A choroid plexus cyst in a newborn is by far the most dangerous pathology in children in the first year of life. As a rule, it is detected during intrauterine development of the fetus at a period of 24-30 weeks. During the development of the fetus, education does not pose a threat to its health and life. In addition, in most cases, the cyst can resolve on its own after childbirth. However, it is necessary to conduct a comparative analysis to exclude the formation of a cyst of vascular origin, which forms against the background of pathological processes in the body.
What is education?
A choroid plexus cyst is a benign formation with clear contours, filled with fluid. It occurs among normal pregnancies with a frequency of approximately 3%.
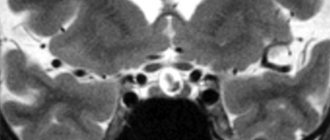
Cystic formations of the choroid plexus tend to self-resolve, suggesting that they are pseudocysts. Bilateral choroid plexus cysts of the brain are very often observed, but by the 28th week of pregnancy they resolve, which is associated with the active development of the fetal nervous system. In cases where the cyst continues to be detected during an ultrasound scan until childbirth, then its significance does not particularly increase.
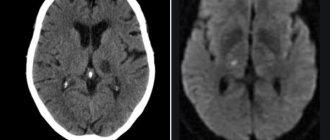
MRI images show cysts in both hemispheres
One of the early signs of the formation of the central nervous system in the embryo is the choroid plexus. They act as structural units in the formation of the right and left hemispheres of the brain. The choroid plexuses do not have nerve endings, but they ensure timely maturation and sufficient blood supply to the brain in the fetus.
A choroid plexus cyst of the brain has the following characteristics:
- minimal harm to health;
- lack of significance for concomitant pathologies;
- not affecting any of the vital systems and functions of the body;
- lack of growth and deformation.
Education does not cause significant harm or danger to either the fetus or the infant; it does not affect the functioning of the brain. However, they can increase the risk of developing other pathologies or cause functional impairment of all body systems.
What is a subepindymal cyst?
In newborns, hemorrhages from the damaged vessel wall, localized under the ependyma, are not multiple. Usually one or two cavities containing blood are found. Gradually, the blood clots dissolve, and the vacated space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Formations are recorded by neurosonogram until the fontanelles close after the birth of the child.
Minor hemorrhages do not affect the functionality of the brain. There is no infection of the formations. Multiple subependymal pseudocysts do not cause neurological disorders.
Some doctors consider early closure of the fontanelles of the skull in an infant to be the reason for the long-term persistence of pseudocysts. For this reason, the child is contraindicated in taking vitamin D3, which accelerates the calcification of cartilage tissue. Physiologically, the closure of the large fontanel occurs by twelve months.
Most experts do not consider the relationship between fontanelles and brain cysts to be real. There are no objective studies confirming the presence of a relationship between nosologies.
Subepindymal pseudocysts are small (up to 4 millimeters), medium and large (about 10 mm) in size. Small cavities in children disappear on their own by the age of one year. Medium and large formations can provoke irritation of the nearby parenchyma, and therefore persist for a long time (up to 6 years). If electroencephalography reveals increased excitability of the cerebral cortex, medications are prescribed.
The localization of the subependymal cyst determines the clinical picture:
- A space-occupying formation in the back of the head is characterized by damage to the visual centers;
- Cerebellar cavity – dysfunction of the motor sphere;
- Cyst of the temporal region - hearing damage;
- Pituitary pseudocyst – endocrine imbalance.
The side of the lesion determines the location of the lesion - right or left.
What is the difference between a pseudocyst and a cyst?
A cavity formation containing cerebrospinal fluid in the central part, which occurs after the birth of a child, in adults causes clinical symptoms and is capable of progression.
Pseudocysts form in utero or directly during childbirth. The soft bones of the baby's skull, when moving along the birth canal, can cause excess pressure on the brain tissue. Lack of oxygen supply (hypoxia) leads to the formation of cystic cavities as a result of rupture of blood vessels. Gradually, such cavities resolve.
False cystic cavities are formed under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- No genetic predisposition;
- Multichamber cavities of the lateral ventricles arise due to abundant vascular ruptures;
- Pseudoformations are localized between the caudate nucleus and the optic thalamus.
The absence of damage to the tissue of the lateral ventricles and periventricular space is not accompanied by clinical symptoms.
Reasons for education
One of the hypotheses for the formation of cysts is the theory of congenital pathologies provoked by genetic mutations of cells. In this case, the localization of the formation cavity on the left, right or simultaneously on both sides does not matter. It is important to note that the cyst does not provoke the development of anomalies, but, on the contrary, pathologies of intrauterine formation contribute to their formation.
The main reason for the development of vascular pathology in the fetus is the presence of the herpes virus in the pregnant woman
Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus are detected at 14-22 weeks of intrauterine development. This type of education is safe for the child, as it does not cause neurological symptoms. In the future, the mental abilities of such children do not differ from the abilities of their peers.
In rare cases, this type of formation occurs in newborns, so its detailed diagnosis and constant monitoring of size are required. The causes of late lumps in infants are infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. Quite common causes of formations can be herpes and toxoplasmosis. Also, the trigger mechanism in the formation of late seals is severe pregnancy and childbirth, as well as late toxicosis.
Types of true brain cysts
There are several types of cerebral cystic cavities:
- Pathological manifestations of cystic cavities of the retrocerebellar space arise due to damage to the thickness of the brain tissue. Damage to the cerebral parenchyma occurs due to circulatory disorders, inflammatory processes (encephalitis, meningitis), after surgical interventions. Retrocerebellar cavities increase with repeated infections and bleeding;
- Arachnoid cysts are localized between the membranes. In children, education may have a congenital etiology. In adults, it forms after injury or inflammation. The danger of the arachnoid cavity lies in compression of the brain parenchyma, which is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure;
- The pineal cystic cavity is localized between the hemispheres. Damage to the area of the pineal gland is accompanied by disturbances in hormonal metabolism. The cause of the nosology is duct blockage, echinococcal damage;
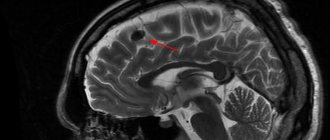
- Subarachnoid intracerebral cyst has a congenital etiology. The clinical picture of the formation is characterized by intracranial pulsation, a feeling of instability, and muscle cramps. Diagnosis of formation is carried out using magnetic resonance imaging;
- An epiphyseal cyst of the brain is accompanied by drowsiness, disorientation in space, and double vision of objects. The symptoms are varied, but signs of damage to the pineal gland predominate. An abnormal structure is detected using magnetic resonance imaging. If the cavity is large, surgery is required to decompress the brain structures;
- Choroid plexus cyst is a type of pseudocyst. Detected by neurosonography of a pregnant woman;
- The lacunar cyst is located in the pons and subcortical structures. The main cause in older people is atherosclerosis of the arteries of the brain;
- Pineal cystic cavity is an etiological factor in the disorder of metabolic processes and motor activity. Pathology causes encephalitis and hydrocephalus;
- A limited cerebrospinal fluid cavity is located between the meninges. Etiological factors of nosology are injuries, inflammatory processes, strokes. The formation causes leg paralysis, muscle cramps, psychosis, and a gag reflex;
- Porencephalic cystic cavity is the result of past infections. The nosology is dangerous due to the development of hydrocephalus and increased intracranial hypertension. Some scientists argue about the hereditary etiology of education, as it is found in children after birth.
The described types differ from pseudo-formations on tomograms by establishing a specific location of the cavities.
By what signs can you identify a cyst in a child?
Vascular compactions are diagnosed during special diagnostic methods, so ultrasound and neurosonography can provide a complete description of the cyst. According to accepted WHO recommendations, these studies must be carried out on all children under one year of age to exclude possible neurological disorders.
In infants, cystic formation is practically asymptomatic
Mandatory indications for neurosonography are:
- trauma during childbirth;
- high risk of intrauterine infection;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- severe pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the mother;
- intense physical activity during pregnancy;
- deviations in the physical development of the newborn (underweight, insufficient growth);
- severe deformation of the anatomical parts of the skull.
According to statistical data, cystic formations are recorded both in children without deviations in physiological development and in those with developmental delays.
The concept of pseudocyst
Formations of the cystic type are peculiar cavities, characterized by a round shape and having a small size. They are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (exudate or other substances). The bulges are concentrated on one or both sides at the same time. The mechanism of development of this pathology in infants has not been fully studied to this day. It may happen that, in the presence of alarming prognosis, a baby is born absolutely healthy, and a second newborn is born with damage to the nervous system, with completely normal prognosis.
With the rather rapid intrauterine development of the brain, the vacated territory located in the area of the choroid plexuses is filled with a special fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). These are the processes that are observed during the development of a pseudocyst. It is safe for the life of the baby and is most often detected during an ultrasound scan of the fetus in the womb.
A large percentage of cystic formations resolve before birth. If this does not happen, then experts explain this by the presence of a herpes infection in the mother.
Types of cystic formations
The plexus of cerebral vessels takes an active part in the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which subsequently provides nutrition to the brain and is responsible for its functional development. Cystic formations are a consequence of intensive growth of the brain, when a free cavity appears between the plexuses of blood vessels, which is filled with fluid inside. Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus are a fairly common diagnosis, especially during fetal development and in children under one year of age.
Left choroid plexus cyst
Formations occur against the background of viral and infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother, as well as during severe pregnancy. The cyst is localized in the intracranial space close to the choroid plexuses. This type of formation does not require any therapeutic measures, since they do not pose a threat to the health and life of the child. In most cases, they resolve as the child grows.
Cyst of the right vascular formation
This type of formation is diagnosed in both newborns and infants. In some cases, it can be detected in adulthood, but since cysts do not have pronounced symptoms, a person may not be aware of the presence of pathology. Right-sided cystic formations do not harm the body and do not affect the psychomotor development of the child.
Bilateral pseudocysts
There are no visible changes or disturbances in the structure of the brain. The choroid plexuses of the lateral ventricle are involved in the process. As a rule, as the body grows, the neoplasm goes away without outside help. Bilateral cysts are numerous, they are recorded in adults and children. In some cases, the formation of a bilateral cyst may indicate a disruption in the course of pregnancy, but this does not mean that the baby will be born with a pathology.
Such cysts are called neoplasms of the choroid plexus; they are visualized in the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle as formations with clear, even edges. Neoplasms do not cause disturbances in the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid and an increase in extracellular space.
Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns and adults
Cystic pseudocysts are cavity formations with liquid contents and a thin wall that limits the size of the structure.
The false cavity differs from the true analogue by its formation from the germinal matrix, which is clearly visible on MRI of the brain. Nosology refers to developmental anomalies. The most common location of a cystic cavity formation is between the head of the caudate nucleus, the optic thalamus, and the lateral angles of the lateral ventricles. In adults, the main cause of cystic cavities is brain infections (Toxoplasma, Cryptococcus).
Possible complications
Echo signs of a vascular neoplasm should make a specialist wary. Cysts themselves are not dangerous, but their presence may increase the risk of developing chromosomal pathologies in the future.
Increases in the frequency of cysts are largely influenced by Edwards syndrome
With normal laboratory test results, a vascular cyst does not indicate a pathological process in the body. To exclude genetic abnormalities, the doctor prescribes amniocentesis (sampling of a small amount of amniotic fluid).
In cases where genetic abnormalities are detected in the fetus, their consequences are the following developmental anomalies:
- Down syndrome.
- Edwards syndrome.
Pseudocysts have no absolute influence on the development of genetic defects, since they also occur in healthy children.
Diagnostic measures
Today, a vascular cyst is not a sign of the disease, but it can increase the risk of developing other pathologies.
For early detection of abnormalities in fetal development, all pregnant women must undergo ultrasound diagnostics
Diagnosis of cystic formation using special research methods:
- Ultrasound diagnostics. It is carried out during the intrauterine life of the fetus, which makes it possible to identify the formation at an early stage of its development.
- Biopsy of the placenta. At high risk of developing trisomy 18.
- Amniocentesis. It is highly accurate and is performed up to 22 weeks of pregnancy. The technique consists of studying the skin cells of the embryo.
- Neurosonography. It is carried out in children under one year of age. The procedure allows you to identify a tumor on both sides, but before the anterior fontanelle closes.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is used in adults to determine possible neurological disorders, during which cysts can be detected.
Diagnosis of cysts and pseudocysts of the brain
Ultrasound scanning of the brain parenchyma is a safe and informative diagnostic method. Indications for examination:
- Hypoxic conditions;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Complication of childbirth;
- Restless behavior of the baby;
- Suspicion of pathology of intracerebral circulation.
Detection of pseudocystic cavities in newborns is not difficult. If the fontanelles become overgrown, tissue examination is carried out using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI).
Headaches, dizziness, muscle cramps with the combined presence of cystic cavities require combined diagnostics using neuroimaging methods:
- Positron emission tomography (PET);
- Neurosonography;
- Doppler encephalography;
- Cerebral scintigraphy;
- Computed tomography and MRI of the head.
A comprehensive study reveals concomitant pathology that occurs during complicated pregnancy or childbirth. Using intravenous administration of a contrast agent, the condition of the cerebral arteries is monitored, areas of hemorrhage and hematomas are identified.
If chromosomal abnormalities are suspected (Edward's disease, Down's disease), amniocentesis is performed - taking material from the amniotic fluid for genetic examination.
Features of treatment
As a rule, treatment for a vascular cyst is not carried out, since the body can cope with it on its own. However, there are cases when specialists are forced to prescribe medications to resolve the cyst.
Before using medications, you must consult your doctor.
Most often, neurologists prescribe the following medications:
- Cavinton. Used to eliminate cerebral circulation disorders.
- Cinnarizine. The product has a beneficial effect on the vascular system, which helps the body destroy pathological formations and stabilize.
In other cases, therapeutic measures are not carried out. For continuous monitoring of cysts, experts recommend undergoing ultrasound diagnostics of the brain once every 3 months until they are completely resolved.
Thus, the presence of a cystic neoplasm does not harm the baby’s health and does not affect his mental abilities in the future. It does not require the use of special treatment methods; it is only necessary to control the dynamics of education in a timely manner. The cyst is of great importance in assessing the risk of the formation of genetic mutations in the fetus, in cases where other pathological symptoms are also detected.
Treatment methods for liquor cysts
The most common indications for surgical treatment of a cyst: it grows too quickly, causes seizures, causes neurological deficits, the cyst interferes with the child’s development.
The main, safest and most effective method for treating cerebrospinal fluid cysts today is fenestration. That is, dissection of the walls of the cyst for communication between the cyst and other cerebrospinal fluid spaces, where this accumulated fluid is normally located.
It is possible to install a stent (catheter) connecting the cavity of the cyst and the ventricles. It happens that the operation turns out to be ineffective and forces you to use another method of treatment - bypass surgery.
Shunt surgery (today practically not used as a primary method of treatment), although it allows you to quickly reduce the size of the cyst, but creates a lifelong dependence on the shunt system. If this method can be avoided, neurosurgeons try to avoid it.
However, when treating young children (up to two years old), as well as when treating cysts that were complicated by hemorrhage, shunt operations are inevitable.
In general, surgeries to treat cysts have a low risk of complications in the hands of experienced doctors. This operation involves hospitalization for only three to four days and several subsequent consultations with a surgeon. Deviations from this rule occur only in 10% of cases.
Most often, in such a situation, endoscopic surgery is used, but in some cases, an open microsurgical approach is more correct. An uninitiated person will not see the difference after the operation; the size of access to the brain cavity will be the same. In this case, it is not so important for the patient which instrument is used to perform this operation. It is important to make the patient feel better.
Reviews
Tatyana, 32 years old At 22 weeks of pregnancy, she underwent an ultrasound, where a unilateral cyst was discovered. The ultrasound specialist assured that this would not cause any harm to the child’s development, and with the further growth of the child, it could resolve on its own. The consultation prescribed screening. The results are good. They were sent to a geneticist. He recommended waiting for the third ultrasound, on the basis of which it would be possible to consider the dynamics of the tumor. And indeed, the baby grew in size and the cyst resolved.
Ekaterina, 36 years old Both children, 5 years apart, were diagnosed with a cyst; in the first child it resolved without a trace, although I was very worried. The second one was also diagnosed early in pregnancy; perhaps this is a hereditary trait. In the first and second cases, I always waited for the planned ultrasound, since there was no point in undergoing the study earlier. After identifying cysts, I underwent repeated diagnostics no earlier than a month after their discovery.
Elena, 26 years old At 20 weeks, she had an ultrasound, where she was diagnosed with a choroid plexus cyst. The specialist did not explain anything and referred me for a consultation with a geneticist, since the tumors were quite large - 8 mm. I took tests, 3 days later I found out the results, they turned out to be good, and the size of the formation was significantly less than 3 mm. The consultation prescribed an ultrasound scan at 32 weeks. During the waiting period, I was very worried, I studied a lot of specialized literature, all sources spoke of a benign outcome. Finally, the time came to undergo an ultrasound. It did not reveal any formations in the brain; they all resolved.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure in children, symptoms of which can appear in the first minutes and hours after birth, often leads to the development of serious complications.
When parents may suspect something is wrong:
In young children:
- The baby constantly cries and does not calm down;
- Lack of thirst in the child, reluctance to drink;
- The baby is irritated by bright lights and sharp sounds;
- The child burps frequently and profusely;
- The baby's fontanel bulges;
- The baby's chin is shaking;
- Rapid head growth (this is due to stagnation of venous blood);
- The child throws his head back.
In older children
- Severe headaches;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Increased fatigue, weakness;
- Drowsiness;
- Tearfulness, irritability;
- Apathy;
- Double vision.
Knowing the key signs of the disease, you can establish the correct diagnosis in the early stages and prescribe the correct treatment for your child. Even if you have only one of the listed symptoms, you need to immediately contact a neurologist! The sooner your baby receives help, the fewer consequences it will have for the child’s body in the future.