it is carried out only according to the symptoms of those disorders that were caused by agenesis. In this case, all measures are aimed at the effect, but do not in any way affect the cause.
From this we can conclude that there are no effective measures to prevent agenesis of the corpus callosum.