Rathke's pouch cyst is a benign formation located inside the sella turcica of the skull base. They are epithelial-lined intrasellar cysts that are thought to develop from residual structures of Rathke's pouch. They usually appear as round, ovoid or dumbbell-shaped formations. They are common, affecting 13-33% of people, and sometimes cause compression of underlying structures, leading to symptoms such as headaches, visual disturbances, or pituitary hormone deficiency.
Studies have shown that cysts identified using radiation methods do not change over time or slightly decrease in size; this suggests that in the absence of compression symptoms, a conservative treatment approach is preferable.
Imaging has improved significantly with the introduction of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) into clinical practice.
Get an MRI of the pituitary gland in St. Petersburg
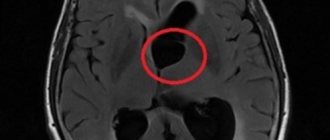
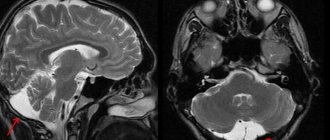
In the images below you can see how a Rathke's cyst looks in the picture.
MRI: Rathke's pouch cyst. A precontrast T1-weighted sagittal image shows a well-defined mass in the sella region extending into the suprasellar cistern. There is a homogeneously high signal intensity in the formation compared to the brain parenchyma.
T2-weighted axial image (same patient as previous image).
T2-weighted axial image: cortical isointense mass (same patient as in previous image).
Pituitary cyst: how it is treated in Israel
Israeli schools of neurosurgery and oncology are considered one of the best and most progressive in the world.
Since the late 80s of the 20th century, a medical field such as neuro-oncology, which is still not represented in the countries of the former USSR, began to develop in the Promised Land. Neuro-oncologists specialize in the treatment of tumor diseases of the spinal cord and brain, as well as tumors of the peripheral nervous system, coordinating the work of an entire team of doctors consisting of neurologists, oncologists, neurosurgeons, endocrinologists, radiologists, etc. Thanks to modern treatment methods, new technologies and qualified specialists (chief neurooncologists) treatment of pituitary cysts in Israel is performed at the highest level.
Diagnostic methods
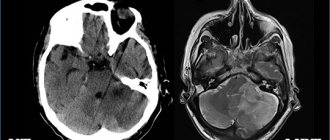
The method of choice for diagnosis is MRI of the chiasmatic-sellar region (pituitary gland). Thin sections should be obtained in the sagittal and coronal planes through the sella turcica. The study must be accompanied by contrast enhancement. CT scans may also be helpful in their evaluation. CT findings are particularly useful in diagnosing associated bone changes and calcification deposits.
Limitations of Methods
MRI is superior to CT in the quality of visualization and assessment of the size of the Rathke cyst. Sagittal and coronal MRI images provide reliable information about the relative position of the formation and the optic nerves, optic chiasm and hypothalamus. MRI in the coronal projection also allows us to identify the lateral spread of the cyst beyond the sella turcica and evaluate its location relative to the internal carotid arteries and cavernous sinuses. The Magnetic Resonance Imaging method is superior to CT in terms of multiplanar imaging capabilities and contrast resolution.
The advantage of CT is better display of small calcifications. This advantage is significant because the presence of calcifications may indicate an alternative diagnosis, such as craniopharyngioma, although small calcifications are sometimes found in this disease. CT is also superior to MRI in assessing associated bone remodeling.
What is important to know
It is important not to confuse Rathke with cystic pituitary adenoma. In the case of adenoma, complaints include symptoms of hormonal disorders, visual disturbances and headaches. Often the diagnosis of adenoma is made when the patient has Rathke, and vice versa. To reliably distinguish between these two conditions, expert MRI interpretation by an experienced neuroradiologist can be useful. A second opinion helps make an accurate diagnosis.
What is a pituitary cyst: general information about the disease
The pituitary gland is a tiny gland in the brain that is responsible for coordinating almost the entire endocrine system of the body. It is in the pituitary gland that thyroid-stimulating, follicle-stimulating, luteinizing and somatotropic hormones are produced, which affect a number of glands in the body. Therefore, problems with the pituitary gland affect all endocrine glands, which leads to disruption of the activity of many organs and systems.
A pituitary cyst is a neoplasm with liquid contents and a dense shell. It is difficult to talk about the prevalence of this pathology, because for quite a long time this pathology does not manifest itself in any way. Moreover, people with a pituitary cyst often live to a very old age, unaware of the tumor in the brain.
The exact reasons for the development of this pathology are unknown, but the accumulated observational experience allows us to talk about factors that can contribute to the appearance of cysts.
- Hereditary factors. If one of your direct relatives has a pituitary cyst, then there is an increased likelihood of its formation.
- Traumatic brain injuries. In some cases, head injuries lead to the appearance of cysts in the brain.
- Infectious diseases of the nervous system (mainly the brain).
Symptoms
A pituitary cyst may remain asymptomatic for a long time. An asymptomatic course is observed in 33-85% of patients. Often, cystic formations in the area of the pituitary gland are detected accidentally during a diagnostic examination (MRI, CT) prescribed for another reason (traumatic brain injury, stroke). Symptoms appear if the pituitary cyst increases in size and compresses the surrounding brain structures. Main features:
- Visual dysfunction (loss of visual fields, appearance of foreign objects in the field of view) – 67% of cases.
- Pain in the head area – 60% of cases.
- Nausea accompanied by bouts of vomiting.
- Changes in behavior, psycho-emotional disorders.
- Epileptic seizures (rare).
- Increased fatigue.
A cyst in the pituitary gland often causes hormonal disorders. The compression to which the tissues of the pituitary gland are subjected provokes an increase or decrease in the production of hormones. The pathological process is accompanied by signs:
- Delayed sexual development in childhood.
- Slowing or accelerating growth.
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle in women.
- Hyperprolactinemia (amenorrhea - absence of menstruation, galactorrhea - milk secretion from the mammary glands outside the feeding period, infertility) - 38% of cases.
- Erectile dysfunction in men – 50% of cases.
- Hypoglycemia is a decrease in blood glucose levels.
- Hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure values.
- Diabetes insipidus (increased urine production, unquenchable thirst).
- A sharp change in body weight values (usually upward).
- Impaired sensitivity (increased sensitivity to cold, thermoregulation disorder).
- Dry skin.
If a pituitary cyst detected in adults and children does not show symptoms and does not affect brain function, it does not require treatment. How dangerous a pituitary cyst is and whether it requires treatment will be determined by the attending physician, taking into account its size and effect on the functioning of the brain.
Pituitary cyst: main manifestations
A pituitary cyst may be asymptomatic and may be discovered accidentally during a brain examination for another reason. Depending on the size and location of the cyst, it can manifest itself with different symptoms.
- Visual impairment. The patient often loses lateral visual fields, blind spots appear, visual acuity decreases, and in the case of optic nerve atrophy, blindness develops.
- Increased intracranial pressure. This disorder is manifested by fatigue, sleep problems, pain in the head, nausea, vomiting, memory problems, decreased sex drive and even depression.
- Symptoms associated with disruption of the hormonal activity of the pituitary gland. The patient experiences various symptoms associated with an increase or decrease in the production of hormones, which are directly affected by the pituitary gland. Possible release of colostrum from the mammary glands (in both women and men), developmental delay (in children), obesity or thinness, dry skin, muscle atrophy and other symptoms.
It is worth keeping in mind that problems with hormonal levels arise already in the later stages, when the cyst reaches a large size or degenerates into a tumor (benign or malignant).
Why does a Rathke's pouch cyst form?
As established by Voelker et al., according to the most generally accepted theory of origin, these formations develop from the true residual structures of Rathke's pouch that existed in the prenatal period.
Rathke's pouch appears approximately on the 24th day of embryonic development in the form of a dorsal diverticulum of the oral fossa; this formation is lined with epithelial cells of ectodermal origin. Around the same time, the pituitary funnel is formed in the form of an outgrowth of the neuroepithelium from the diencephalon. By the fifth week it grows to the funnel and becomes obliterated at the buccal-pharyngeal membrane. During the sixth week it separates from the oral epithelium. Then the distal part of the pituitary gland develops from its anterior wall. The posterior wall does not proliferate and remains in the form of a poorly visible intermediate part of the pituitary gland.
The residual lumen of the pocket is reduced to a narrow gap, which, in most cases, disappears. It is believed that persistence and widening of this fissure leads to the development of a Rathke cyst.
Diagram of the development of a cyst from Rathke's embryonic pouch.
Some authors adhere to other theories regarding the formation of these cysts: in particular, according to some theories, the source of development is the neuroepithelium or endoderm, or their development is assumed to be through metaplasia of the cells of the anterior pituitary gland.
How pituitary cysts are diagnosed in Israeli hospitals
Accurate diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of any disease. Neurosurgical departments of Israeli clinics have modern diagnostic equipment, thanks to which it is possible to determine the exact location, size and structure of the tumor.
A set of examinations in Israeli clinics for suspected pituitary cysts consists of the following measures:
- consultation with a leading neurosurgeon or neuro-oncologist at the clinic;
- laboratory tests: blood test, determination of hormonal levels, urine analysis, etc.;
- instrumental diagnostics: CT, MRI, study of cerebral vessels (angiography), X-ray examination of the skull;
- analysis of the data obtained, establishment of a diagnosis and prescription of a treatment regimen.
How reliable is MRI?
There is not a single characteristic MRI sign that could be used for a reliable differential diagnosis of Rathke's pouch cysts and other cystic formations of the sellar or suprasellar region. Simple cysts may be indistinguishable from arachnoid or epidermoid cysts. More complex ones may be difficult to distinguish from craniopharyngiomas or pituitary adenomas.
Cystic pituitary adenomas may resemble the former in the absence of a solid contrast-enhancing component on MRI. Features such as the presence of a fluid-liquid level, a hypointense rim on T2-weighted images, internal septa, and a location lateral to the midline are more often consistent with pituitary adenomas, while the presence of an intracystic nodule may be more often associated with the research topic.
Due to the significant variability in CT and MRI findings, preoperative diagnosis requires a combination of clinical, biochemical, and radiographic findings. Differential diagnosis is very important because the treatment and surgical approach differ significantly from those for other possible pathologies. If you are in doubt about the diagnosis, you can get a second opinion with an MRI of the pituitary gland.
How is pituitary cyst treated in Israel?
For pituitary cysts, patients in Israeli clinics can be offered complex treatment, including surgery and conservative methods.
- It is noteworthy that therapeutic measures for pituitary cysts may not be required. If the cyst does not affect the patient’s well-being in any way and does not lead to abnormalities in the tests, then it is better not to touch such a cyst. Naturally, over time, the cyst may increase in size or change structure. Therefore, such a patient is recommended to have regular follow-up with a doctor to keep the situation under control. Depending on the data obtained during diagnosis, the patient is recommended to undergo examination 1 or 2 times a year.
- Surgery is the only effective method of treating cysts, including those located in the brain. Modern technologies for brain surgery have come a long way, and Israeli clinics present all the latest brain surgery techniques. In the vast majority of cases, neurosurgeons in Israel remove pituitary cysts using minimally invasive endoscopic methods. An endoscope and surgical instruments are inserted into the brain through the nasal cavity. Under X-ray control, the doctor brings instruments to the cyst, removes it and removes it. After surgery, the cyst tissue is sent for histological analysis to identify malignant cells (which is extremely rare). In rare cases, endoscopic surgery is not possible for the patient, and in such situations open surgery is performed. Many Israeli clinics practice the craniotomy technique, in which the patient is conscious. This is necessary so that the doctor can monitor the quality of the patient’s speech and motor functions during the operation. Indeed, when carrying out such complex operations, it is possible to influence some brain structures that are responsible for performing important functions of the body. During such an operation, the patient is conscious, but does not feel any pain.
- The use of medications for pituitary cysts is aimed mainly at eliminating symptoms. Hormonal drugs are prescribed for hormonal imbalances.
Thanks to modern treatment protocols, excellent doctors and the latest medical equipment, reviews about the treatment of pituitary cysts in Israel are the most positive. Patients from the countries of the former USSR successfully cope with this problem in Israel, even in particularly severe cases.
MRI for Rathke's pouch cyst
The MR picture can be very different (see images below). Although no specific MRI features have been identified, most can be divided into the following two groups:
1) With low signal intensity on T1-weighted images and high signal intensity on T2-weighted images
2) With high signal intensity on T1-weighted images and variable signal intensity on T2-weighted images
T1-weighted sagittal image obtained before contrast enhancement shows a well-defined cyst in the area of the sella turcica, isointense to the cerebrospinal fluid. There is a normal high signal intensity of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland from behind.
On a T1-weighted coronal image, it is visible just under a centimeter in size at the central part of the sella turcica. Slightly hyperintense compared to cerebrospinal fluid.
On this T2-weighted image, it is isointense to the cerebrospinal fluid.
The large one is hyperintense compared to the cerebrospinal fluid on axial proton-weighted image. There is an expansion of the sella turcica with a lateral deviation of the slightly obscured but patent cavernous part of the internal carotid artery.
Get an MRI of the pituitary gland in St. Petersburg
The contents of the first group resemble cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In the second group, increased signal on T1-weighted images is associated with high levels of mucopolysaccharides, which is believed to be a consequence of an increase in the number of mucin-secreting cells in the wall, as well as increased activity of these cells.
Rare cases of high signal intensity on T1-weighted images and low intensity on T2-weighted images are associated with a combination of various factors, including the presence of mucopolysaccharides, old hemorrhage, significant cholesterol or cellular debris from the cyst wall. They are almost always homogeneous in signal intensity, while other pathological formations, such as craniopharyngiomas and hemorrhagic adenomas, are more often characterized by heterogeneity in signal intensity.
They have a thin wall that can be contrasted when injecting gadolinium-based contrast agents. Various patterns of gadolinium enhancement may reflect squamous metaplasia of the wall or pituitary tissue displaced to the periphery in the form of a rim.
Data on the relationship between signal intensity and its clinical manifestations are very rare. In 1997, Takeichi and colleagues studied 78 patients, including 9 of their own patients, and reported that cerebrospinal fluid signal intensity was slow growing, large in size, and often caused visual symptoms. Symptomatic ones with different signal intensities were smaller in size.
The DWI-SSFSE mode with ICD values can also be used in the differential diagnosis of craniopharyngiomas and hemorrhagic pituitary adenomas.
Clinics in Israel where you can undergo treatment for pituitary cysts
In Israel, many public and private clinics offer high-quality treatment and diagnosis of pituitary cysts. Here is a list of the most popular ones.
- Ichilov Medical Center (Sourasky) is the flagship of Israeli medicine. The clinic is located in Tel Aviv and offers services in almost all medical areas.
- Assuta is the largest private medical institution in Israel, located in Tel Aviv. The neurosurgical department of the Assuta Clinic has the most modern methods of treating and diagnosing diseases of the brain and spinal cord.
- Sheba is a multidisciplinary public hospital in the city of Ramat Gan. Sheba is Israel's largest hospital, with 1,700 hospital beds. The neurosurgical department is recognized as one of the most developed in the clinic. The most complex surgical interventions on the brain and spinal cord are performed here using modern technologies.
Cost of treatment for pituitary cysts in Israel
Prices for pituitary cyst treatment in Israel may vary depending on the clinic you choose. Thus, in public medical institutions the price of diagnosis and treatment is lower than in private ones. This is due to the fact that the state provides good funding for budget-funded clinics, and they pose serious competition to private centers.
The full cost of medical services will be known only after all diagnostic procedures have been completed. On average, for a diagnosis of a suspected pituitary cyst, you need to pay from $1,500, and surgery to excise the cyst in Promised Land clinics costs $27,000-30,000.
It is noteworthy that the cost of medical services in Israel is 30-40% less than in Western European countries. Moreover, unlike Germany and other European countries, in Israel patients can pay for all procedures separately, rather than depositing the entire amount immediately into the clinic’s account.
For more information, see the Neurosurgery section.
Forecast and possible consequences
Adverse consequences of surgical treatment of a brain cyst formed on the pituitary gland are relatively rare. Typically, postoperative disorders are associated with the development of diabetes mellitus (4% of cases), secondary infection (4% of cases), rhinorrhea - copious discharge of mucous substrate from the nasal passages (7% of cases).
The prognosis is relatively favorable - in most cases (about 80%), the operation leads to relief from the manifestations of the pathology. If a large cyst is not treated, complications may develop - loss of vision, seizures, hormonal imbalance, increased intracranial pressure.
A pituitary cyst is a space-occupying formation, which is often a congenital pathology of brain development. Less commonly, a cystic cavity is formed as a result of previous infections, injuries in the head area, or neurosurgical interventions. Most often it is asymptomatic. If severe neurological symptoms occur, surgical removal is usually performed.
240