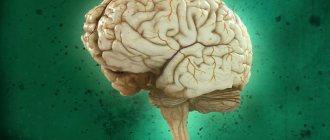
Prefrontal functions
The prefrontal cortex is an area of great importance for our survival in the environment in which we live and our coexistence in society.
The functions of this area of the brain are multiple, which integrates and coordinates a large number of processes. Some of them are described in detail below.
Executive functions
The prefrontal cortex is especially known for being the area of the brain more associated with executive functions. They are defined as a set of skills and fundamental cognitive skills that enable adaptation to the environment and problem solving by integrating different information and making predictions and behaviors based on them.
- Preventing problems
- Implementation of the plan
- Clinical significance
- Prefrontal cortex disorders
- Connections and interactions
- Security inhibition or protective capacity of the prefrontal cortex
- Injuries to this area of the brain
- Functions
- Negative manifestations of decreased functionality of the prefrontal cortex
- Functions
- Definition
- Self-control
Within these functions we find the ability to anticipate, set goals, initiate and maintain action, make decisions and inhibit behavior, plan based on memory, the ability to change our strategies or develop concepts and abstract ideas.
2
Attention, memory and intelligence. Fixation of attention or working memory is also mediated by the prefrontal cortex, as well as cognitive abilities and adaptation to the environment
This does not mean that this is the only area dedicated to these purposes, but it has a very high participation
Fixation of attention or working memory is also mediated by the prefrontal cortex, as well as cognitive abilities and adaptation to the environment. This does not mean that this is the only area dedicated to these purposes, but it has very high participation.
Social behavior
Another of the main functions of the prefrontal is the control of social behavior. Based on our interactions and the learning learned from both them and the rest of the information we collect, we can regulate our expressions and behavior, feel empathy, limit behavior based on possible consequences, and consider other points of view that are foreign to one's own.
Motivation
The connection between emotion and cognition in order for us to develop a plan to carry out certain actions is also due to the good functioning of the prefrontal cortex. In this way, we can motivate ourselves and direct our behavior towards achieving the goal that tempts us
Emotionality
Although it is the limbic system that has the greatest connection to the field of emotions, the prefrontal region of the brain is of great importance in both the perception and expression of emotions, translating them into physiological reactions or allowing your conscious control.
personality
Various aspects of personality are largely mediated by the functioning of the prefrontal cortex. The establishment of more or less stable patterns of behavior in various aspects of life, as well as typical characteristics such as inhibition or shyness or responsibility are some of the elements mediated by this area of the brain.
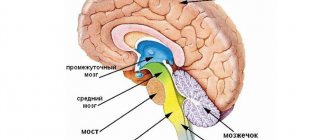
Three brains
If you look at the picture, you will see that the theory of three types of brain is quite realistic.
Scientific research proves that each of them has its own specific location in our body.
He is responsible for instincts, speed and survival. Reacts without thinking in order to protect the body from danger.
Hit! Run! Freeze! Thanks to these reactions, living beings were saved from their enemies. Instinctively and without emotion.
A purely muscular reaction that turns on and off the motor activity of a creature when it senses danger or hunger, fear or pleasure.
It fits around the reptilian brain like a glove. And is responsible for emotions and behavior in the pack, that is, collectivism, teamwork, family.
Thanks to this brain, animals learn. They have emotions. They follow a hierarchy. They know how to act together: in pairs or in a flock.
The limbic brain is responsible for feelings, dominance, learning, defense, awareness of the present, similarity and the desire to adhere to familiar patterns of life, auditory perception and discrimination of rhythm and intonation.
It is complex, unstable, flexible and continues to evolve.
The neocortex is NOT integrated with the emotional and reptilian brain.
He knows how to analyze, synthesize, generalize, plan and reason.
The neocortex allows you to visualize the future, create dissociated images. That is, images that you and I can look at from the outside, from the position of an observer.
But most importantly, he knows how to foresee, fantasize and dream. And express thoughts using words. By the way, the language system is the youngest in the neocortex.
In the book by the philosopher George Gurdjieff, “Everything and Everything,” the hero tells his grandson all about the “incomprehensible behavior of three-brained creatures on this strange planet Earth,” in which each of the three minds is in charge of its own sphere.
I am very grateful to my reptilian brain, which once, and maybe dozens of times, saved me in critical situations. For example, from a head-on collision with a bus. This happened in Malta, when my neocortex, wrapped in dreams of warm sand and gentle sea waves, almost killed me. I walked and dreamed. I was walking and didn’t notice how I stepped onto the roadway. She walked, staring inside herself, rejoicing in her dreams. What made me jump back and press myself against the wall exactly a second before a huge tourist bus squeezed into the narrow street? Reptilian brain.
I am very grateful to my limbic brain, which makes it possible to feel the experiences and states of other people, to empathize, sympathize, build relationships with different people and groups, and avoid relationships that destroy me.
The relationship with the smart neocortex is always complex. It is beautiful and powerful when you start a new project, plan, go towards a goal, look for ideas to solve problems and tasks. But it also makes you worry and worry about imaginary dangers, gives false directions and leads you into a dead end.
Preventing problems
There are a number of measures that can not only prevent disorders of the prefrontal cortex, but also enhance its performance. For this purpose, specialized medications are used that activate the work of the central nervous system and brain (glycine, undevit, aminalon, bilobil, Brain Rush, etc.).
In addition, the good condition of the body as a whole has a positive effect on the functioning of this zone. To maintain it, it is necessary to: limit or completely abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages, follow a fruit and vegetable diet, and also engage in physical exercise daily. It is also recommended to use meditative practices that help relax the central nervous system and help activate the prefrontal cortex.
If the cause of problems is stress, age or sleep, then a visit to psychologists may be prescribed to undergo specialized training that is aimed at developing the functions performed by the prefrontal cortex.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=JePzHFrPbTc
An example would be exercises that help you plan your day wisely, set and step-by-step fulfill life goals, and control your behavior in stressful situations.
Differences from old bark
The old cortex (archicortex) is an earlier emerging part of the cerebral cortex than the neocortex. But in the process of evolution, the new cortex became more developed and extensive. In this regard, the archicortex ceased to play a dominant role and became one of the constituent parts of the limbic system.
If we compare the old one in terms of the functions performed, then the first is assigned the role of fulfilling innate reflexes and motivation, and the second - managing emotions and actions at a higher level.
In addition, the neocortex is significantly larger in size than the old cortex. So the first occupies about 96% of the total surface of the hemispheres, and the size of the second is no more than 3%. This ratio shows that the archicortex cannot perform higher nervous functions.
Implementation of the plan
In order to obtain a specific result, it is not enough for a person to simply evaluate the initial data and see an image of what he wants to receive. He needs to have a plan for achieving the goal, step-by-step instructions compiled for him by his brain. At the same time, we are not necessarily talking about solving important and complex problems.
For example, after experiencing a feeling of hunger, a person may realize that a bowl of hot soup is a good solution to the problem that has arisen. But if he is not able to create an algorithm of actions for himself: go to the kitchen, open the refrigerator, cook food, then his ability to know what he needs is absolutely useless.
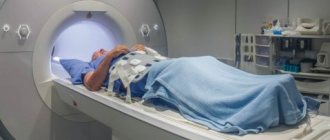
Clinical significance
Behavioral and neuroscientific methods are used to better understand how the human brain thinks, feels, and acts. Diagnosis of brain activity is carried out using instrumental studies. For example, an electroencephalogram (EEG), which records the electrical activity of brain tissue, and functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) speaks about the characteristics of brain functions.
Important Diogenes syndrome
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, are markers of gray matter atrophy in the brain. A variety of genetic and chromosomal disorders, some of which are often acquired, can have a negative impact on the cortex. Other neurological disorders such as epilepsy, speech problems (aphasia) are also diseases of the central nervous system.
When the brain is damaged as a result of disease or injury, only one specific lobe may be affected, resulting in impairment of the functions associated with it. The fetus that develops in the womb is very sensitive to various environmental factors. Therefore, toxic effects, for example, the use of alcohol or drugs by a pregnant woman, can cause disruption of the development of the nervous system.
A very rare congenital pathology is lissencephaly, in which the surface of the brain is absolutely smooth, that is, it has no convolutions. This phenomenon is associated with improper migration of neurons at 12–24 weeks of gestation. Children with such a brain are significantly behind their peers in development, most often do not live long and outwardly differ from a healthy child.
Previous
AnatomyThe human lymphatic system, pattern of lymph movement, location of lymph nodes, formation, structure and functions of the lymph node, the meaning of lymph
Next
AnatomyHuman blood vessels main types, structural features, classification, functions and differences of veins, arteries and capillaries, functional groups
Human endocrine glands, structure and functions, where hormones secreted by the endocrine glands are supplied, table with characteristics
Stabilization of the psyche with the help of practices
The works of N.N. Iovleva [3] emphasize that meditation is also an effective way to achieve psycho-emotional stability. Regular practice contributes to the development of higher mental qualities, which in a person are directly related to conscious activity. Meditation has long gone beyond the boundaries of cultural and religious practice and has found wide application in the field of psychotherapy.
The positive effect of the practices is observed after several weeks of regular exercises aimed at stabilizing the psyche and relaxation. Positive transformations concern not only the subjective improvement of attention, memory, and volitional control. The bioelectrical activity of the brain changes, the biochemical balance is normalized - in particular, the level of the hormones acetylcholine and cortisol is stabilized [2].
There are also studies confirming the effectiveness of meditation exercises for children suffering from ADHD [3]. This effect is achieved through relaxation and normalization of vegetative balance.
It is important to understand that the state of meditation is different from the usual sleep, wakefulness or relaxation. Most often, practitioners correlate it with a state of happiness and emotional fullness. One cannot discount the fact that often in the process of meditation states can arise that have an ecstatic overtones. Therefore, it is safer to conduct serious meditation practices under the guidance of an experienced trainer or teacher.
Prefrontal cortex disorders
Problems with the activity of the prefrontal cortex can be easily recognized by the signs listed below
But it is important to understand that these signs are not specific, that is, they can be caused by defects of the prefrontal cortex or other diseases
Problems with attention - a person cannot concentrate on a problem, task, conversation, it is difficult for him to concentrate on any subject for a long time, even if we are talking about watching a movie. Errors in the interpretation of events happening around, that is, a person may incorrectly perceive the attitude of other people towards him, not understand the danger of close contact with them, or, on the contrary, harbor resentment, suspecting that behind every word or deed of another person there is an intention to harm him. Repeating the same mistakes - a person's ability to learn from experience is one of the most important tools of evolution. Having put his hand into the fire and realizing that it is painful and dangerous, a person enters this information into his consciousness and in the future is careful not to allow direct contact of the flame with the skin
With pathologies of the prefrontal cortex, a person may repeat the same mistakes over and over again, causing physical or emotional harm to himself. Disorganization - we can talk about the inability to plan your day and complete all tasks on time. The popular psychological term “procrastination,” which refers to the pathological desire to put things off until later, may also be a consequence of disruption of the prefrontal cortex. Impulsivity, or more precisely, the inability to suppress one’s impulses. This may be expressed in the inability to control one’s emotions or in the inability to deny oneself pleasure: eating foods prohibited for medical reasons, drinking alcohol, and so on.
Connections and interactions
The prefrontal cortex is highly reciprocally connected to most brain structures, including particularly strong connections to other cortical, subcortical, and brainstem structures.
The dorsal prefrontal cortex is most interconnected with brain regions involved in attention, cognition, and motor skills, while the ventral prefrontal cortex is most interconnected with brain regions involved in emotion. The prefrontal cortex also has reciprocal connections with the brainstem activating system, and the functioning of the prefrontal regions is highly dependent on the balance of activation/inhibition, which, in accordance with the concept of three functional blocks of A. R. Luria, is a reflection of the interaction between the first - energy - and third - block programming, regulation and control of mental activity - by brain blocks.
The medial prefrontal cortex is involved in the generation of the third and fourth stages of slow-wave sleep (these stages are collectively called “deep sleep”), and its atrophy is associated with a reduction in the proportion of deep sleep relative to total sleep time, which, accordingly, leads to a deterioration in memory consolidation.
Atrophy of the prefrontal cortex occurs naturally as we age, and older adults have been shown to experience problems with memory consolidation consistent with the degradation of their medial prefrontal cortex. In older adults, memories, instead of being transmitted and stored in the neocortex, begin to remain in the hippocampus where they were encoded, as evidenced by increased hippocampal activation compared to younger adults during recall tasks where subjects were learning word associations. slept and then had to reproduce the learned words.
Consciousness and unconsciousness. Higher intelligence. Three Minds Model
In all world religions there is the idea that a person has three aspects of consciousness, or let’s call them three minds.
Let's call the first mind the Conscious Mind.
The second is the Unconscious Mind.
And the third - by the Higher Mind.
And let’s agree that these three minds are three aspects of any personality.
If you look at the picture at the beginning of this article showing the structure of the brain and look for where our three minds reside, it looks like the Conscious Mind and the Higher Mind are located in the neocortex.
And the Unconscious wanders between the reptilian and limbic brain, from time to time sending signals to the neocortex, where the Higher and Conscious minds are located, in the form of images, sounds, feelings and bodily sensations.
- The higher mind resides not only in the neocortex of a particular person, but is somehow connected to the field of the collective unconscious beyond the individual person.
- The Higher Mind and the Conscious Mind do not communicate directly. They ALWAYS interact through the Unconscious. This is why a person has psychological problems. But we'll talk about this a little later.
So, what is our Higher Mind responsible for?
For ideas, foresight, values, meaning, spirituality, self-control.
It seems that the Higher Mind of each person has a special task regarding the life of a person.
This task can be called a mission or purpose. This most important task in life is closely related to deep identity, the awareness of who I am, and without which my life has no meaning.
What is under the control of the Conscious Mind?
Perception of reality, that is, those images, sounds, bodily sensations, internal dialogues that we are aware of.
Rational and logical thinking.
Making informed decisions.
The unconscious is a giant repository of everything, everyone, everyone
events that have ever happened to us,
emotions we've ever felt
the decisions we made
internal and external conflicts,
beliefs and principles,
physiological processes in our body.
How do Consciousness, the Unconscious and the Higher Mind interact with each other?
Creates tensions and diseases in our body.
Cuts scars on our emotions.
It clouds our states.
It creates traffic jams and stagnation in our thoughts and actions.
Silences the call of our true values and important life goals.
Security inhibition or protective capacity of the prefrontal cortex
This ability to “give up” on something is a kind of protection for the prefrontal cortex, which allows you to avoid its depletion. The side part of the PC regulates behavior and habits, thereby preventing the perception of events for which a person is very worried. This inhibition is an activated nervous process that occurs or prevents a negative flow of nerve impulses.
Important Drugs to improve cerebral circulation: description, principle of action
This process also allows us to ensure the normal functioning of all human systems and organs. First of all, a protective function is formed for the nerve cells of the cerebral cortex, thereby protecting it from overexcitation.
In simple terms, security inhibition is the ability not to waste valuable PC resources on events of secondary importance. This is quite important if a person wants to maintain his energy and ability to think throughout the day.
Therefore, “scratching everything” allows you to preserve the functionality of your PC for more important moments in your life.
Injuries to this area of the brain
The presence of lesions in the prefrontal region can cause serious changes in the psyche and capabilities of people. In particular, it can lead to loss of emotional expression (especially at the facial level), impulse control deficits, disinhibition, personality changes, antisocial behavior, hypersexuality and hyperorality, severe errors in planning, judgment and delay of gratification. Also thoughts are flattened, slowed down and with little creativity.
These aspects can be seen in a large number of cases, such as injuries caused by traumatic brain injury or dementia such as frontotemporal or Huntington's chorea.
Example of a prefrontal injury: the case of Phineas Gage
One of the most famous cases and the first documented lesion of the prefrontal area is that of Phineas Gage, a young man who was preparing explosives for this purpose, which caused an iron bar to penetrate his head through the prefrontal cortex. and, in particular, the orbitofrontal part. The young man managed to survive the accident and recover from his injuries.
However, over time, it became clear that Phineas Gage had changed: he became aggressive, impulsive and hostile, could hardly wait, and was unable to plan actions or keep them in time. In addition to this, he would suffer epilepsy, a problem that would cause his death at 38 after losing his job, family and friends.
Bibliographical links:
Goldberg E. (2009). The executive brain: the frontal lobes and the civilized mind. Criticism.
Kandel E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of neurobiology. Madrird: MacGrawHill.
Kolb, B., & Whishaw, I. (2006). Human Neuropsychology Madrid: Panamericana Medical Publishing House.
Pineda D (2000) Executive function and its impairments. In: Revista de Neurología, 30 (8) 764.
Causes of nervous breakdowns
When we got home after the pancake episode, I was still angry with my son. I went into one of the rooms, leaving my son in the other, took a deep breath, stretched and tried to calm down before doing anything.
I knew that physical activity in the fresh air would be good for me, so my daughter and I went rollerblading. This has been one of our favorite things to do since she was six years old. We rode in silence for a while, holding hands. I felt the rhythm of our movements and the resistance of the air. Gradually, I literally began to come to my senses.
After some time, my daughter asked me why I yelled at my brother over some pancake.
Good question. I replied that it is important to be able to share with others. A dubious excuse, yes, but I couldn't think of anything else.
At that moment, a whole stream of associations arose in me, similar to the pages of a children's photo album flashing before my eyes. I realized that I saw myself as a child in my daughter, and my older brother in my son. I remembered my brother playing with me when we were little and even protecting me from other kids in elementary school. But then he grew into a teenager and we didn't get along so well and rarely spent time together. Despite the fact that now we communicate closely and remember that time with laughter, then I perceived it very painfully. I told my daughter that I once decided that if I had children, I would try to do everything to make them friends.
To this, my daughter, with exceptional insight, stated that this was my problem and had nothing to do with her and her brother. She even added that I should solve it without involving the children.
My daughter, of course, was right. We drove around some more, my mind gradually calmed down, my prefrontal cortex kicked in, and I began to think about what had happened. Now I could look inside myself, analyze my emotions and see what led to my breakdown.
But what brought back my ability to mindsight while my daughter and I were rollerblading?
Functions
The basic function of the prefrontal cortex is the complex control of mental and motor activity in accordance with internal goals and plans.
It plays a major role in the creation of complex cognitive patterns and action plans, decision making, control and regulation of both internal activity and social behavior and interaction.
The executive functions of the prefrontal cortex are manifested in the differentiation of conflicting thoughts and motives and the choice between them, the differentiation and integration of objects and concepts, predicting the consequences of present activity and adjusting it in accordance with the desired result, emotional regulation, volitional control, focusing attention on necessary objects.
The prefrontal cortex - its dorsolateral part - is also the substrate of short-term memory: Jacobsen showed in 1936 that damage to the prefrontal cortex in primates leads to short-term memory deficits; in 1952, K. Pribram identified the region of the prefrontal cortex responsible for this deficit as Brodmann area 46, also known as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; Further, in 1993, Goldman-Rakic and colleagues conducted an experiment where, using temporary inactivation of areas of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, the loss of memories stored in short-term memory was caused.
Models and participation in games
- CB1
- boss fight. - CB2
- splash screens (only without the wreath),
CB3
- bossfight with Tiny. - CB2
- bossfight. - CB2
is a hologram in warprooms. - CB3
,
CTR
,
Bash
,
XS
- screensavers - CB3
- cutscenes before entering the level. - CB3
is the last splash screen. - CTR
- game model and icons (regular and Japanese). - Bash
is a game model and icon. - WoC
- cutscenes and the last bossfight. - XS
- bossfight. - Fusion
is a joint bossfight with Ripto. - Fusion
is a card. - CNK
, Fusion - screensavers. - CNK
is a game model and icon. - CNK
on Game Boy is a game sprite. - Twinsanity
is a gaming model. - Twinsanity
is a model in flashback scenes. - Boom Bang!
- game model. - TTR
is a gaming model. - Titans
,
Mutants
- screensavers. - Titans
on Game Boy is a bossfight. - Mutants
- boss fight. - CNK 3D
is a gaming model. - CNK2
is a game model and icon. - Skylanders: Imaginators - game model
- Neo Cortex (CB N. Sane Trilogy)
1 of 27
Add a photo
Negative manifestations of decreased functionality of the prefrontal cortex
When diagnosing PC using a technique such as SPECT, specialists carry out diagnostics in two versions: in the first, when the brain is at rest, in the second, during additional stimulation. When assessing brain functionality, the results taken in the state of brain activity are primarily taken into account.
With additional stimulation, PC activity will increase. If you have a brain pathology such as schizophrenia or ADHD, PC activity will decrease during stimulation.
If PC dysfunction is detected, patients may present with a number of disorders, such as:
- Absent-mindedness
- Weakening or lack of control over impulsivity (the patient wanted to do something and at the same moment did it thoughtlessly)
- Signs of hyperactivity
- Decreased concentration and comprehension
- Disorganization
- Procrastination or the tendency to constantly put things off until later
- Distortion of judgment and perception of what is happening around, incorrect interpretation of events and emotions of other people
- Lack of learning from experience, that is, a person is not able to learn from his past mistakes
- Short term memory disorder
- Social phobia (presence of fear when deciding to take any step)
Important Causes and differences of brain asymmetries, their impact on human life
Weakening of the PC also occurs as a person ages. It is older people who often experience disturbances in the transition of memory from short-term to long-term, in accordance with the degradation of their medal cortex. In older adults, memories are not stored but remain in the hippocampus, indicating increased hippocampal activation.
PC structure
The structure is based on three areas of the frontal lobe - dorsolateral, medial and orbitofrontal.
The dorsolateral region controls the expression of emotions in a specific situation through its connection with the limbic system. In addition, this area of the cerebral cortex influences a person’s attention.
The medial region is responsible for recording information into short-term memory and allows you to compare data received by the senses and stored in the brain. Also, this part of the cortex allows you to transfer information from short-term memory to its permanent storage location.
The orbitofrontal region helps to use accumulated experience when making decisions.
Functions
The PC is one of the most developed areas of the brain, which performs a large number of functions. The main ones are:
- Concentration of attention, allowing a person to focus on isolating only the necessary information, ignoring extraneous sensations and thoughts. This is due to the ability to send impulses to the sensory and limbic areas of the brain, which reduce distracting signals. Concentration is very important when studying and having to work for a long time on the same project.
- Perseverance in achieving set goals and objectives, which allows you to continue to strive for the intended result, despite difficulties and force majeure circumstances.
- Assessment of the current situation. In this case, all factors influencing the ongoing event are taken into account, and not just a limited set. This PC function allows a person to comprehensively consider problems, which greatly facilitates the search for solutions.
- Critical thinking, which allows you to develop the necessary set of actions to find reliable and verified information. In other words, a person must ensure that the data is correct before using it.
- Planning allows you to develop specific measures and actions to achieve the intended goal. This PC function significantly reduces the number of uncertain factors and force majeure circumstances when performing the assigned task.
- Forecasting events, which allows planning to take into account even those factors and circumstances that may arise in the future.
- Using accumulated experience. Thanks to this function, a person will take into account mistakes made in the past and if similar situations arise, he will choose the option that will prevent a repetition of the unfavorable outcome.
When considering functions, special attention must be paid to its management of human emotions. In the PC, the processes occurring in the simpler limbic system are perceived and translated into certain feelings and emotions (love, hatred, joy, grief, desire, etc.)
The prefrontal cortex is also responsible for empathy, which allows you to determine the feelings and mood of another person by the emotions they express.
In addition, the PC constantly monitors the limbic system for strong emotional outbursts and extinguishes them when they occupy a dominant role. This helps a person to react to events happening around him not impulsively, but only after careful analysis and selection of the best solution, which will take into account possible future consequences.
Large-scale study by neurophysiologists from the USA
One of the most interesting studies was conducted by scientists from Massachusetts [1]. Scientists have suggested that the brain centers of experienced meditators are much more centralized due to the abundance of functional neural connections. Subsequently, these data were confirmed experimentally.
47 people took part in the study. 16 of them practiced yoga, 16 - meditation. 15 people made up the control group. Yoga practitioners were mainly trained in Kripala Yoga. Their total practice experience was impressive, amounting to 9,950 hours of yoga. The meditators practiced Vipassana. Each participant had an average of 7,458 hours of meditative experience. As for the control group, its representatives never practiced yoga or meditation, or practiced it only a few times in their lives, out of amateur interest.
Scientists carefully examined the brains of each participant. Data on the physiological characteristics of the subjects' brains were collected using an MRI scanner. The information obtained was processed using statistical analysis.
The results of the study were amazing. The prefrontal cortex has received particular attention from scientists. It turned out that it was larger in size in the subjects who selflessly spent dozens of hours on meditation. The difference from participants with zero experience of spiritual practices was obvious. Researchers believe that in this case an analogy with the work of building a muscle is appropriate - the longer the training takes place, the more our brain transforms. Moreover, these transformations have a very specific physiological substrate. Just as a muscle grows larger and stronger through exercise, the brain grows through meditation practice.
Definition
There are three possible definitions of the prefrontal cortex:
- granular frontal cortex (that is, the one in which neurons of layers II and IV predominate - the outer and internal granular layer, respectively - the cerebral cortex)
- projection zone of the mediodorsal nuclei of the thalamus
- part of the frontal lobes, electrical stimulation of which does not cause motor acts.
The weakness of the first definition is that it only works for primates, since non-primates do not have a granular cortical layer IV; that is, although it applies to man, it is not universal.
The weakness of the second definition was revealed by subsequent studies: it turned out that the mediodorsal nuclei of the thalamus give projections not only to the granular frontal cortex. Thus, the definition has been adjusted to read: “The prefrontal cortex is a region of the cerebral cortex that has stronger reciprocal connections with the mediodorsal nuclei of the thalamus than with any other thalamic nuclei.”
The third definition also has its own difficulties: the areas of the frontal lobes that do not respond to electrical stimulation with observable motor activity include both the granular and agranular cortex.
And now the most wonderful news!
Creative people have already come up with a lot of affordable and environmentally friendly ways to consciously synchronize the work of our brain.
That is, we have everything you need to create!
Download the unique book “2 Secrets of Inspiration”
This book will talk about how to quickly bring yourself into a working creative state of mind and soul, how to invite Inspiration at the right moment in time.
An inspired person is very effective and productive, he is so strongly involved in the process of inventing that he very quickly and with pleasure composes, writes, speaks, invents, draws, creates, sculpts, improvises.
What do you need to do to get inspired?
How to get ideas out of your own head?
How can you enter the Creative space at your will at the right moment, without waiting for the Muse?
Download the free book and find out!