Hydrocephalus on MRI Magnetic resonance imaging is actively used in neurology and neurosurgery. The method is used to visualize the brain. Layer-by-layer images fully reflect cerebral structures, allow you to identify pathological changes in any area and collect detailed information about deviations.
MRI is of great importance for the early diagnosis of brain diseases. In the images, the radiologist sees signs of life-threatening conditions, such as dropsy. Hydrocephalus of the brain on MRI manifests itself with characteristic symptoms, even at the initial stages of development. An experienced diagnostician will quickly identify the pathology, establish the form, and the clinician will select the correct treatment tactics.
Features and mechanism of disease development
Hydrocephalus or dropsy of the brain is a disease that is accompanied by the accumulation of excess cerebrospinal fluid inside the ventricles, in the meningeal spaces of the brain and leads to their expansion, and also causes an increase in intracranial pressure.
The ventricles of the brain produce cerebrospinal fluid. It serves as a kind of pillow, protects the brain and spinal cord, delivers nutrients, and is responsible for removing waste. Normally, the fluid moves before being absorbed into the bloodstream. With hydrocephalus, its movement is blocked and absorption is limited. In the absence of adequate treatment, complications develop, including death.
Types of disease
There are several types of hydrocephalus of the brain. Pathology can be congenital or acquired. The first progresses under the influence of unfavorable factors during intrauterine development. The second is formed under the influence of various pathologies and external factors.
Depending on the location of the disease, it can be:
- External - with accumulation of fluid under the meninges;
- Internal – with a violation of the outflow of CSF from the ventricles;
- Common – combines the characteristics of both previous forms.
According to the mechanism of development, hydrocephalus can be open, with preservation of the connection between the ventricular system and the subarachnoid space, or closed, with a disruption of this connection.
Why does dropsy of the brain occur?
In adult patients, acquired hydrocephalus is often encountered, which develops either due to any mechanical damage to the head, or as a result of the development of pathological processes. Why does cerebrospinal fluid accumulate outside the cerebral hemispheres? The explanation is simple: brain structures are disrupted, adhesions appear in the veins, arachnoid villi are destroyed, and as a result, the cerebrospinal fluid does not circulate as it should.
If we delve deeper into the question of the causes of such a disease as external dropsy of the brain, we can identify some factors:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis);
- post-stroke condition, development of sepsis, extensive hemorrhage;
- concussion, head or cervical spine injury;
- malignant tumors that develop in the stem region.
Frequent intoxication of the body leads to the appearance of external hydrocephalus. For example, alcohol abuse, which damages neurons and leads to tissue death. Those patients who suffer from metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, encephalopathy, and atherosclerosis are also at risk. Another reason that deserves due attention is irreversible age-related changes that cause aging of blood vessels and brain tissue.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Forms of pathology
The form of hydrocephalus determines the nature of the disease and its severity. The following criteria are most often used for classification:
- The intensity of the manifestation of the pathology - when severe, a lot of fluid accumulates, which disrupts the activity of the nervous system. In this case, the disease is accompanied by severe neurological symptoms. A moderate degree is characterized by the accumulation of a small volume of cerebrospinal fluid and the absence of symptoms;
- The degree of impact on brain structures - in a compensated form, the liquid has no effect on the brain; in a decompensated form, it worsens its functioning;
- The nature of the course - hydrocephalus of the brain in the chronic form is accompanied by a gradual increase in symptoms, in the acute form it leads to a sharp deterioration in the person’s condition.
Modern diagnostic measures allow determining the type of disease, its form and developmental features.
Treatment of hydrocephalus
The therapy is based on a set of measures aimed at activating the outflow of pathological fluid accumulation.
If therapeutic agents do not have a positive effect, the patient undergoes surgery. Endoscopic treatment demonstrates the greatest effectiveness against the background of minimal invasiveness:
- endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the bottom of the third ventricle,
- aqueductoplasty – arrangement of a kind of “water pipeline” through which fluid will be effectively removed from the skull.
- septostomy – removal of cysts and elimination of occlusion of the “foramen of Monroe”.
- removal of brain tumors by endoscopic method.
After such a surgical intervention, the patient very soon returns to normal life, since his brain is not subject to serious trauma. This procedure allows you to regulate the flow of fluid in the skull, however, after surgery to eliminate hydrocephalus, the patient requires constant supervision by a specialist and regular monitoring of the condition of the brain.
The prognosis for hydrocephalus depends on the cause and time of diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Children who receive treatment are able to live normal lives with few, if any, limitations. In rare cases, speech dysfunction may occur.
Stages of development
External hydrocephalus has 3 stages of development, each of them has its own characteristics:
- Mild - the size of the dropsy is small, the body itself tries to cope with disturbances in the flow of CSF. A person usually feels a headache that is not too intense, he periodically feels dizzy, feels slightly worse, and sometimes gets dark in his eyes;
- Moderate – manifestations become more noticeable, the intensity of headaches increases, especially during physical activity. Possible disturbances in visual function, rapid onset of fatigue, pressure changes, depression and severe irritability;
- Severe - at this stage, hydrocephalus of the brain can cause seizures, apathetic state, fainting, apathy, and also lead to the development of conditions in which a person is no longer capable of self-care.
At the initial stages of development of the pathology, neurological symptoms may be absent. They appear due to organic processes that occur in the cerebral substance, as well as against the background of circulatory disorders and atrophy of some areas.
Symptoms of external hydrocephalus
The clinical picture in each specific case will be different, and the nature of the manifestation of the disease depends on the severity of the pathological process and the state of the central nervous system. Common symptoms are frequent headaches, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and weakness. By the way, pain is more localized in the frontoparietal region and in the area of the eyeballs. A person with dropsy experiences pain in the first half of the day, with sudden movements, coughing, sneezing, or severe physical exertion.
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disease. Scientists distinguish 3 stages, and each has its own characteristics:
Mild external hydrocephalus. With a minimal amount of dropsy, the human body will try on its own to cope with such a problem as impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, you will feel a slight malaise, periodic dizziness, short-term darkening in the eyes, and a tolerable headache.
The middle stage of development of the disease. At this stage of the spread of the disease, symptoms appear intensely and are more pronounced. Due to an increase in intracranial pressure, severe headaches occur during physical activity, swelling of the optic nerve and facial tissues, increased fatigue, nervousness, depression, and surges in blood pressure.
Severe form of the disease. Signs of pathology in severe forms of external hydrocephalus are reduced to convulsive seizures, frequent fainting, a state of apathy, loss of intellectual abilities, memory loss and inability to care for oneself. Progressive dropsy can even lead to death, so there is no need to delay going to the doctor. It is better to do this at the first suspicion and a slight deterioration in health.
With chronic accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, symptoms such as unsteady gait, paralysis of the upper and lower extremities, urinary incontinence, nighttime insomnia and daytime sleepiness, depressed mood, and a complex of psychoneurological disorders can be observed.
Hydrocephalus in children
Signs of hydrocephalus are determined by the person’s age and stage of the disease. In children, including newborns, the development of pathology may be indicated by capricious behavior and poor appetite, marbled skin and slow reactions, eyelid retraction and gaze almost always directed downward, as well as swelling of the fontanelle and excessively enlarged head size.
It is the size and shape of a child’s head that often indicates pathological processes. By the age of six months, babies with hydrocephalus have a head circumference greater than the chest, the skull becomes oblong, pear-shaped, and this is noticeable to the naked eye.
With hydrocephalus in children, the normal functioning of the brain is blocked, which leads to a lag in mental, physical, and mental development. The risk of pathology increases in newborns born prematurely with low body weight. The cause may also be intracranial birth injuries or infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy.
A child with this disease begins to roll over, hold his head up, and sit up later than his peers. In severe forms of the pathology, these skills are not formed, muscle strength in the limbs decreases up to paralysis, and muscle tone increases. After fusion of the fontanelles, a severe headache begins, often in the morning, frequent vomiting, and nosebleeds.
Disease prevention
The list of measures that can prevent the development of pathology includes:
- pregnancy planning;
- prevention of birth injuries;
- giving up bad habits before conceiving a baby and during pregnancy;
- vaccine prevention of infectious diseases of the brain (meningitis, encephalitis);
- early perinatal diagnosis;
- regular monitoring of children at risk by a pediatrician and neurologist;
- timely completion of preventive examinations up to a year;
- providing the child with safe living conditions to prevent household traumatic brain injuries.
Parents need to closely monitor the development and condition of young children, promptly contacting doctors in case of infectious diseases, falls and injuries affecting the head and neck area.
Specialists at the SM-Doctor clinic will conduct a detailed diagnosis if hydrocephalus is suspected, plan treatment and monitor the child throughout therapy and rehabilitation.
Symptoms of the disease in adults
Hydrocephalus in adults manifests itself:
- Headaches for which neither sleep nor painkillers can help;
- Nausea, feeling of approaching vomiting;
- Feeling of constant fatigue;
- Sudden changes in mood, tendency to irritability;
- Changes in behavior;
- Fogging of consciousness, difficulties with memory, the thinking process;
- Balance imbalance;
- Inability to control urination;
- Seizures and convulsions;
- Sleep disorders;
- Problems with appetite;
- Blurred vision, a feeling of double vision, movement of the eyeballs downwards.
Headache with hydrocephalus intensifies when changing a horizontal position to a vertical one. Fluctuations in blood pressure are possible. With normal pressure hydrocephalus, signs of dementia, urinary incontinence, and gait disturbances appear in combination with pronounced dilatation of the cerebral ventricles, but without an increase in CSF pressure.
Symptoms
The disease may not manifest itself in any way for a long time. The patient may only be bothered by morning headaches. But at a certain point, the pathology will still make itself felt, since excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid disrupts the blood supply to the brain. Such processes lead to oxygen starvation (hypoxia) of the brain, which is fraught with very serious consequences, for example, the patient may develop dementia or have a stroke.
Symptoms of the disease in adults
The acute form of moderately severe external hydrocephalus is characterized by high intracranial pressure, which provokes severe headaches in the morning. They may subside throughout the day. The patient may suffer from digestive system disorders, nausea and vomiting. If after vomiting the headache is less, then the person has obvious problems with the brain.
The most dangerous sign of the disease is drowsiness. It indicates the presence of high intracranial pressure, which will subsequently cause a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition. Also, moderate external hydrocephalus is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Dizziness.
- Hearing or vision impairment.
- Partial memory loss.
- Decrease in intelligence.
- Loss of orientation in space.
- Irritability.
- Impaired movement coordination.
- Deterioration in health when weather conditions change.
With an exacerbation of any form of moderate hydrocephalus, a person may experience urinary incontinence, fainting, and cerebral edema. This indicates the development of an occlusal crisis. In this case, the patient should be urgently hospitalized, as complete leakage of cerebrospinal fluid may occur.
Symptoms in children
The most obvious signs of the disease in children are an enlarged skull and head growth that is faster than age.
Symptoms of the disease in newborns:
- Constantly throwing your head back.
- The fontanel is too tense.
- The eyeballs may move downward.
- Sometimes squint appears.
- Pulsating protrusions may be observed between the unfused bones of the skull.
Moderate external hydrocephalus has a negative impact on the development of the child’s nervous system. It provokes the development of defects that affect the properties and dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Causes of pathology
The main reasons for the development of hydrocephalus in adulthood are:
- Pathologies of the vascular system;
- Infectious diseases;
- Neurosurgical operations;
- Head injuries;
- Tumor processes;
- Previous stroke;
- Anomalies of the development of the central nervous system.
Hydrocephalus can be a complication of meningoencephalitis, meningitis, rupture of an aneurysm or intraventricular hemorrhage, the formation of a cyst or tumor in the brain.
The cause of hydrocephalus in adults may be regular intoxication, for example, frequent consumption of alcohol. Alcohol has a damaging effect on neurons, causing tissue areas to die. An increased risk is created by chronic diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, metabolic disorders, and encephalopathy. Often the disease develops against the background of age-related changes in the body associated with the aging of brain tissue and blood vessels.
What is the disease characterized by?
The function of nourishing the brain and protecting it from concussions is performed by the liquid that washes it - cerebrospinal fluid. Excessive accumulation or disruption of outflow causes the development of moderate external hydrocephalus.
Some neurologists say that this disease can only appear in children and is a congenital pathology. Of course, there are quite a lot of newborn babies who suffer from dropsy. But it is not necessary to unequivocally classify hydrocephalus only as a congenital pathology.
In adults, the disease is difficult to diagnose. The patient may be treated for an entirely different mental or neurological condition without suspecting hydrocephalus. Dropsy is a dangerous disease that can provoke various neurological disorders.
Moderate hydrocephalus often has two stages of development. The acute stage is characterized by the appearance of signs of the disease that caused hydrocephalus. During the chronic stage, symptoms appear that indicate brain pathology itself.
Effectiveness of MRI in hydrocephalus
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose hydrocephalus. This is the most informative imaging method, allowing an accurate diagnosis to be made, regardless of the stage of the pathology.
The essence of MRI is to obtain layer-by-layer images of the area used by scanning. The operating principle of tomography is associated with the influence of a magnetic field and recording radio frequencies emanating from the human body.
Unlike X-rays, MRI does not have a negative effect on the body. This is a non-invasive and absolutely safe method that allows you to obtain high-quality images, including three-dimensional ones. They clearly show brain tissue of different densities and the boundaries between them, tumors and blood vessels. Thanks to the study in several projections at a given depth, it becomes possible to assess the condition of any part of the brain.
Types of hydrocephalus
Depending on the cause of development, hydrocele of the brain can be congenital or acquired. Based on the distribution of cerebrospinal fluid, pathology is classified into types:
- external;
- internal (mono-, bi-, tri- or tetraventricular);
- mixed.
Based on the mechanism of development, hydrocele of the brain occurs:
- open (communicating);
- closed (occlusal).
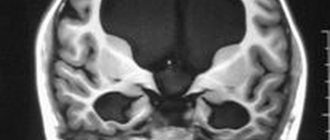
Internal triventricular occlusive hydrocephalus on MRI in the frontal and sagittal planes: the left image shows a giant cystic-solid formation, which was the cause of obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid ducts at the level of the aqueduct of Sylvius
How is the procedure performed?
MRI of the brain is performed with or without contrast enhancement. In the first case, the patient is injected intravenously with special drugs that create a clear image of the affected areas and improve the quality of visualization. For example, with this approach, not only the tumor itself is clearly visible, but also its exact boundaries.
No special preparation is required for the procedure, but before it begins, you will have to remove all metal jewelry. The tomography machine itself looks like a large cylinder, inside of which there is a movable platform. The patient is placed on it lying on his back. To protect against the noise produced by the device, earplugs are used.
The table slides inside the tomograph, and the doctor performs the procedure from an adjacent office, controlling the device using a computer. Throughout the examination, voice communication with the doctor is maintained, so the patient can report unpleasant or uncomfortable sensations at any time.
The tomograph sequentially takes a series of images, which ultimately form the finished image. In order for the images to be of high quality, the patient must remain completely still. On average, the procedure takes about 30-45 minutes.
Treatment
Moderate external hydrocephalus can be treated using conservative techniques or surgery. The postoperative period is necessarily accompanied by physiotherapy and medication.
Conservative methods
Minor external hydrocephalus at the initial stage is usually treated using conservative methods. These include:
- Complexes of therapeutic gymnastics exercises (the program is developed by a doctor).
- Significant reduction in daily fluid intake.
- Taking oil baths with pine needle oil.
- Taking certain medications.
- Following a special diet.
To remove excess fluid from the body, the patient usually takes potassium supplements and Diacarb. If the cause of the pathology is an infectious disease, then a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Treatment with medications that help regulate blood circulation in the brain is mandatory.
The listed methods are carried out with the aim of reducing intracranial pressure and restoring normal functioning of the brain. But they often turn out to be useless in the fight against this disease. Then they resort to surgical treatment of the disease.
Surgical methods of treatment
Today, the method of surgical intervention in the fight against moderate hydrocephalus is the main one. It is aimed at preventing the acute form of the disease from developing. If the operation is successful, the patient can forever get rid of such a disease as moderate external hydrocephalus.
Nowadays, a modern method, endoscopy, is used more for surgery. An important positive point here is the creation of all conditions so that the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid occurs through natural openings (without the use of foreign objects). This method of conducting surgery helps to avoid the development of autoimmune reactions in the patient.
Other methods of surgical intervention for moderate external hydrocephalus include drainage and shunting. The first method is used only in emergency situations that require an immediate decrease in brain fluid pressure. The second method (bypass surgery) causes a large number of postoperative complications, so it is now rarely used. Shunts must be replaced periodically, which exposes the patient to the risk of infection.
Evaluation of results
This technique makes it possible to identify not only hydrocephalus of the brain, but also concomitant diseases, and accurately determine the type of pathology. The picture shows both direct and indirect signs of the disease. Direct ones include enlargement of the ventricles of the brain and subarachnoid space.
Indirect signs are:
- The value of the interventricular index is 0.5 or more;
- Downward displacement of the hypothalamus;
- Swelling with intense dropsy;
- Partial protrusion of the upper part of the lateral ventricles.
Based on the results of the study, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed. MRI may show replacement hydrocephalus. This means that a certain amount of fluid is present in the subarachnoid space, but its presence is not a sign of dropsy, but a manifestation of a compensatory mechanism associated with age-related or organic changes in tissue.
Diagnostics
All forms of hydrocephalus are diagnosed using skull x-rays and brain tomography. Tomography is carried out to check the contours of the brain, ventricles, and also scans the skull. X-rays help determine the direction of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Using MRI, specialists detect the presence (absence) of tumors and various neoplasms. This method of studying the disease allows you to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as determine the form in which the disease occurs.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic procedures:
- Angiography. This method is based on the introduction of a contrast agent into the circulatory system, which makes it possible to notice vascular pathologies.
- Ultrasound.
- General blood analysis.
- Lumbar puncture. To identify pathogenic organisms in the cerebrospinal fluid, cerebrospinal fluid is collected.
In addition to the listed methods for diagnosing moderate hydrocephalus, the patient may be sent for examination to specialized specialists: an ophthalmologist, an endocrinologist, or a neuropsychiatrist. For children, the diagnosis of “Moderate external hydrocephalus of the brain” is made on the basis of existing symptoms, measurements taken from the head circumference, tomography, ultrasound, and MRI.
A complete examination helps the doctor accurately diagnose the disease itself and the form in which it occurs. Accurate diagnosis makes it possible to begin timely treatment, which will be prescribed taking into account the patient’s age, intracranial pressure, and the state of brain structures.
Methods and principles of treatment
The main task is to eliminate the accumulated excess cerebrospinal fluid in order to restore its normal flow.
In some cases, drug therapy is performed. Improvement from conservative treatment of hydrocephalus usually occurs when the disease is a complication of an infectious or inflammatory disease or traumatic exposure. When medications do not provide the desired effect, surgery is performed to install special shunts. This element ensures the drainage of fluid to the abdominal cavity, where it is absorbed by the body. As a result, pressure decreases and the size of edema in the brain decreases.
Another surgical treatment option is to create an opening in the 3rd cerebral ventricle to allow cerebrospinal fluid to flow between brain regions. Both methods allow you to relieve symptoms and block the development of dangerous complications. If the disease is caused by the appearance of a tumor, it is removed.
The earlier hydrocephalus is detected, the better the prognosis for treatment.
If the operation is timely and successful, the patient can return to normal life, and a full recovery is possible. Advanced stages of the disease not only worsen the quality of life, but also lead to dangerous consequences, including death. That is why accurate diagnosis, primarily MRI, plays an important role. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Treatment of external hydrocele in adults
Treatment methods are selected at a consultation with a neurosurgeon or neurologist after diagnosing the disease. Intervention must be timely, otherwise the risk of various neurological complications increases. It is important to take into account both the type of pathology and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev practice only effective methods of treating external hydrocele of the brain. Methods are divided into two large groups: conservative (medicinal) and surgical (operative), each of which has its own characteristics and advantages.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
Drug treatment is only relevant at a mild stage of the disease. Special medications accelerate the outflow of fluid from the brain, increase urination, relieve inflammation and swelling, strengthen blood vessels, and normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. To combat severe headaches, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Common groups of medications are vascular, neurotropic, venotonics, diuretics. But in acute illness they will be ineffective. Mixed hydrocephalus is poorly corrected. In this case, conservative treatment will not get rid of the disease, but will only restore or improve the functioning of individual systems and functions of the human body. Often surgical intervention is not possible.
SURGERY
If acute external dropsy is diagnosed, in most cases drainage of the cerebral ventricles is prescribed. The main technologies are endoscopy and open surgery.
In the first case, we are talking about manipulations that are characterized by minimal trauma, a very low risk of complications, and fairly rapid postoperative recovery. Endoscopy methods allow, with minor intervention, not only to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, but also to eliminate vein defects, hematomas, and blood clots.
Currently, open surgery is chosen only in exceptional cases. Why? It is difficult to imagine performing open surgery without craniotomy. And trepanation always means increased risks and a long postoperative recovery period.
Another way to get rid of external dropsy is bypass surgery. Doctors use a system of valves and silicone tubes to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. The fluid is redirected to other cavities of the body, in particular to the abdominal cavity, right atrium, and superior vena cava. According to statistics, the effectiveness of this technique is 85%.
Is it possible to protect against the occurrence of external hydrocephalus of the brain? This is a very difficult question. But, if you completely give up bad habits and avoid traumatic brain injuries, there is a high probability that trouble will bypass you. Another important point is the timely and professional treatment of such serious diseases as encephalitis, polio, meningitis, as well as other infectious diseases.
Prevention
In order to avoid the appearance of such a dangerous disease as moderate external hydrocephalus in newborns and adults, it is necessary to follow basic preventive measures:
- It is important for pregnant women to monitor their health throughout the entire period of pregnancy. There is no need to allow the development of infectious diseases, seek medical help on time, undergo all scheduled examinations in a timely manner, and avoid injury. Early detection of pathology in the fetus will help to provide timely treatment for the newborn.
- Due to the fact that the most common cause of moderate cerebral hydrocephalus in an adult is a concussion, you should first try to avoid head injuries.
- You should lead a healthy lifestyle, do not abuse alcohol, and control your blood pressure.
- It is necessary to treat infectious diseases in a timely manner and periodically undergo examination by a doctor.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
The patient must remember, if he is diagnosed with moderate external hydrocephalus, that this is such a dangerous disease that, if not consulted in a timely manner, can lead to serious complications. Therefore, it is recommended that every person be examined at least once a year by a therapist or specialist.